Die Anleitung zu Java JAXB
1. Die Vorstellung
JAXB wurde in JDK ab der Version 6.0 integriert. Falls Sie die vorherigen Version der Java benutzen, sollen Sie sie herunterladen und die Bibliothek zum Verwendung anmelden
Das Dokument schreibt die Hinweise auf die Java6. So sollen Sie kein Bibliothek herunterladen
Model of example:
Das ist das Bild vom Projekt nach der Erledigung
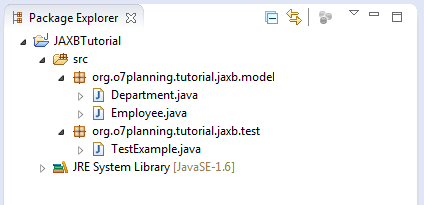
2. Das Projekt erstellen
Erstellen Sie ein normales Java Projekt
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jaxb.model;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement(name = "employee")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
public class Employee {
private String empNo;
private String empName;
private String managerNo;
/**
* This default constructor is required if there are other constructors.
*/
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String empNo, String empName, String managerNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.managerNo = managerNo;
}
public String getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(String empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public String getManagerNo() {
return managerNo;
}
public void setManager(String managerNo) {
this.managerNo = managerNo;
}
}
Department.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jaxb.model;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElementWrapper;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
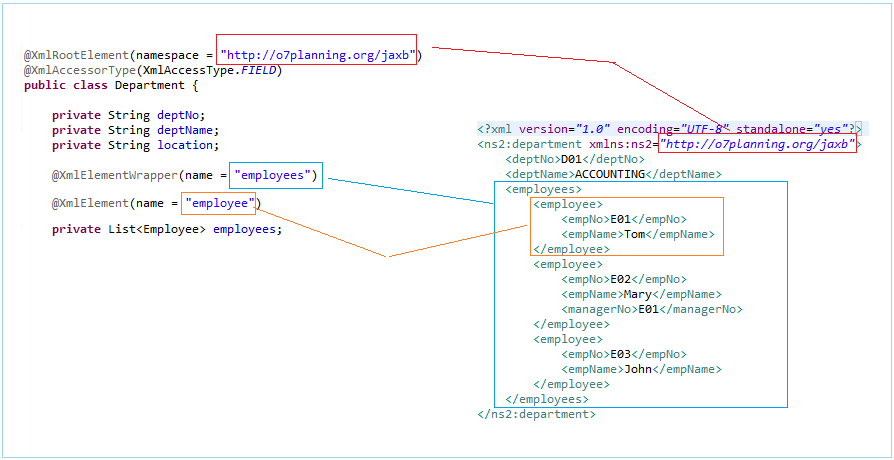
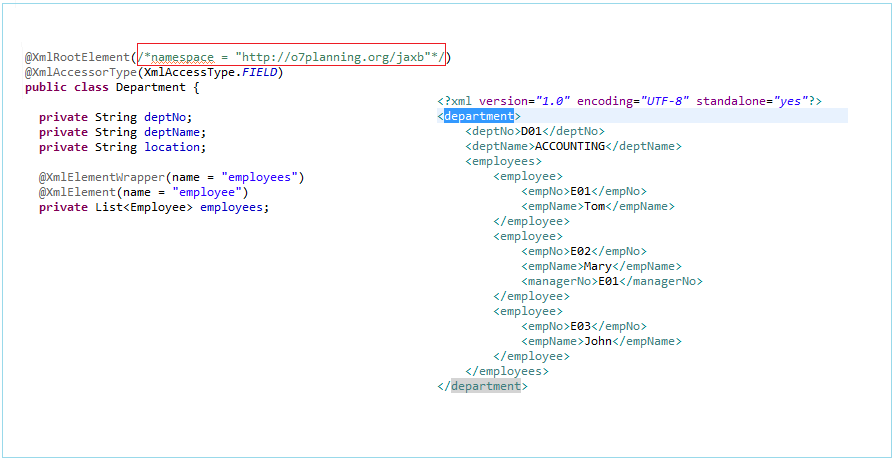
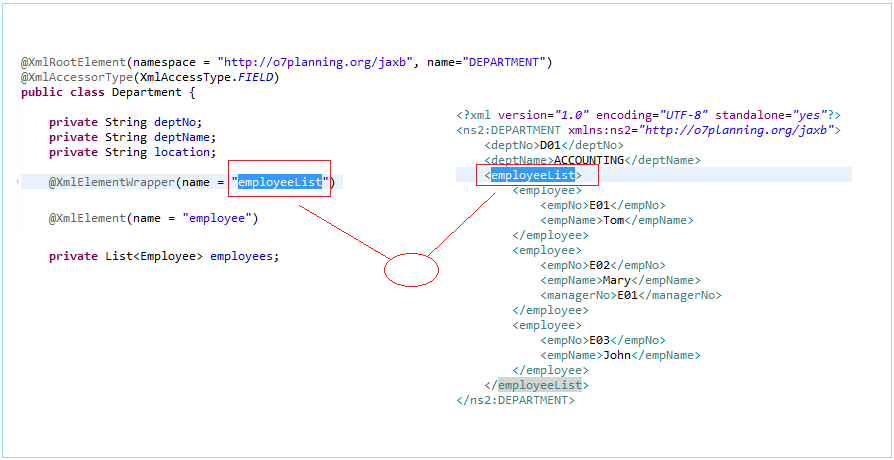
@XmlRootElement(namespace = "http://o7planning.org/jaxb")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
public class Department {
private String deptNo;
private String deptName;
private String location;
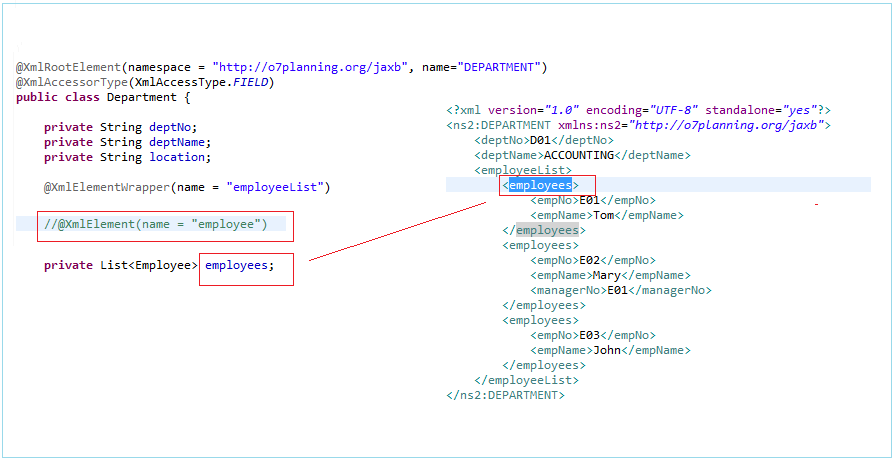
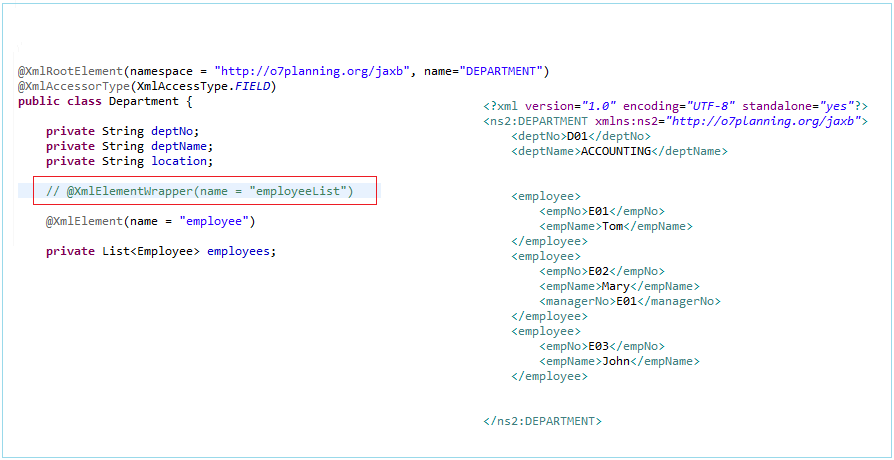
@XmlElementWrapper(name = "employees")
@XmlElement(name = "employee")
private List<Employee> employees;
/**
* This default constructor is required if there are other constructors.
*/
public Department() {
}
public Department(String deptNo, String deptName, String location) {
this.deptNo = deptNo;
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public String getDeptNo() {
return deptNo;
}
public void setDeptNo(String deptNo) {
this.deptNo = deptNo;
}
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
public void setEmployees(List<Employee> employees) {
this.employees = employees;
}
}TestExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.jaxb.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.jaxb.model.Department;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.jaxb.model.Employee;
public class TestExample {
private static final String XML_FILE = "dept-info.xml";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee emp1 = new Employee("E01", "Tom", null);
Employee emp2 = new Employee("E02", "Mary", "E01");
Employee emp3 = new Employee("E03", "John", null);
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
list.add(emp1);
list.add(emp2);
list.add(emp3);
Department dept = new Department("D01", "ACCOUNTING", "NEW YORK");
//
dept.setEmployees(list);
try {
// create JAXB context and instantiate marshaller
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Department.class);
// (1) Marshaller : Java Object to XML content.
Marshaller m = context.createMarshaller();
m.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, Boolean.TRUE);
// Write to System.out
m.marshal(dept, System.out);
// Write to File
File outFile = new File(XML_FILE);
m.marshal(dept, outFile);
System.err.println("Write to file: " + outFile.getAbsolutePath());
// (2) Unmarshaller : Read XML content to Java Object.
Unmarshaller um = context.createUnmarshaller();
// XML file create before.
Department deptFromFile = (Department) um.unmarshal(new FileReader(
XML_FILE));
List<Employee> emps = deptFromFile.getEmployees();
for (Employee emp : emps) {
System.out.println("Employee: " + emp.getEmpName());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Das Ergebnis beim Starten von der Klasse TestExample.:
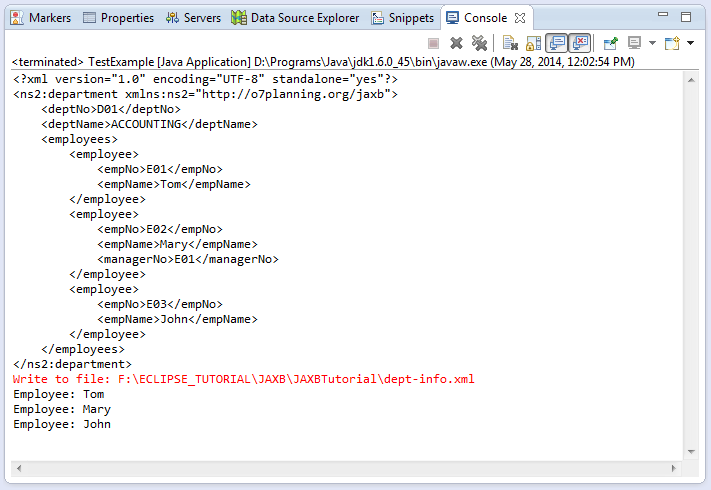
Das unten Bild bezeichnet die Arbeitsweise vom JAXB