Verzweigung in Python
1. Der Vergleichsoperator
Die üblichen Vergleichsoperator sind
Operator | Meaning | Example |
> | greater than | 5 > 4 is true |
< | less than | 4 < 5 is true |
>= | greater than or equal | 4 >= 4 is true |
<= | less than or equal | 3 <= 4 is true |
== | equal to | 1 == 1 is true |
!= | not equal to | 1 != 2 is true |
and | and | a > 4 and a < 10 |
or | or | a == 1 or a == 4 |
2. Die Statement if-else
if ist ein Befehl zur Überprüfung einer Bedingung im Python. Zum Beispiel: If a > b, dann machen etwas...
Die Syntax
if condition_1 :
# Do something
elif condition_2 :
# Do something
elif condition_N:
# Do something
else :
# Do something
Das Programm prüft die Bedingungen vom oben nach hinten. Wenn eine betreffende Bedingung richtig ist, wird der Befehl dort laufen. Und das Programm prüft die restlichen Bedingungen in der Verzweigungstruktur nicht
Zum Beispiel (if - else):
ifElseExample.py
option = 5
if option == 1:
print("Hello")
else :
print("Bye!")Output:
Bye!Example (if - elif - else):
ifElseExample2.py
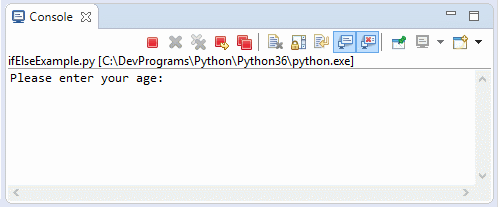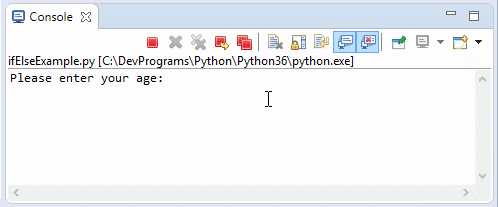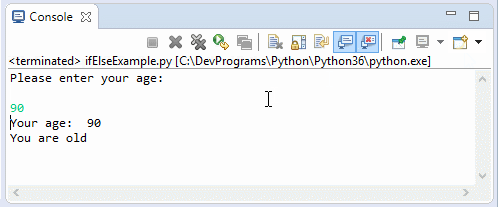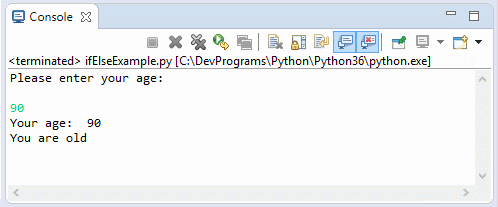
print("Please enter your age: \n")
# Declare a variable to store the user input from the keyboard.
inputStr = input()
# int(..) function convert string to integer
age = int(inputStr)
# Print out your age
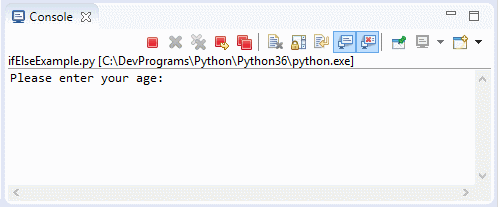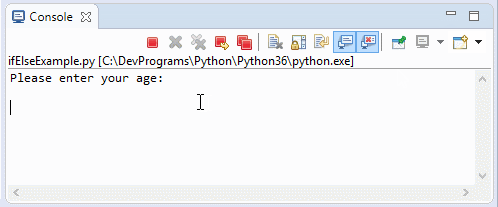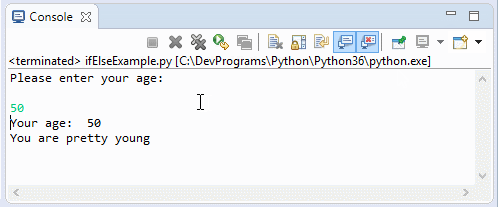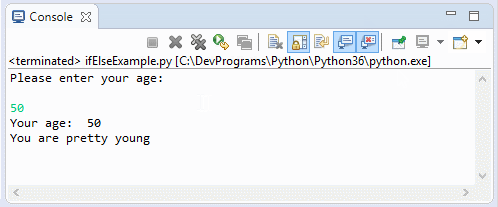
print("Your age: ", age)
# If age < 80 then ..
if (age < 80) :
print("You are pretty young")
# Else if age between 80, 100 then
elif (age >= 80 and age <= 100) :
print("You are old")
# Else (Other case)
else :
print("You are verry old")Laufen Sie ein Beispiel
Anleitungen Python
- Lookup Python-Dokumentation
- Verzweigung in Python
- Die Anleitung zu Python Function
- Klasse und Objekt in Python
- Vererbung und Polymorphismus in Python
- Die Anleitung zu Python Dictionary
- Die Anleitung zu Python Lists
- Die Anleitung zu Python Tuples
- Die Anleitung zu Python Date Time
- Stellen Sie mit PyMySQL eine Verbindung zur MySQL-Datenbank in Python her
- Die Anleitung zu Python Exception
- Die Anleitung zu Python String
- Einführung in Python
- Installieren Sie Python unter Windows
- Installieren Sie Python unter Ubuntu
- Installieren Sie PyDev für Eclipse
- Konventionen und Grammatik-Versionen in Python
- Die Anleitung zum Python für den Anfänger
- Schleifen in Python
Show More