Die Anleitung zu Java SequenceInputStream
1. SequenceInputStream
Mit SequenceInputStream können Sie zwei oder mehrere InputStream miteinander verketten (concatenate). Es liest vom ersten byte bis zum letzten byte von erstem InputStream , und dann macht gleich mit dem nächsten InputStream bis zum letzten InputStream .
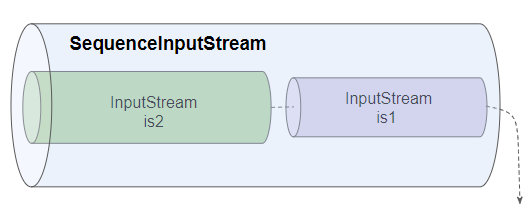
SequenceInputStream ist eine Unterklasse von InputStream:
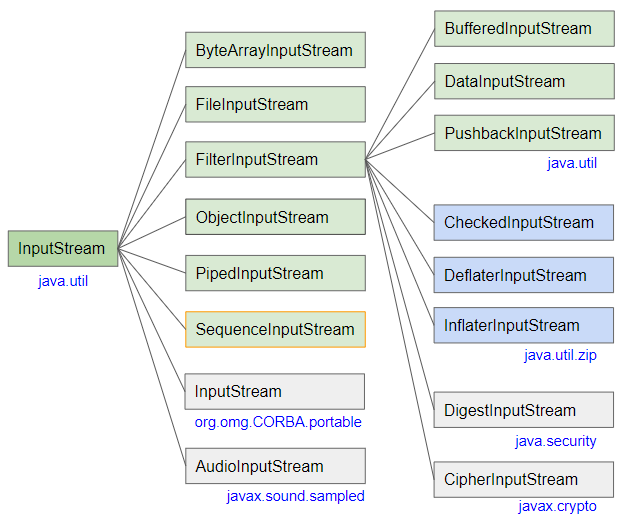
- InputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- FileInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- PipedInputStream
- AudioInputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- DataInputStream
- PushbackInputStream
- CheckedInputStream
- InflaterInputStream
- DigestInputStream
- DeflaterInputStream
- CipherInputStream
SequenceInputStream Methods
final void nextStream() throws IOException
// Methods inherited from InputStream
public int available() throws IOException
public int read() throws IOException
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException
public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException
public byte[] readAllBytes() throws IOException
public byte[] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException
public int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
public long skip(long n) throws IOException
public boolean markSupported()
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit)
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException
public void close() throws IOException
public long transferTo(OutputStream out) throws IOExceptionDie meisten Methode von SequenceInputStream werden von InputStream geerbt. Daher erfahren Sie im Artikel über InputStream , wie Sie diese Methoden verwenden:
SequenceInputStream Constructors
public SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1, InputStream s2)
public SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e)2. Examples
Angenommen, wir haben zwei UTF-8 codierte Textdateien. Jede Datei enthält eine Liste mit Blumennamen.
flowers-1.txt
# Flower names (1)
Tulip
Daffodil
Poppy
Sunflower
Bluebell
Rose
Snowdrop
Cherry blossomflowers-2.txt
# Flower names (2)
Orchid
Iris
Peony
Chrysanthemum
Geranium
Lily
Lotus
Water lily
Dandelion
Hyacinth
Daisy
CrocusWir werden mit der Verwendung von SequenceInputStream, InputStreamReader und BufferedReader zwei oben gemeinten Dateien lesen
SequenceInputStreamEx1.java
package org.o7planning.sequenceinputstream.ex;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
public class SequenceInputStreamEx1 {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/flowers-1.txt
private static String file_path1 = "/Volumes/Data/test/flowers-1.txt";
private static String file_path2 = "/Volumes/Data/test/flowers-2.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is1 = new FileInputStream(file_path1);
InputStream is2 = new FileInputStream(file_path2);
// Create SequenceInputStream:
InputStream is = new SequenceInputStream(is1, is2);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
while((line = br.readLine())!= null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}Output:
# Flower names (1)
Tulip
Daffodil
Poppy
Sunflower
Bluebell
Rose
Snowdrop
Cherry blossom
# Flower names (2)
Orchid
Iris
Peony
Chrysanthemum
Geranium
Lily
Lotus
Water lily
Dandelion
Hyacinth
Daisy
CrocusVerbessern Sie das obige Beispiel, drücken Sie einfach die Zeile aus, die nicht leer und keine Kommentarzeile ist (beginnen Sie mit "#").
SequenceInputStreamEx2.java
package org.o7planning.sequenceinputstream.ex;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
public class SequenceInputStreamEx2 {
// Windows: C:/Data/test/flowers-1.txt
private static String file_path1 = "/Volumes/Data/test/flowers-1.txt";
private static String file_path2 = "/Volumes/Data/test/flowers-2.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is1 = new FileInputStream(file_path1);
InputStream is2 = new FileInputStream(file_path2);
// Create SequenceInputStream:
InputStream is = new SequenceInputStream(is1, is2);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
br.lines() // Stream
.filter(line -> !line.isBlank()) // Not blank
.filter(line -> !line.startsWith("#")) // Not start with "#"
.forEach(System.out::println);
br.close();
}
}Output:
Tulip
Daffodil
Poppy
Sunflower
Bluebell
Rose
Snowdrop
Cherry blossom
Orchid
Iris
Peony
Chrysanthemum
Geranium
Lily
Lotus
Water lily
Dandelion
Hyacinth
Daisy
CrocusDie Anleitungen Java IO
- Die Anleitung zu Java CharArrayWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java FilterReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java FilterWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java PrintStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java BufferedReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java BufferedWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java StringReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java StringWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java PipedReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java LineNumberReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java PushbackReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java PrintWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java IO Binary Streams
- Die Anleitung zu Java IO Character Streams
- Die Anleitung zu Java BufferedOutputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java ByteArrayOutputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java DataOutputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java PipedInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java OutputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java ObjectOutputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java PushbackInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java SequenceInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java BufferedInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java Reader
- Die Anleitung zu Java Writer
- Die Anleitung zu Java FileReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java FileWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java CharArrayReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java ByteArrayInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java DataInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java ObjectInputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java InputStreamReader
- Die Anleitung zu Java OutputStreamWriter
- Die Anleitung zu Java InputStream
- Die Anleitung zu Java FileInputStream
Show More
- Anleitungen Java Servlet/JSP
- Die Anleitungen Java New IO
- Anleitungen Spring Cloud
- Die Anleitungen Oracle Java ADF
- Die Anleitungen Java Collections Framework
- Java Grundlagen
- Die Anleitungen Java Date Time
- Java Open Source Bibliotheken
- Anleitungen Java Web Services
- Die Anleitungen Struts2 Framework
- Anleitungen Spring Boot