Operator instanceof in der TypeScript-Sprache
1. Der Operator instanceof
Der Operator instanceof wird verwendet, um zu überprüfen, ob ein Objekt ein Objekt einer angegebenen Klasse ist. Dieser Operator gibt true oder false zurück.
Die Syntax:
anObject instanceof AClass;
let result = anObject instanceof AClass;Die Eigenschaften des Operators instanceof:
- Die linke Seite des Ausdrucks instanceof darf kein primitiver Datentyp sein. Es muss ein Objekt sein.
- Die rechte Seite des Ausdrucks instanceof muss eine Klasse sein.
Wir werden die oben genannten Eigenschaften des Operators instanceof anhand von Beispielen verdeutlichen:
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, dass der Compiler einen Fehler meldet, wenn die linke Seite des Ausdrucks instanceof ein primitiver Wert ist.
- null, string, number, boolean, NaN, undefined, Symbol
instanceof_ex1a.ts
class Abc { }
let aNaN = NaN;
aNaN instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let aNumber = 123;
aNumber instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let anUndefined = undefined;
anUndefined instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let aSymbol = Symbol("Something");
aSymbol instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let aNull = null;
aNull instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let aBoolean = true;
aBoolean instanceof Abc; // Compile Error!!!
let aBooleanObject = new Boolean(true); // Boolean Object
aBooleanObject instanceof Abc; // Compile OK!Beispiel: Die linke Seite des Ausdrucks instanceof muss ein Objekt sein:
instanceof_ex1b.ts
interface IEmployee {
empId: number,
empName: string
}
class Mouse {}
class Cat {}
var anObject1 = {name: 'Tom', gender: 'Male'};
anObject1 instanceof Mouse; // Compile OK!
var anObject2:IEmployee = {empId: 1, empName: 'Donald'};
anObject2 instanceof Cat; // Compile OK!
var anObject3 = new Mouse();
anObject3 instanceof Cat; // Compile OK!Beispiel: Der Compiler meldet einen Fehler, wenn die rechte Seite des Ausdrucks instanceof keine Klasse ist.
instanceof_ex2a.ts
interface IStaff {
staffId: number,
staffName: string
}
class Person {}
let aAnyObject = {}; // Any Objet
aAnyObject instanceof IStaff; // Compile Error !!!! (IStaff is not a class).
aAnyObject instanceof Person; // Compile OK!- Schnittstellen in TypeScript
- Classes
2. Zum Beispiel:
In diesem Beispiel haben wir die Klassen Animal, Duck und Horse und die Interface IMove. Lassen Sie uns einige Objekte erstellen und sehen, wie der Operator instanceof funktioniert.
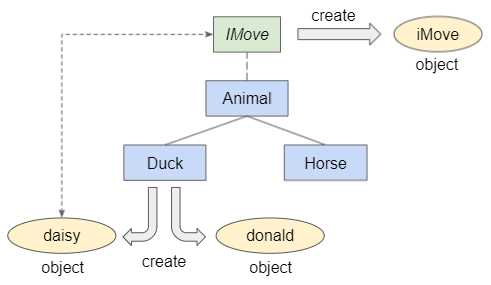
instanceof_ex3.ts
interface IMove {
move(): void;
}
class Animal implements IMove {
move() {
console.log("Animal move!");
}
}
class Duck extends Animal {}
class Horse extends Animal {}
let donald = new Duck();
console.log("donald instancef Duck? " + (donald instanceof Duck)); // true
console.log("donald instancef Animal? " + (donald instanceof Animal)); // true
console.log("donald instancef Horse? " + (donald instanceof Horse)); // false
let daisy: IMove = new Duck();
console.log("daisy instancef Duck? " + (daisy instanceof Duck)); // true
console.log("daisy instancef Animal? " + (daisy instanceof Animal)); // true
console.log("daisy instancef Horse? " + (daisy instanceof Horse)); // false
let iMove: IMove = {
move : function() {
console.log('IMove move!');
}
};
console.log("iMove instancef Duck? " + (iMove instanceof Duck)); // false
console.log("iMove instancef Animal? " + (iMove instanceof Animal)); // false
console.log("iMove instancef Horse? " + (iMove instanceof Horse)); // falseOutput:
donald instancef Duck? true
donald instancef Animal? true
donald instancef Horse? false
daisy instancef Duck? true
daisy instancef Animal? true
daisy instancef Horse? false
iMove instancef Duck? false
iMove instancef Animal? false
iMove instancef Horse? false
Beispiel: Verwenden Sie den Operator instanceof, um den an die Funktion übergebenen Parametertyp zu unterscheiden.
instanceof_cls_ex1.ts
class Food {
foodName: string;
constructor(foodName: string) {
this.foodName = foodName;
}
}
class Drink {
drinkName: string;
constructor(drinkName: string) {
this.drinkName = drinkName;
}
}
function getName(arg: Food | Drink) {
if(arg instanceof Food) {
let food = arg as Food;
return food.foodName;
} else {
let drink = arg as Drink;
return drink.drinkName;
}
}
let coca = new Drink("Cocacola");
console.log(getName(coca)); // Cocacola
let pho = new Food("Vietnamese Pho");
console.log(getName(pho)); // Vietnamese PhoOutput:
Cocacola
Vietnamese PhoDuck Typing
Der Operator instanceof wird verwendet, um zu überprüfen, ob ein Objekt ein Objekt einer Klasse ist. Es kann nicht für Interface verwendet werden, und Sie benötigen eine andere Technik, siehe Beispiel:
duck_typing_ex1.ts
interface IWorker {
workerId: number,
workerName: string
}
interface IStudent {
studentId: number,
studentName: string
}
function getNameOf(arg: IWorker | IStudent) {
let test1 = arg as IWorker;
if(test1.workerId && test1.workerName) {
return test1.workerName;
}
let test2 = arg as IStudent;
return test2.studentName;
}
let tom = {workerId: 1, workerName: 'Tom'};
let jerry = {studentId: 1, studentName: 'Jerry'};
console.log(getNameOf(tom)); // Tom
console.log(getNameOf(jerry)); // JerryOutput:
Tom
JerryAnleitungen Typescript
- Führen Sie Ihr erstes TypeScript-Beispiel in Visual Studio Code aus
- Die Anleitung zu TypeScript Namespaces
- Die Anleitung zu TypeScript Module
- Typeof-Operator in der TypeScript-Sprache
- Schleifen in TypeScript
- Installieren Sie das TypeScript unter Windows
- Funktionen in TypeScript
- Die Anleitung zu TypeScript Tuples
- Schnittstellen in TypeScript
- Die Anleitung zu TypeScript Arrays
- Operator instanceof in der TypeScript-Sprache
- Methoden in TypeScript
- Die Anleitung zu TypeScript Closures
- Konstruktoren in TypeScript
- Eigenschaften in TypeScript
- Analysieren von JSON in TypeScript
- Analysieren von JSON in TypeScript mit der json2typescript-Bibliothek
- Was ist Transpiler?
Show More