Java-Remote-Methodenaufruf - Java RMI
1. Die Vorstellung
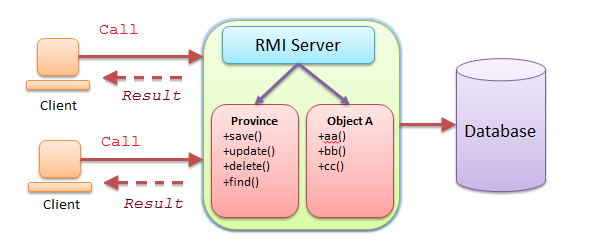
RMI ist eine Möglichkeit, um eine Methode aus der Ferne aufzurufen, wie Aufrufen einer in PC B laufenden Methode. Und die zurückgegebene Ergebnisse erhalten. Deshalb gilt das PC B als einen Server der Dienstleistungsversorgung.
2. Das Projekt erstellen
Ein Projekt mit dem Name RMITutorial neu erstellen
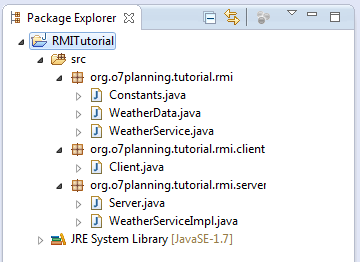
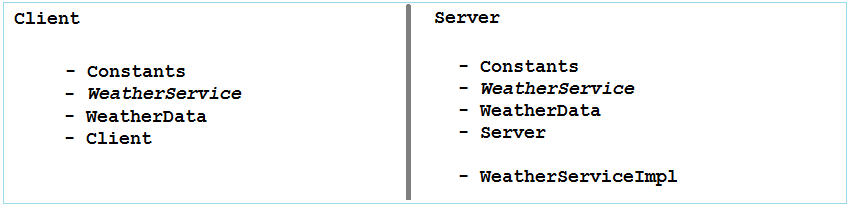
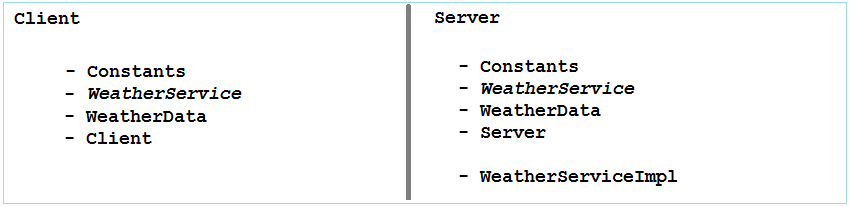
Das ist die Modelle von der Class, die für Client und Server eingepackt wird
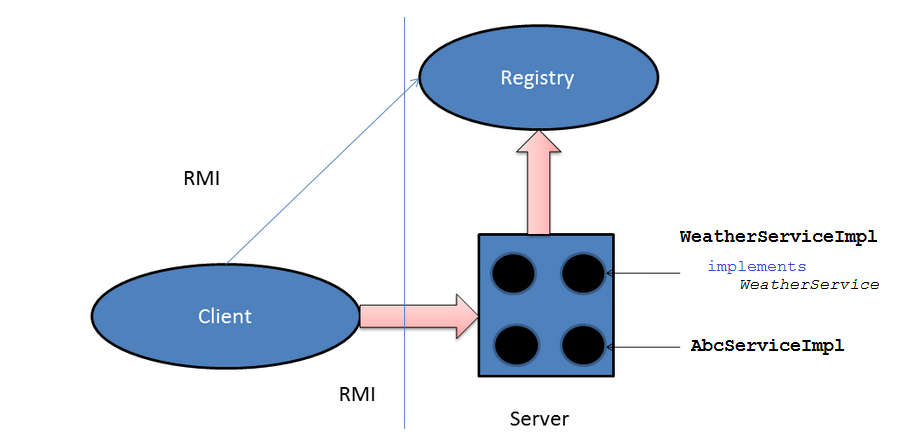
Das ist die Modelle der Operation von RMI. Server registriert den Objekt in der Registrierung (registry). Client sucht die Registrierung nach der IP Addresse und Port (Host + Port) um die Method aus den Object bei Server aufzurufen
Constants.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
public class Constants {
public static final String LOCATION_HANOI = "HaNoi";
public static final String LOCATION_TOKYO = "Tokyo";
public static final String LOCATION_CHICAGO = "Chicago";
public static final String WEATHER_RAIN ="rain";
public static final String WEATHER_SUNNY ="sunny";
}WeatherData.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class WeatherData implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Date date;
private String location;
private String weather;
public WeatherData(Date date, String location, String weather) {
this.date = date;
this.location = location;
this.weather = weather;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
}WeatherService.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.Date;
public interface WeatherService extends Remote {
// Method to retrieve weather information.
public WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException;
}WeatherServiceImpl.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class WeatherServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements
WeatherService {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public WeatherServiceImpl() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
@Override
public synchronized WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(date);
int dayOfWeek = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
// Sunday, Monday
if (dayOfWeek == 1 || dayOfWeek == 2) {
if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO)) {
// Rain
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_RAIN);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_HANOI)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_TOKYO)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else {
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
}
}Client.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.client;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Client {
// Host or IP of Server
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Search the registry in the specific Host, Port.
registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(HOST, PORT);
// Lookup WeatherService in the Registry.
WeatherService service = (WeatherService) registry
.lookup(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName());
Date today = new Date();
// Get Chicago weather info:
WeatherData chicagoWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO);
System.out.println("Chicago weather today: "
+ chicagoWeather.getWeather());
// Get Hanoi weather info:
WeatherData hanoiWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_HANOI);
System.out.println("Hanoi weather today: " + hanoiWeather.getWeather());
}
}Server.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Server {
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void startRegistry() throws RemoteException {
// Create server registry
registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(PORT);
}
public static void registerObject(String name, Remote remoteObj)
throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException {
// Bind the object in the registry.
// It is bind with certain name.
// Client will lookup on the registration of the name to get object.
registry.bind(name, remoteObj);
System.out.println("Registered: " + name + " -> "
+ remoteObj.getClass().getName() + "[" + remoteObj + "]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Server starting...");
startRegistry();
registerObject(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName(), new WeatherServiceImpl());
// Server was the start, and was listening to the request from the client.
System.out.println("Server started!");
}
}3. Die Applikation laufen
Sie brauchen die Project in der 2 jar einzupacken, um die oben Applikation zu starten. File jar 1 besteht aus die Class für das Starten der Applikation bei Client. Und File 2 besteht aus die Class für das Starten der Applikation bei Server
Das ist die Image für Beispiel
Aber Sie können eine Demo in Eclipse tun
Die Class Server zuerst laufen
Server starting...
Registered: WeatherService -> org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server.WeatherServiceImpl[WeatherServiceImpl[UnicastServerRef [liveRef: [endpoint:[192.168.0.102:64865](local),objID:[6aadac58:179707abf4c:-7fff, -728182817779393915]]]]]
Server started!Server läuft gerade. Er registrierte die Remote Object in der Registrierung (registry). Nächste laufen Sie die Class bei Client. Die Class Client starten:
Chicago weather today: sunny
Hanoi weather today: sunnyJava Grundlagen
- Anpassen von Java-Compiler, der Ihre Annotation verarbeitet (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programmierung für Team mit Eclipse und SVN
- Die Anleitung zu Java WeakReference
- Die Anleitung zu Java PhantomReference
- Komprimierung und Dekomprimierung in Java
- Konfigurieren von Eclipse zur Verwendung des JDK anstelle von JRE
- Java-Methoden String.format() und printf()
- Syntax und neue Funktionen in Java 8
- Die Anleitung zu Java Reguläre Ausdrücke
- Die Anleitung zu Java Multithreading Programming
- JDBC Driver Bibliotheken für verschiedene Arten von Datenbank in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java JDBC
- Holen Sie sich die automatisch erhöhenden Wert der Spalte bei dem Insert eines Rekord, der JDBC benutzt
- Die Anleitung zu Java Stream
- Die Anleitung zu Java Functional Interface
- Einführung in Raspberry Pi
- Die Anleitung zu Java Predicate
- Abstrakte Klasse und Interface in Java
- Zugriffsmodifikatoren (Access modifiers) in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Enum
- Die Anleitung zu Java Annotation
- Vergleichen und Sortieren in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java String, StringBuffer und StringBuilder
- Die Anleitung zu Java Exception
- Die Anleitung zu Java Generics
- Manipulieren von Dateien und Verzeichnissen in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiPredicate
- Die Anleitung zu Java Consumer
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiConsumer
- Was ist erforderlich, um mit Java zu beginnen?
- Geschichte von Java und der Unterschied zwischen Oracle JDK und OpenJDK
- Installieren Sie Java unter Windows
- Installieren Sie Java unter Ubuntu
- Installieren Sie OpenJDK unter Ubuntu
- Installieren Sie Eclipse
- Installieren Sie Eclipse unter Ubuntu
- Schnelle lernen Java für Anfänger
- Geschichte von Bits und Bytes in der Informatik
- Datentypen in Java
- Bitweise Operationen
- if else Anweisung in Java
- Switch Anweisung in Java
- Schleifen in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Array
- JDK Javadoc im CHM-Format
- Vererbung und Polymorphismus in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Function
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiFunction
- Beispiel für Java Encoding und Decoding mit Apache Base64
- Die Anleitung zu Java Reflection
- Java-Remote-Methodenaufruf - Java RMI
- Die Anleitung zu Java Socket
- Welche Plattform sollten Sie wählen für Applikationen Java Desktop entwickeln?
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons IO
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons Email
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons Logging
- Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode und Object.equals verstehen
- Die Anleitung zu Java SoftReference
- Die Anleitung zu Java Supplier
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming mit AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Anleitungen Java Servlet/JSP
- Die Anleitungen Java Collections Framework
- Java API für HTML & XML
- Die Anleitungen Java IO
- Die Anleitungen Java Date Time
- Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Anleitungen Maven
- Anleitungen Gradle
- Anleitungen Java Web Services
- Anleitungen Java SWT
- Die Anleitungen JavaFX
- Die Anleitungen Oracle Java ADF
- Die Anleitungen Struts2 Framework
- Anleitungen Spring Cloud