Java-Methoden String.format() und printf()
1. printf()
Bei der Programmierung Java stößt man oft auf den Code System.out.printf(..). Tatsächlich ist die Methode printf(..) sowohl in der Klasse PrintStream als auch in der Klasse PrintWriter definiert. Ihre Verwendung ist ähnlich, printf steht für "Print + Format".
printf methods
// Definition of the printf methods in the PrintWriter class:
public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object... args)
public PrintStream printf(String format, Object... args)
// Definition of the printf methods in PrintWriter class:
public PrintWriter printf(Locale l, String format, Object... args)
public PrintWriter format(String format, Object... args)System.out.printf(..) ist ein Sonderfall, der verwendet wird, um einen formatierten Text in den Bildschirm Console zu schreiben, wobei System.out im Wesentlichen ein Objekt vom Typ PrintStream ist.
System class
package java.lang;
public final class System {
public static final PrintStream out = ...;
}Bevor wir beginnen, sehen wir uns ein einfaches Beispiel an:
Printf_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.printf.ex;
public class Printf_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String firstName = "James";
String lastName = "Smith";
int age = 20;
System.out.printf("My name is %s %s, I'm %d years old.", firstName, lastName, age);
}
}Output:
My name is James Smith, I'm 20 years old.2. Formatregeln
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterDiese Parameter: flags, width, precision sind optional.
3. conversion-character
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterconversion-character | Description | Type |
d | decimal integer | byte, short, int, long |
f | floating-point number | float, double |
b | Boolean | Object |
B | will uppercase the boolean | Object |
c | Character Capital | String |
C | will uppercase the letter | String |
s | String Capital | String |
S | will uppercase all the letters in the string | String |
h | hashcode - A hashcode is like an address. This is useful for printing a reference | Object |
n | newline - Platform specific newline character - use %n instead of \n for greater compatibility |
conversion-character: n
System.out.printf("One%nTwo%nThree");Output:
One
Two
Threeconversion-character: s
System.out.printf("My name is %s %s", "James", "Smith");Output:
My name is James Smithconversion-character: S
System.out.printf("My name is %S %S", "James", "Smith");Output:
My name is JAMES SMITHconversion-character: b
System.out.printf("%b%n", null);
System.out.printf("%b%n", false);
System.out.printf("%b%n", 5.3);
System.out.printf("%b%n", "Any text");
System.out.printf("%b%n", new Object());Output:
false
false
true
true
trueconversion-character: B
System.out.printf("%B%n", null);
System.out.printf("%B%n", false);
System.out.printf("%B%n", 5.3);
System.out.printf("%B%n", "Any text");
System.out.printf("%B%n", new Object());Output:
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
TRUE
TRUEconversion-character: d
System.out.printf("There are %d teachers and %d students in the class", 2, 25);Output:
There are 2 teachers and 25 students in the classconversion-character: f
System.out.printf("Exchange rate today: EUR %f = USD %f", 1.0, 1.2059);Output:
Exchange rate today: EUR 1.000000 = USD 1.205900conversion-character: c
char ch = 'a';
System.out.printf("Code of '%c' character is %d", ch, (int)ch);Output:
Code of 'a' character is 97conversion-character: C
char ch = 'a';
System.out.printf("'%C' is the upper case of '%c'", ch, ch);Output:
'A' is the upper case of 'a'conversion-character: h
Printf_cc_h_ex.java
package org.o7planning.printf.ex;
public class Printf_cc_h_ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// h (Hashcode HEX)
Object myObject = new AnyObject("Something");
System.out.println("Hashcode: " + myObject.hashCode());
System.out.println("Identity Hashcode: " + System.identityHashCode(myObject));
System.out.println("Hashcode (HEX): " + Integer.toHexString(myObject.hashCode()));
System.out.println("toString : " + String.valueOf(myObject));
System.out.printf("Printf: %h", myObject);
}
}
class AnyObject {
private String val;
public AnyObject(String val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (this.val == null || this.val.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
return 1000 + (int) this.val.charAt(0);
}
}Output:
Hashcode: 1083
Identity Hashcode: 1579572132
Hashcode (HEX): 43b
toString : org.o7planning.printf.ex.AnyObject@43b
Printf: 43b4. width
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterwidth - gibt den Mindestabstand (Anzahl der Zeichen) an, der die Platze zum Drucken des Inhalts eines entsprechenden Arguments halten
printf(format, arg1, arg2,.., argN)5. flags
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterflag | Description |
- | left-justify (default is to right-justify ) |
+ | output a plus ( + ) or minus ( - ) sign for a numerical value |
0 | forces numerical values to be zero-padded (default is blank padding ) |
, | comma grouping separator (for numbers > 1000) |
space will display a minus sign if the number is negative or a space if it is positive |
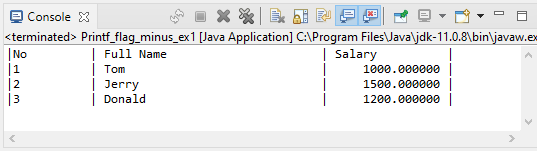
flag: -
String[] fullNames = new String[] {"Tom", "Jerry", "Donald"};
float[] salaries = new float[] {1000, 1500, 1200};
// s
System.out.printf("|%-10s | %-30s | %-15s |%n", "No", "Full Name", "Salary");
for(int i=0; i< fullNames.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("|%-10d | %-30s | %15f |%n", (i+1), fullNames[i], salaries[i]);
}Output:
flag: +
// flag: +
System.out.printf("The world's economy increased by %+f percent in 2020. %n", -3.3);
System.out.printf("China's economy increased by %+f percent in 2020. %n", 2.3);
System.out.println();
// without flag: +
System.out.printf("The world's economy increased by %f percent in 2020. %n", -3.3);
System.out.printf("China's economy increased by %f percent in 2020. %n", 2.3);Output:
The world's economy increased by -3.300000 percent in 2020.
China's economy increased by +2.300000 percent in 2020.
The world's economy increased by -3.300000 percent in 2020.
China's economy increased by 2.300000 percent in 2020.flag: 0 (zero)
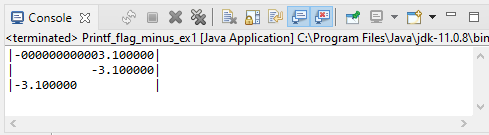
// flag: 0 & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%020f|%n", -3.1);
// without flag & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%20f|%n", -3.1);
// flag: - (left align) & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%-20fOutput:
flag: , (comma)
// flag: ,
System.out.printf("%,f %n", 12345678.9);
// flag: ,
System.out.printf("%,f %n", -12345678.9);Output:
12,345,678.900000
-12,345,678.900000flag: (space)
// flag: (space)
System.out.printf("% f %n", 12345678.9);
System.out.printf("% f %n", -12345678.9);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", 12345678.9);
System.out.printf("% ,Output:
12345678.900000
-12345678.900000
12,345,678.900000
-12,345,678.9000006. precision
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterSystem.out.printf("%f %n", 12345678.911);
System.out.printf("%f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flag: , (comma)
System.out.printf("%,f %n", 12345678.911);
// flag: , (comma)
System.out.printf("%,f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", 12345678.911);
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flag: , (comma) & precision: .2
System.out.printf("%,.2f %n", 12345678.911);
// flag: , (comma) & precision: .3
System.out.printf("%,.3f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma) & precision: .2
System.out.printf("% ,.2f %n", 12345678.911);
// flags: , (space + comma) & precision: .3
System.out.printf("% ,.3f %n", -12345678.911);Output:
12345678.911000
-12345678.911000
12,345,678.911000
-12,345,678.911000
12,345,678.911000
-12,345,678.911000
12,345,678.91
-12,345,678.911
12,345,678.91
-12,345,678.911Java Grundlagen
- Anpassen von Java-Compiler, der Ihre Annotation verarbeitet (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programmierung für Team mit Eclipse und SVN
- Die Anleitung zu Java WeakReference
- Die Anleitung zu Java PhantomReference
- Komprimierung und Dekomprimierung in Java
- Konfigurieren von Eclipse zur Verwendung des JDK anstelle von JRE
- Java-Methoden String.format() und printf()
- Syntax und neue Funktionen in Java 8
- Die Anleitung zu Java Reguläre Ausdrücke
- Die Anleitung zu Java Multithreading Programming
- JDBC Driver Bibliotheken für verschiedene Arten von Datenbank in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java JDBC
- Holen Sie sich die automatisch erhöhenden Wert der Spalte bei dem Insert eines Rekord, der JDBC benutzt
- Die Anleitung zu Java Stream
- Die Anleitung zu Java Functional Interface
- Einführung in Raspberry Pi
- Die Anleitung zu Java Predicate
- Abstrakte Klasse und Interface in Java
- Zugriffsmodifikatoren (Access modifiers) in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Enum
- Die Anleitung zu Java Annotation
- Vergleichen und Sortieren in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java String, StringBuffer und StringBuilder
- Die Anleitung zu Java Exception
- Die Anleitung zu Java Generics
- Manipulieren von Dateien und Verzeichnissen in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiPredicate
- Die Anleitung zu Java Consumer
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiConsumer
- Was ist erforderlich, um mit Java zu beginnen?
- Geschichte von Java und der Unterschied zwischen Oracle JDK und OpenJDK
- Installieren Sie Java unter Windows
- Installieren Sie Java unter Ubuntu
- Installieren Sie OpenJDK unter Ubuntu
- Installieren Sie Eclipse
- Installieren Sie Eclipse unter Ubuntu
- Schnelle lernen Java für Anfänger
- Geschichte von Bits und Bytes in der Informatik
- Datentypen in Java
- Bitweise Operationen
- if else Anweisung in Java
- Switch Anweisung in Java
- Schleifen in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Array
- JDK Javadoc im CHM-Format
- Vererbung und Polymorphismus in Java
- Die Anleitung zu Java Function
- Die Anleitung zu Java BiFunction
- Beispiel für Java Encoding und Decoding mit Apache Base64
- Die Anleitung zu Java Reflection
- Java-Remote-Methodenaufruf - Java RMI
- Die Anleitung zu Java Socket
- Welche Plattform sollten Sie wählen für Applikationen Java Desktop entwickeln?
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons IO
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons Email
- Die Anleitung zu Java Commons Logging
- Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode und Object.equals verstehen
- Die Anleitung zu Java SoftReference
- Die Anleitung zu Java Supplier
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming mit AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Anleitungen Java Servlet/JSP
- Die Anleitungen Java Collections Framework
- Java API für HTML & XML
- Die Anleitungen Java IO
- Die Anleitungen Java Date Time
- Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Anleitungen Maven
- Anleitungen Gradle
- Anleitungen Java Web Services
- Anleitungen Java SWT
- Die Anleitungen JavaFX
- Die Anleitungen Oracle Java ADF
- Die Anleitungen Struts2 Framework
- Anleitungen Spring Cloud