Verwenden Sie in Spring MVC mehrere DataSources
1. Das Zweck des Unterlagen
Manchmal sollen Sie eine Website applikation verbindend mit vielen unterchiedlichen Database erstellen. Und Sie können es im Spring MVC einfach machen.
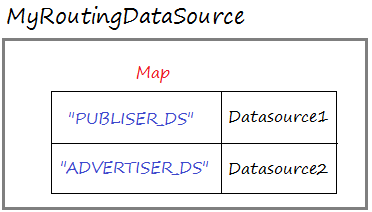
Spring bietet Sie die Klasse AbstractRoutingDataSource, Sie sollen eine Klasse schreiben, die aus der Klasse ausgeweitert wird. Routing Datasource enthaltet ein Map der echten Datasource. Und sie entscheidet, welche entspechende DataSource der Anforderung aus dem Benutzer benutzt werden
Spring bietet Sie die Klasse AbstractRoutingDataSource, Sie sollen eine Klasse schreiben, die aus der Klasse ausgeweitert wird. Routing Datasource enthaltet ein Map der echten Datasource. Und sie entscheidet, welche entspechende DataSource der Anforderung aus dem Benutzer benutzt werden
Routing Datasource ist auch eine Datasource, Sie ist eine besondere Datasource .
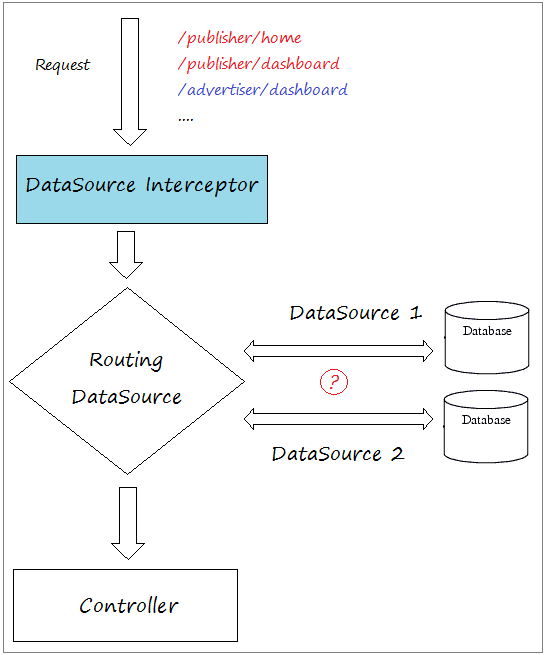
Im Dokument bezeichne ich eine Website benutzend 2 datasource. Jede datasource verbindet mit einer verschiedenen Database. Eine Database speichert die Information für das System Publisher und eine Database speichert die Information für das System Advertiser
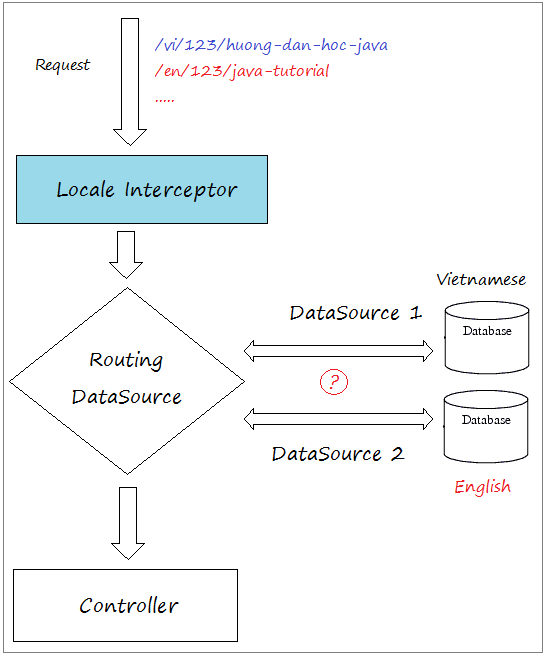
In einiger Situation können Sie eine MultispracheWebsite machen. Sie können viele Database erstellen. Jede Database speichert den Artikel einer bestimmten Sprache
2. Die Database vorbereiten
Ich werde 2 Database erstellen. Eine Database ist für das System PUBLISHER und eine Database für das System ADVERTISER . 2 Database können die gleichen Typ sein. Sie können Oracle, MySQL oder SQL Server, ... benutzen
Database1:
Das DB System vom PUBLISHER hat eine Tabelle Publishers.
Database1 - (ORACLE)
-- Create table
create table PUBLISHERS
(
NAME VARCHAR2(50)
);
insert into publishers (NAME)
values ('publisher 1');
insert into publishers (NAME)
values ('publisher 2');
Commit;Database1 - (MySQL or SQL Server)
-- Create table
create table PUBLISHERS
(
NAME VARCHAR(50)
);
insert into publishers (NAME)
values ('publisher 1');
insert into publishers (NAME)
values ('publisher 2');Database 2:
Das DB System vom ADVERTISER hat eine Tabelle Advertisers.
Database2 - (ORACLE)
-- Create table
create table ADVERTISERS
(
NAME VARCHAR2(50)
);
insert into advertisers (NAME)
values ('Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (NAME)
values ('Advertiser 2');
Commit;Database2 (MySQL or SQL Server)
-- Create table
create table ADVERTISERS
(
NAME VARCHAR(50)
);
insert into advertisers (NAME)
values ('Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (NAME)
values ('Advertiser 2');3. Maven Web App Project erstellen
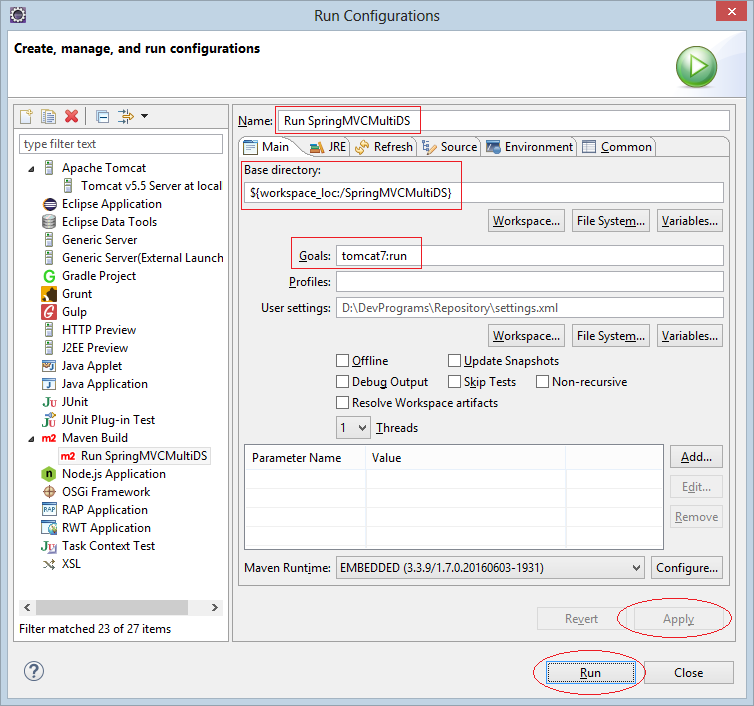
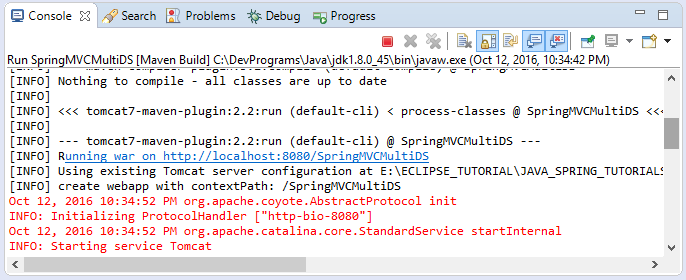
Auf Eclipse erstellen Sie ein leeres Maven Web App Project mit dem Name vom SpringMVCMultiDS.
4. web.xml & pom.xml konfigurieren
WebApp >= 3 benutzen
web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<display-name>SpringMVCMultiDS Web Application</display-name>
</web-app>In pom.xml habe ich die JDBC für 3 DB Oracle, MySQL und SQL Server erklärt.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMVCMultiDS</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringMVCMultiDS Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE JDBC Driver -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet API -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Jstl for jsp page -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/jstl -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSP API -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet.jsp/jsp-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring dependencies -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-tx -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>4.3.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Commons DataSources -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-dbcp/commons-dbcp -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL JDBC driver -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Oracle JDBC driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- SQLServer JDBC driver (JTDS) -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sourceforge.jtds/jtds -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.jtds</groupId>
<artifactId>jtds</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMVCMultiDS</finalName>
<plugins>
<!-- Config: Maven Tomcat Plugin -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.tomcat.maven/tomcat7-maven-plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<!-- Config: contextPath and Port (Default - /SpringMVCMultiDS,8080) -->
<!--
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<port>8899</port>
</configuration>
-->
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>5. Spring MVC konfigurieren
SpringWebAppInitializer.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.config;
import javax.servlet.FilterRegistration;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
public class SpringWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext appContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
appContext.register(ApplicationContextConfig.class);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("SpringDispatcher",
new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
//
dispatcher.setInitParameter("contextClass", appContext.getClass().getName());
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(appContext));
// UTF8 Charactor Filter.
FilterRegistration.Dynamic fr = servletContext.addFilter("encodingFilter", CharacterEncodingFilter.class);
fr.setInitParameter("encoding", "UTF-8");
fr.setInitParameter("forceEncoding", "true");
fr.addMappingForUrlPatterns(null, true, "/*");
}
}Im WebMvcConfig sollen Sie DataSourceInterceptor registrieren. Der Interceptor analysiert URL von geschickten Anforderung (request) um welche Datasource zur Benutzung zu entscheiden
WebMvcConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.config;
import org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.interceptor.DataSourceIntercetor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// Default..
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
//
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new DataSourceIntercetor())//
.addPathPatterns("/publisher/*", "/advertiser/*");
}
}ApplicationContextConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.config;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.routing.MyRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.*")
@EnableTransactionManagement
// Load to Environment.
@PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:ds/datasource-cfg.properties") })
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
// The Environment class serves as the property holder
// and stores all the properties loaded by the @PropertySource
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean(name = "viewResolver")
public InternalResourceViewResolver getViewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/pages/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
// Returns Routing DataSource (MyRoutingDataSource)
@Autowired
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DataSource getDataSource(DataSource dataSource1, DataSource dataSource2) {
System.out.println("## Create DataSource from dataSource1 & dataSource2");
MyRoutingDataSource dataSource = new MyRoutingDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dsMap = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
dsMap.put("PUBLISHER_DS", dataSource1);
dsMap.put("ADVERTISER_DS", dataSource2);
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(dsMap);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "dataSource1")
public DataSource getDataSource1() throws SQLException {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
// See: datasouce-cfg.properties
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("ds.database-driver1"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("ds.url1"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("ds.username1"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("ds.password1"));
System.out.println("## getDataSource1: " + dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource getDataSource2() throws SQLException {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
// See: datasouce-cfg.properties
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("ds.database-driver2"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("ds.url2"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("ds.username2"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("ds.password2"));
System.out.println("## getDataSource2: " + dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Autowired
@Bean(name = "transactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager txManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
txManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return txManager;
}
}Die Information von Database wird in die File ds/datasource-cfg.xml konfiguriert und wird von der Klasse ApplicationContextConfig gelesen.
ds/datasource-cfg.properties (ORACLE + ORACLE)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
ds.database-driver1=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
ds.url1=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
ds.username1=publisher
ds.password1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
ds.database-driver2=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
ds.url2=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
ds.username2=advertiser
ds.password2=12345ds/datasource-cfg.properties (MySQL + MySQL)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
ds.database-driver1=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ds.url1=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/publisher
ds.username1=root
ds.password1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
ds.database-driver2=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ds.url2=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/advertiser
ds.username2=root
ds.password2=12345ds/datasource-cfg.properties (SQL Server + SQL Server)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
ds.database-driver1=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
ds.url1=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/simplehr;instance=SQLEXPRESS
ds.username1=publisher
ds.password1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
ds.database-driver2=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
ds.url2=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/simplehr;instance=SQLEXPRESS
ds.username2=advertiser
ds.password2=123456. Model, Interceptor, Routing, Controller ...
DataSourceIntercetor ist ein Interceptor, der nach URL von der geschickten Anforderung (request) die Benutzung von der Datasource entscheidet
DataSourceIntercetor.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.interceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
public class DataSourceIntercetor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
// Request:
// /publisher/list
// /advertiser/list
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
String contextPath = request.getServletContext().getContextPath();
// /SpringMVCMultiDS/publisher
String prefixPublisher = contextPath + "/publisher";
// /SpringMVCMultiDS/advertiser
String prefixAdvertiser = contextPath + "/advertiser";
// /SpringMVCMultiDS/publisher/dashboard
// /SpringMVCMultiDS/advertiser/dashboard
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println("URI:"+ uri);
if(uri.startsWith(prefixPublisher)) {
request.setAttribute("keyDS", "PUBLISHER_DS");
}
else if(uri.startsWith(prefixAdvertiser)) {
request.setAttribute("keyDS", "ADVERTISER_DS");
}
return true;
}
}MyRoutingDataSource íst eine DataSource, die ein Map zwischen die Schlüssel und die echtlichen Datasource enhaltet.
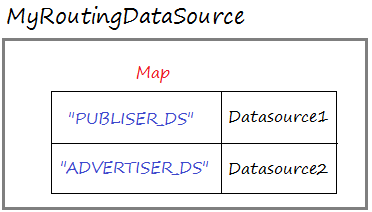
MyRoutingDataSource.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.routing;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
// This is a DataSource.
public class MyRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())
.getRequest();
// See more: DataSourceInterceptor
String keyDS = (String) request.getAttribute("keyDS");
System.out.println("KeyDS=" + keyDS);
if (keyDS == null) {
keyDS = "PUBLISHER_DS";
}
return keyDS;
}
}DataDAO ist eine Utiliity Klasse, die die Daten aus der Database abfragen
DataDAO.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class DataDAO extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@Autowired
public DataDAO(DataSource dataSource) {
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
}
public List<String> queryPublishers() {
String sql = "Select name from Publishers";
List<String> list = this.getJdbcTemplate().queryForList(sql, String.class);
return list;
}
public List<String> queryAdvertisers() {
String sql = "Select name from Advertisers";
List<String> list = this.getJdbcTemplate().queryForList(sql, String.class);
return list;
}
}MainController.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.controller;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.springmvcmultids.dao.DataDAO;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private DataDAO dataDAO;
@RequestMapping(value = { "/advertiser/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String advertiser(Model model) throws SQLException {
List<String> list = dataDAO.queryAdvertisers();
model.addAttribute("advertisers", list);
return "advertiser";
}
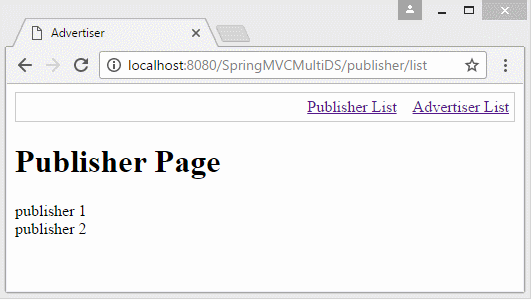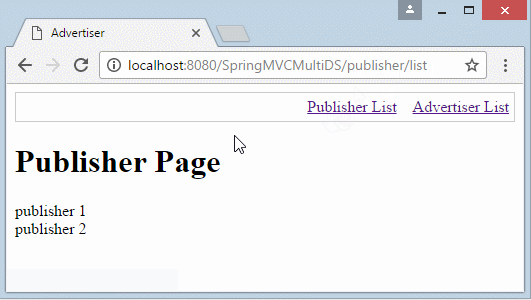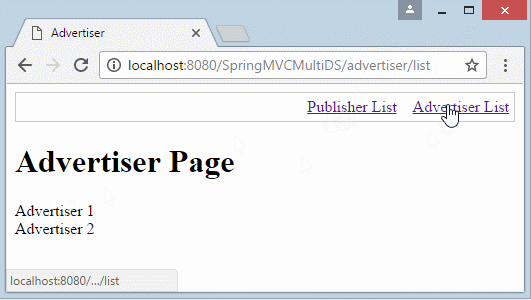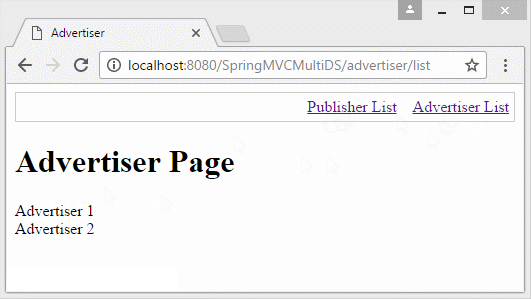
@RequestMapping(value = { "/publisher/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String publisher(Model model) throws SQLException {
List<String> list = dataDAO.queryPublishers();
model.addAttribute("publishers", list);
return "publisher";
}
}7. Views
/WEB-INF/pages/advertiser.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Advertiser</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="border:1px solid #ccc;text-align:right;padding:5px;">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/publisher/list">Publisher List</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/advertiser/list">Advertiser List</a>
</div>
<h1>Advertiser Page</h1>
<c:forEach var="item" items="${advertisers}" varStatus="status">
${item} <br/>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>/WEB-INF/pages/publisher.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Advertiser</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="border:1px solid #ccc;text-align:right;padding:5px;">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/publisher/list">Publisher List</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/advertiser/list">Advertiser List</a>
</div>
<h1>Publisher Page</h1>
<c:forEach var="item" items="${publishers}" varStatus="status">
${item} <br/>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>No ADS
Anleitungen Spring MVC
- Die Anleitung zum Sping für den Anfänger
- Installieren Sie die Spring Tool Suite für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum Sping MVC für den Anfänger - Hello Spring 4 MVC
- Konfigurieren Sie statische Ressourcen in Spring MVC
- Die Anleitung zu Spring MVC Interceptor
- Erstellen Sie eine mehr Sprachen Web-Anwendung mit Spring MVC
- Datei hochladen und herunterladen mit Spring MVC
- Einfache Anmeldung Java Web Application mit Spring MVC, Spring Security und Spring JDBC
- Social Login in Spring MVC mit Spring Social Security
- Die Anleitung zu Spring MVC mit FreeMarker
- Verwenden Sie Template in Spring MVC mit Apache Tiles
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng Spring MVC và Spring JDBC Transaction
- Verwenden Sie in Spring MVC mehrere DataSources
- Die Anleitung zu Spring MVC Form und Hibernate
- Führen Sie geplante Hintergrundaufgaben in Spring aus
- Erstellen Sie eine Java Shopping Cart Web Application mit Spring MVC und Hibernate
- Einfache CRUD Beispiel mit Spring MVC RESTful Web Service
- Stellen Sie Spring MVC auf Oracle WebLogic Server bereit
Show More