Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und JPA
1. Das Zweck des Artikel
Der Artikel wird nach ... geschrieben
Spring Boot 2.x (or >=1.5.9)
JPA
Thymeleaf (Or JSP)
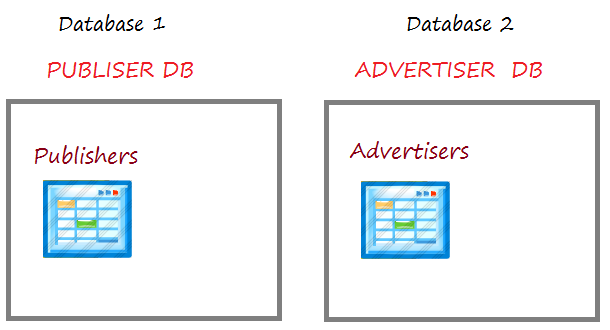
Im Artikel leite ich Sie bei der Erstellung einer Applikation Spring Boot & JPA mit der Verwendung von vielen DataSource. Wir haben 2 Database um mit dem Beispiel durchzuführen
- PUBLISHER: Das ist die Database 1, die eine Tabelle PUBLISHERS hat.
- ADVERTISER: Das ist die Database 2, die eine Tabelle ADVERTISERS hat.
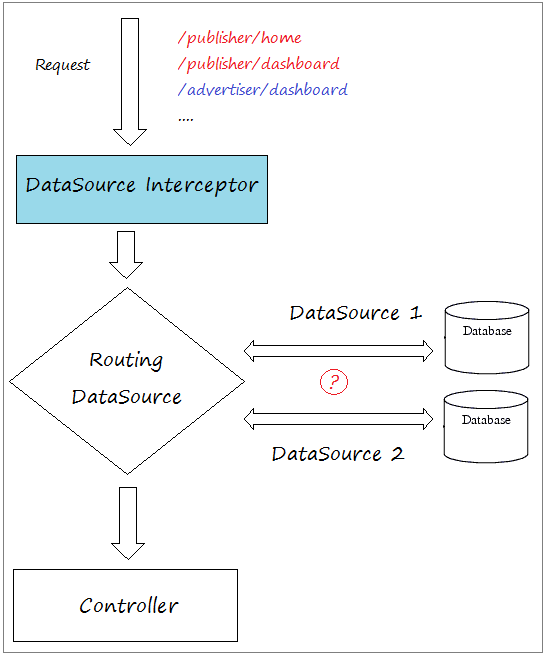
In der Applikation können gleichzeitig 2 obengemeinten Database verwenden. Zum Beispiel eine Seite zeigt die Liste der Publisher und gleichzeitig die Liste der Advertiser an. Deshalb sollen Sie mit 2 obengemeinten Database gleichzeitig arbeiten.
Im anderen Fall wenn Ihre Applikation mehr DataSource braucht, aber arbeitet in jeder Funktion (jeder Seite) nur mit einer bestimmten DataSource , dann sollen Sie Routing DataSource & DataSource Interceptor verwenden.
- Routing DataSource ist eine besondere DataSource. Sie enthaltet die Liste von DataSource , die in Ihrer Applikation verwendet werden.
- DataSource Interceptor wird entscheiden, welche DataSource nach der entsprechenden Funktion (jede Seite) in Ihrer Applikation verwendet werden
2. Database vorbereiten
MySQL, SQL Server, PostGres
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR PUBLISHER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table PUBLISHERS
(
ID Bigint,
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'publisher 1');
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'publisher 2');
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR ADVERTISER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table ADVERTISERS
(
ID Bigint,
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'Advertiser 2');Oracle
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR PUBLISHER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table PUBLISHERS
(
ID NUMBER(19),
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'publisher 1');
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'publisher 2');
Commit;
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR ADVERTISER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table ADVERTISERS
(
ID NUMBER(19),
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'Advertiser 2');
Commit;4. pom.xml konfigurieren
In die folgende pom.xml habe ich konfiguriert, dass die Applikation mit 4 üblichen Database wie MySQL, SQL Server, PostGres, Oracle arbeiten kann.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootJPAMultiDS</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootJPAMultiDS</name>
<description>Spring Boot + JPA + Multiple DataSources</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Remove Thymeleaf, If you want using JSP View -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - Mssql-Jdbc driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - JTDS driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.jtds</groupId>
<artifactId>jtds</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- For JSP VIEW (Need REMOVE spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- For JSP VIEW (Need REMOVE spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE JDBC Driver -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>5. DataSource konfigurieren
datasource-cfg.properties (MySQL)
# ===============================
# DATASOURCE
# ===============================
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=root
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=root
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql.1=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.1=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.1=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
spring.jpa.show-sql.2=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.2=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.2=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContextdatasource-cfg.properties (SQL Server + JTDS Driver)
# ===============================
# DATASOURCE
# ===============================
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/publisher;instance=SQLEXPRESS
spring.datasource.username.1=sa
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/advertiser;instance=SQLEXPRESS
spring.datasource.username.2=sa
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql.1=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.1=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1=org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.1=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
spring.jpa.show-sql.2=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.2=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2=org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.2=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContextdatasource-cfg.properties (SQL Server + Mssql-Jdbc Driver)
# ===============================
# DATASOURCE
# ===============================
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=sa
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=sa
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql.1=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.1=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1=org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.1=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
spring.jpa.show-sql.2=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.2=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2=org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.2=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContextdatasource-cfg.properties (Oracle)
# ===============================
# DATASOURCE
# ===============================
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username.1=publisher
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username.2=advertiser
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql.1=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.1=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.1=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
spring.jpa.show-sql.2=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.2=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.2=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContedatasource-cfg.properties (PostGres)
# ===============================
# DATASOURCE
# ===============================
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:postgresql://tran-vmware-pc:5432/publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=postgres
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:postgresql://tran-vmware-pc:5432/advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=postgres
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql.1=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.1=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL9Dialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.1=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContext
spring.jpa.show-sql.2=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto.2=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL9Dialect
#spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.current_session_context_class.2=org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.SpringSessionContextNach dem Standard wird Spring Boot eine standardmäßige DataSource automatisch konfigurieren. Deshalb brauchen Sie die automatische Konfiguration vom Spring Boot deaktivieren und machen Ihre eigenen Konfiguration vom DataSource
SpringBootJPAMultiDsApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication
// Disable some Spring Boot auto config
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = { //
DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, //
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class, //
HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class })
public class SpringBootJPAMultiDsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootJPAMultiDsApplication.class, args);
}
}Zunächst werden wir 2 DataSource konfigurieren:
- Die Klasse DataSource1Config für die Konfiguration von Datasource 1 (PUBLISHER DB).
- Die Klasse DataSource2Config für die Konfiguration von Datasource 2 (ADVERTISER DB).

Constants.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.config;
public class Constants {
public static final String PACKAGE_ENTITIES_1 = "org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity1";
public static final String PACKAGE_ENTITIES_2 = "org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity2";
public static final String JPA_UNIT_NAME_1 ="PERSITENCE_UNIT_NAME_1";
public static final String JPA_UNIT_NAME_2 ="PERSITENCE_UNIT_NAME_2";
}DataSource1Config.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
@Configuration
// Load to Environment
// (@see resources/datasource-cfg.properties).
@PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:datasource-cfg.properties") })
public class DataSource1Config {
@Autowired
private Environment env; // Contains Properties Load by @PropertySources
@Bean
public DataSource ds1Datasource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url.1"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username.1"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password.1"));
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean ds1EntityManager() {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setDataSource(ds1Datasource());
// Scan Entities in Package:
em.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { Constants.PACKAGE_ENTITIES_1 });
em.setPersistenceUnitName(Constants.JPA_UNIT_NAME_1); // Important !!
//
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
HashMap<String, Object> properties = new HashMap<>();
// JPA & Hibernate
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.1"));
properties.put("hibernate.show-sql", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.show-sql.1"));
// Solved Error: PostGres createClob() is not yet implemented.
// PostGres Only:
// properties.put("hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults", false);
em.setJpaPropertyMap(properties);
em.afterPropertiesSet();
return em;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager ds1TransactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(ds1EntityManager().getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
}DataSource2Config.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
@Configuration
// Load to Environment
// (@see resources/datasource-cfg.properties).
@PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:datasource-cfg.properties") })
public class DataSource2Config {
@Autowired
private Environment env; // Contains Properties Load by @PropertySources
@Bean
public DataSource ds2Datasource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url.2"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username.2"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password.2"));
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean ds2EntityManager() {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setDataSource(ds2Datasource());
// Scan Entities in Package:
em.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { Constants.PACKAGE_ENTITIES_2 });
em.setPersistenceUnitName(Constants.JPA_UNIT_NAME_2);
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
HashMap<String, Object> properties = new HashMap<>();
// JPA & Hibernate
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect.2"));
properties.put("hibernate.show-sql", env.getProperty("spring.jpa.show-sql.2"));
// Solved Error: PostGres createClob() is not yet implemented.
// PostGres Only.
// properties.put("hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults", false);
em.setJpaPropertyMap(properties);
em.afterPropertiesSet();
return em;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager ds2TransactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(ds2EntityManager().getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
}6. Entities, DAO
Publisher.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity1;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Publishers")
public class Publisher implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 746237126088051312L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "Id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "Name", length = 255, nullable = false)
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}Advertiser.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity2;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Advertisers")
public class Advertiser implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 746237126088051312L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "Id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "Name", length = 255, nullable = false)
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}PublisherDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.config.Constants;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity1.Publisher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class PublisherDAO {
@Autowired
@PersistenceContext( unitName= Constants.JPA_UNIT_NAME_1)
private EntityManager entityManager;
public List<Publisher> listPublishers() {
String sql = "Select e from " + Publisher.class.getName() + " e ";
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql, Publisher.class);
return query.getResultList();
}
public Publisher findById(Long id) {
return this.entityManager.find(Publisher.class, id);
}
}AdvertiserDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.config.Constants;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity2.Advertiser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AdvertiserDAO {
@Autowired
@PersistenceContext(unitName = Constants.JPA_UNIT_NAME_2)
private EntityManager entityManager;
public List<Advertiser> listAdvertisers() {
String sql = "Select e from " + Advertiser.class.getName() + " e ";
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql, Advertiser.class);
return query.getResultList();
}
public Advertiser findById(Long id) {
return this.entityManager.find(Advertiser.class, id);
}
}7. Controller
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbmultids.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.dao.AdvertiserDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.dao.PublisherDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity1.Publisher;
import org.o7planning.sbmultids.entity2.Advertiser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private PublisherDAO publisherDAO;
@Autowired
private AdvertiserDAO advertiserDAO;
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String homePage(Model model) {
List<Advertiser> advertisers = advertiserDAO.listAdvertisers();
List<Publisher> publishers = publisherDAO.listPublishers();
model.addAttribute("advertisers", advertisers);
model.addAttribute("publishers", publishers);
return "home";
}
}8. Thymeleaf Template
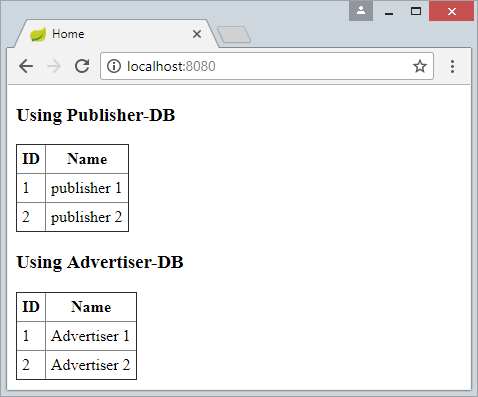
home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Home</title>
<style>
th, td {
padding: 5px;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Using Publisher-DB</h3>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="publisher : ${publishers}">
<td th:utext="${publisher.id}"></td>
<td th:utext="${publisher.name}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
<h3>Using Advertiser-DB</h3>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="advertiser : ${advertisers}">
<td th:utext="${advertiser.id}"></td>
<td th:utext="${advertiser.name}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>9. Der Anhang: JSP View
No ADS
Mehr sehen
Falls Sie die Technologie JSP für View-Layer verwenden:
home.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Home</title>
<style>
th, td {
padding: 5px;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Using Publisher-DB</h3>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${publishers}" var="publisher">
<tr>
<td th:utext="${publisher.id}"></td>
<td th:utext="${publisher.name}"></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<h3>Using Advertiser-DB</h3>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${advertisers}" var="advertiser">
<tr>
<td th:utext="${advertiser.id}"></td>
<td th:utext="${advertiser.name}"></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>No ADS
Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Installieren Sie die Spring Tool Suite für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum Sping für den Anfänger
- Die Anleitung zum Spring Boot für den Anfänger
- Gemeinsame Eigenschaften von Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Thymeleaf
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und FreeMarker
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Groovy
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Mustache
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und JSP
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Verwenden Sie Logging im Spring Boot
- Anwendungsüberwachung mit Spring Boot Actuator
- Erstellen Sie eine mehrsprachige Webanwendung mit Spring Boot
- Verwenden Sie im Spring Boot mehrere ViewResolver
- Verwenden Sie Twitter Bootstrap im Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot Interceptor
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Spring JDBC und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring JDBC
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, JPA und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Spring Data JPA
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Hibernate und Spring Transaction
- Spring Boot, JPA und H2-Datenbank integrieren
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und MongoDB
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und JPA
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und RoutingDataSource
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Erstellen Sie eine Benutzerregistrierungsanwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Beispiel für OAuth2 Social Login im Spring Boot
- Führen Sie geplante Hintergrundaufgaben in Spring aus
- CRUD Restful Web Service Beispiel mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Spring Boot Restful Client mit RestTemplate
- CRUD-Beispiel mit Spring Boot, REST und AngularJS
- Sichere Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Basic Authentication
- Sicherer Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Auth0 JWT
- Beispiel Upload file mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Download File mit Spring Boot
- Das Beispiel: Spring Boot File Upload mit jQuery Ajax
- Das Beispiel File Upload mit Spring Boot und AngularJS
- Erstellen Sie eine Warenkorb-Webanwendung mit Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Email
- Erstellen Sie eine einfache Chat-Anwendung mit Spring Boot und Websocket
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Tomcat Server bereit
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Oracle WebLogic Server bereit
- Installieren Sie ein kostenloses Let's Encrypt SSL-Zertifikat für Spring Boot
- Konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot so, dass HTTP zu HTTPS umgeleitet wird
Show More