Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und RoutingDataSource
1. Das Zweck des Unterlagen
Manchmal sollen Sie eine Web-Applikation verbindend mit vielen unterchiedlichen Database erstellen. Und Sie können es im Spring Boot einfach machen.
Spring bietet Sie die Klasse AbstractRoutingDataSource, Sie sollen eine Klasse schreiben, die aus der Klasse ausgeweitert wird. Routing Datasource enthaltet ein Map der echten Datasource.
Spring bietet Sie die Klasse AbstractRoutingDataSource, Sie sollen eine Klasse schreiben, die aus der Klasse ausgeweitert wird. Routing Datasource enthaltet ein Map der echten Datasource.
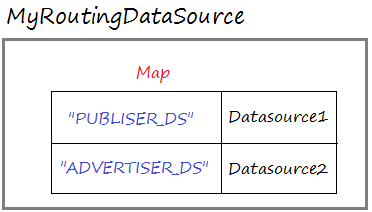
Note: Routing Datasource is also a Datasource but it is a special one.
Und DataSource Interceptor entscheidet, welche entspechende DataSource der Anforderung aus dem Benutzer benutzt werden.
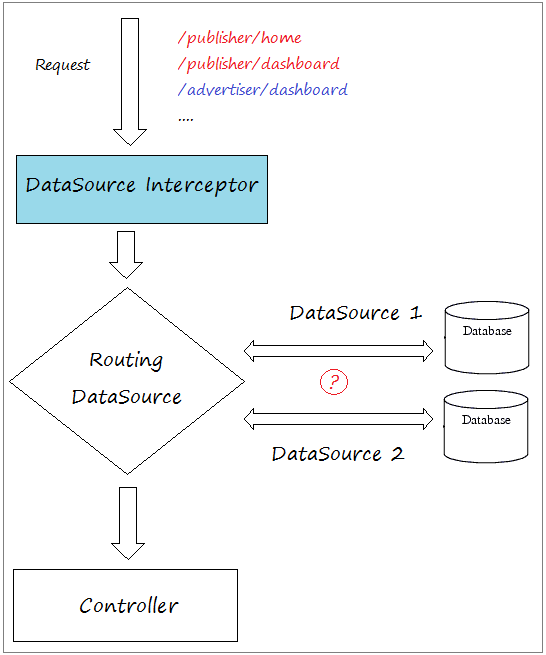
Im Dokument bezeichne ich eine Website benutzend 2 datasource. Jede datasource verbindet mit einer verschiedenen Database. Eine Database speichert die Information für das System Publisher und eine Database speichert die Information für das System Advertiser
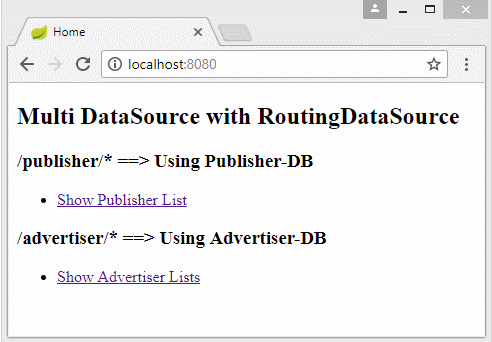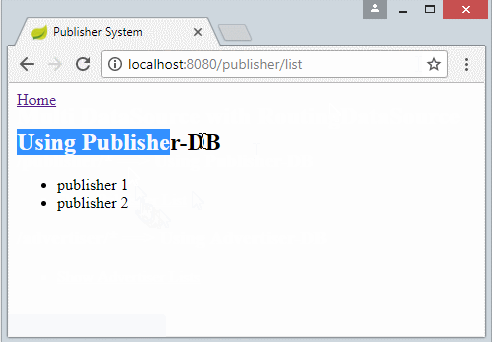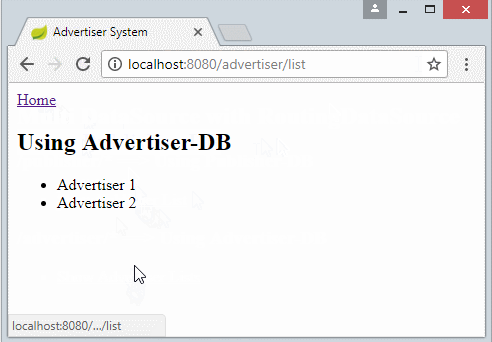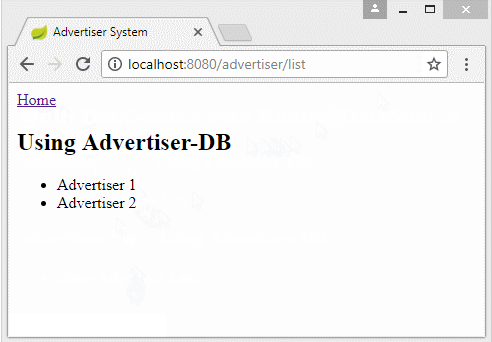
In einiger Situation können Sie eine MultispracheWebsite machen. Sie können viele Database erstellen. Jede Database speichert den Artikel einer bestimmten Sprache
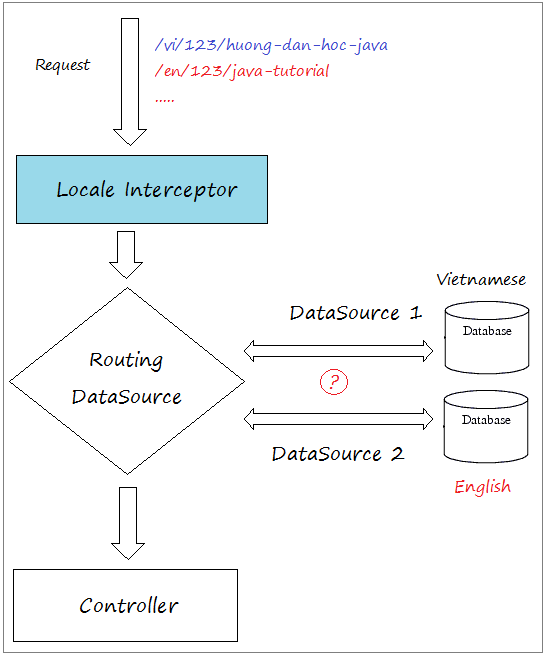
Wenn Ihre Applikation in einem anderen Fall viel DataSource brauchen und jede Funktion (jede Seite) kann mit vielen DataSource gleichzeitig arbeiten, brauchen Sie die folgenden Anleitungen lernen:
2. Die Database vorbereiten
Ich werde 2 Database erstellen. Eine Database ist für das System PUBLISHER und eine Database für das System ADVERTISER . 2 Database können die gleichen Typ sein. Sie können Oracle, MySQL oder SQL Server, ... benutzen
Database1:
Das DB System vom PUBLISHER hat eine Tabelle Publishers.
Database1 - (MySQL, SQL Server, PostGres)
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR PUBLISHER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table PUBLISHERS
(
ID Bigint,
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'publisher 1');
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'publisher 2');Database1 - (ORACLE)
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR PUBLISHER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table PUBLISHERS
(
ID NUMBER(19),
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'publisher 1');
insert into publishers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'publisher 2');
Commit;Database 2:
Das DB System vom ADVERTISER hat eine Tabelle Advertisers.
Database2 (MySQL, SQL Server, PostGres)
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR ADVERTISER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table ADVERTISERS
(
ID Bigint,
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'Advertiser 2');Database2 - (ORACLE)
-- ===========================================
-- DATABASE FOR ADVERTISER SYSTEM
-- ===========================================
create table ADVERTISERS
(
ID NUMBER(19),
NAME VARCHAR(255),
Primary key (ID)
);
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (1, 'Advertiser 1');
insert into advertisers (ID, NAME)
values (2, 'Advertiser 2');
Commit;3. Create Spring Boot Project
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootRoutingDS</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootRoutingDS</name>
<description>Spring Boot + Multi DataSource + Routing DataSource</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- For Thymeleaf VIEW. Remove it if using Jsp VIEW -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - Mssql-Jdbc driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - JTDS driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.jtds</groupId>
<artifactId>jtds</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- For JSP VIEW (Need REMOVE spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- For JSP VIEW (Need REMOVE spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE JDBC Driver -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Die Konfiguration von DataSource & RoutingDataSource
Die Information von Database wird in die File datasource-cfg.properties konfiguriert
datasource-cfg.properties (MySQL + MySQL)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=root
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=root
spring.datasource.password.2=12345datasource-cfg.properties (SQL Server + SQL Server) (JTDS Driver)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/publisher;instance=SQLEXPRESS
spring.datasource.username.1=sa
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/advertiser;instance=SQLEXPRESS
spring.datasource.username.2=sa
spring.datasource.password.2=12345datasource-cfg.properties (SQL Server + SQL Server) (Mssql-Jdbc Driver)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=sa
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=sa
spring.datasource.password.2=12345datasource-cfg.properties (ORACLE + ORACLE)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username.1=publisher
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username.2=advertiser
spring.datasource.password.2=12345datasource-cfg.properties (PostGres + PostGres)
# DataSource (PUBLISHER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url.1=jdbc:postgresql://tran-vmware-pc:5432/publisher
spring.datasource.username.1=postgres
spring.datasource.password.1=12345
# DataSource (ADVERTISER System).
spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url.2=jdbc:postgresql://tran-vmware-pc:5432/advertiser
spring.datasource.username.2=postgres
spring.datasource.password.2=12345
Nach dem Standard wird Spring Boot eine DataSource konfigurieren,deshalb sollen Sie es deaktivieren damit es Ihre DataSource konfigurieren kann. Die automatischen Konfigurationen schließt ein:
- DataSourceAutoConfiguration
- DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration
SpringBootRoutingDsApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.o7planning.sbroutingds.routing.MyRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
@SpringBootApplication
// Disable Auto Config DataSource & DataSourceTransactionManager
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = { //
DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, //
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class })
// Load to Environment
// (@see resources/datasource-cfg.properties).
@PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:datasource-cfg.properties") })
public class SpringBootRoutingDsApplication {
// Stores all the properties loaded by the @PropertySource
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRoutingDsApplication.class, args);
}
// Returns Routing DataSource (MyRoutingDataSource)
@Autowired
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DataSource getDataSource(DataSource dataSource1, DataSource dataSource2) {
System.out.println("## Create DataSource from dataSource1 & dataSource2");
MyRoutingDataSource dataSource = new MyRoutingDataSource();
dataSource.initDataSources(dataSource1, dataSource2);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "dataSource1")
public DataSource getDataSource1() throws SQLException {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
// See: datasouce-cfg.properties
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name.1"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url.1"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username.1"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password.1"));
System.out.println("## DataSource1: " + dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource getDataSource2() throws SQLException {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
// See: datasouce-cfg.properties
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name.2"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url.2"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username.2"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password.2"));
System.out.println("## DataSource2: " + dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Autowired
@Bean(name = "transactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager txManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
txManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return txManager;
}
}MyRoutingDataSource íst eine DataSource, die ein Map zwischen die Schlüssel und die echtlichen Datasource enthaltet.
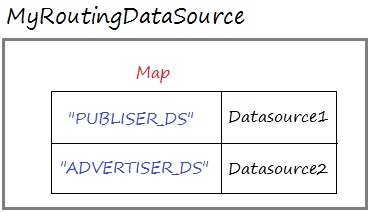
MyRoutingDataSource.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds.routing;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
// This is a DataSource.
public class MyRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())
.getRequest();
// See more: DataSourceInterceptor
String keyDS = (String) request.getAttribute("keyDS");
System.out.println("KeyDS=" + keyDS);
if (keyDS == null) {
keyDS = "PUBLISHER_DS";
}
return keyDS;
}
public void initDataSources(DataSource dataSource1, DataSource dataSource2) {
Map<Object, Object> dsMap = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
dsMap.put("PUBLISHER_DS", dataSource1);
dsMap.put("ADVERTISER_DS", dataSource2);
this.setTargetDataSources(dsMap);
}
}5. DataSourceInterceptor & die Konfiguration
DataSourceInterceptor wird URL vom Request analysieren und entscheidet, welche Datasource verwendet wird.
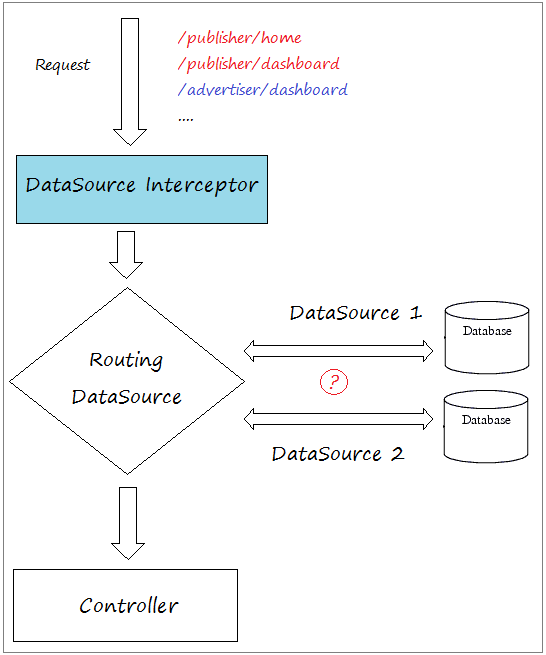
DataSourceIntercetor.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds.interceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
public class DataSourceIntercetor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
// Request:
// /publisher/list
// /advertiser/list
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
String contextPath = request.getServletContext().getContextPath();
// /SomeContextPath/publisher
String prefixPublisher = contextPath + "/publisher";
// /SomeContextPath/advertiser
String prefixAdvertiser = contextPath + "/advertiser";
// /SomeContextPath/publisher/dashboard
// /SomeContextPath/advertiser/dashboard
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println("URI:"+ uri);
if(uri.startsWith(prefixPublisher)) {
request.setAttribute("keyDS", "PUBLISHER_DS");
}
else if(uri.startsWith(prefixAdvertiser)) {
request.setAttribute("keyDS", "ADVERTISER_DS");
}
return true;
}
}Im WebMvcConfig sollen Sie DataSourceInterceptor registrieren.
WebMvcConfig.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds.config;
import org.o7planning.sbroutingds.interceptor.DataSourceIntercetor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new DataSourceIntercetor())//
.addPathPatterns("/publisher/*", "/advertiser/*");
}
}6. DAO, Controller
DataDAO ist eine Utility Klasse, die die Daten aus der Database abfragen
DataDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
@Transactional
public class DataDAO extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@Autowired
public DataDAO(DataSource dataSource) {
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
}
public List<String> queryPublishers() {
String sql = "Select name from Publishers";
List<String> list = this.getJdbcTemplate().queryForList(sql, String.class);
return list;
}
public List<String> queryAdvertisers() {
String sql = "Select name from Advertisers";
List<String> list = this.getJdbcTemplate().queryForList(sql, String.class);
return list;
}
}MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbroutingds.controller;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbroutingds.dao.DataDAO;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private DataDAO dataDAO;
@RequestMapping(value = { "/" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home(Model model) throws SQLException {
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/advertiser/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String advertiser(Model model) throws SQLException {
List<String> list = dataDAO.queryAdvertisers();
model.addAttribute("advertisers", list);
return "advertiser";
}
@RequestMapping(value = { "/publisher/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String publisher(Model model) throws SQLException {
List<String> list = dataDAO.queryPublishers();
model.addAttribute("publishers", list);
return "publisher";
}
}7. Thymeleaf Template
home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Multi DataSource with RoutingDataSource</h2>
<h3>/publisher/* ==> Using Publisher-DB</h3>
<ul>
<li><a th:href="@{/publisher/list}">Show Publisher List</a></li>
</ul>
<h3>/advertiser/* ==> Using Advertiser-DB</h3>
<ul>
<li> <a th:href="@{/advertiser/list}">Show Advertiser Lists</a> </li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>publisher.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Publisher System</title>
</head>
<body>
<a th:href="@{/}">Home</a>
<h2>Using Publisher-DB</h2>
<ul>
<li th:each="publisher : ${publishers}" th:utext="${publisher}"></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>advertiser.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Advertiser System</title>
</head>
<body>
<a th:href="@{/}">Home</a>
<h2>Using Advertiser-DB</h2>
<ul>
<li th:each="advertiser : ${advertisers}" th:utext="${advertiser}"></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Installieren Sie die Spring Tool Suite für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum Sping für den Anfänger
- Die Anleitung zum Spring Boot für den Anfänger
- Gemeinsame Eigenschaften von Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Thymeleaf
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und FreeMarker
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Groovy
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Mustache
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und JSP
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Verwenden Sie Logging im Spring Boot
- Anwendungsüberwachung mit Spring Boot Actuator
- Erstellen Sie eine mehrsprachige Webanwendung mit Spring Boot
- Verwenden Sie im Spring Boot mehrere ViewResolver
- Verwenden Sie Twitter Bootstrap im Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot Interceptor
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Spring JDBC und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring JDBC
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, JPA und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Spring Data JPA
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Hibernate und Spring Transaction
- Spring Boot, JPA und H2-Datenbank integrieren
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und MongoDB
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und JPA
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und RoutingDataSource
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Erstellen Sie eine Benutzerregistrierungsanwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Beispiel für OAuth2 Social Login im Spring Boot
- Führen Sie geplante Hintergrundaufgaben in Spring aus
- CRUD Restful Web Service Beispiel mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Spring Boot Restful Client mit RestTemplate
- CRUD-Beispiel mit Spring Boot, REST und AngularJS
- Sichere Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Basic Authentication
- Sicherer Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Auth0 JWT
- Beispiel Upload file mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Download File mit Spring Boot
- Das Beispiel: Spring Boot File Upload mit jQuery Ajax
- Das Beispiel File Upload mit Spring Boot und AngularJS
- Erstellen Sie eine Warenkorb-Webanwendung mit Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Email
- Erstellen Sie eine einfache Chat-Anwendung mit Spring Boot und Websocket
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Tomcat Server bereit
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Oracle WebLogic Server bereit
- Installieren Sie ein kostenloses Let's Encrypt SSL-Zertifikat für Spring Boot
- Konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot so, dass HTTP zu HTTPS umgeleitet wird
Show More