Erstellen Sie eine Benutzerregistrierungsanwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
1. Das Zweck des Beispiel
Der Unterlagen wird nach ... geschrieben:
Eclipse 3.7 (Oxygen)
Spring Boot 2.x
Spring Validation
Thymeleaf
Im Unterlagen leite ich Sie bei der Erstellung einer Registration-Applikation benutzend Spring Boot + Spring Validation + Thymeleaf. Die Themen werden im Unterlagen erwähnt:
- Eine Registration Form auf Spring erstellen.
- Spring Validator verwenden um die eingegebenen Information zu bestätigen.
- Den Operationsgrundsatz vom Spring Validator erklären.
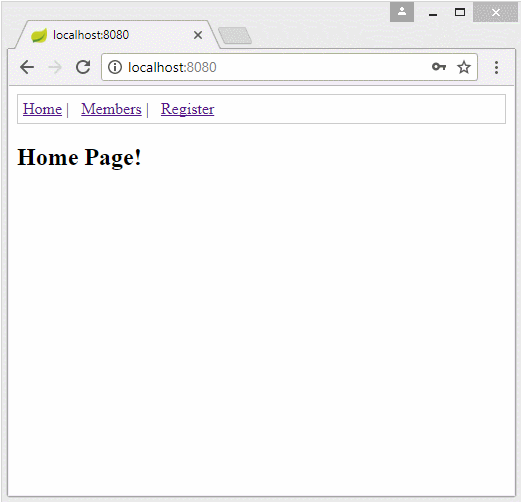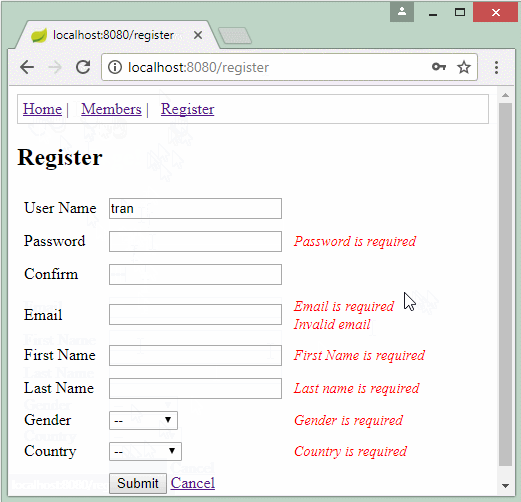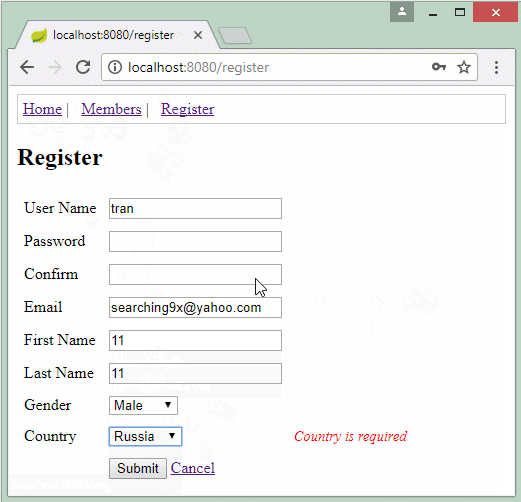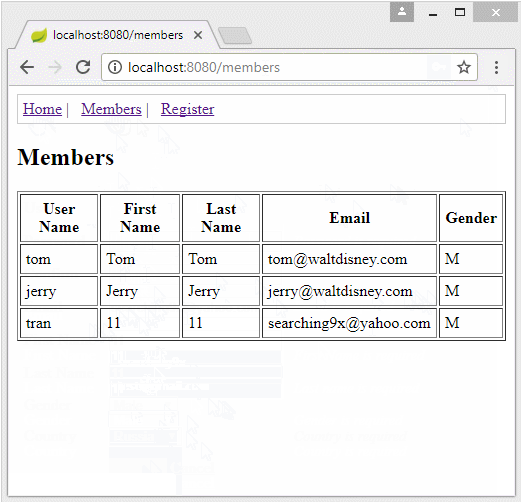
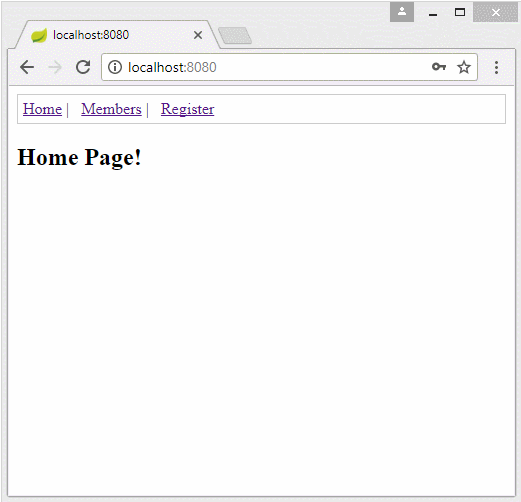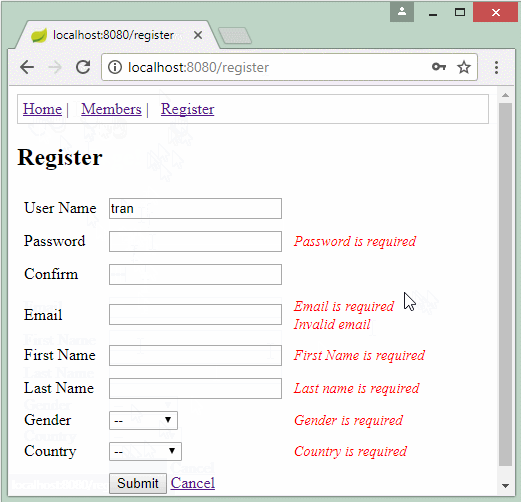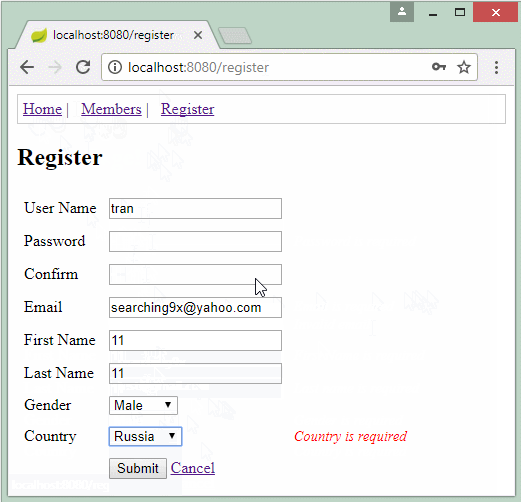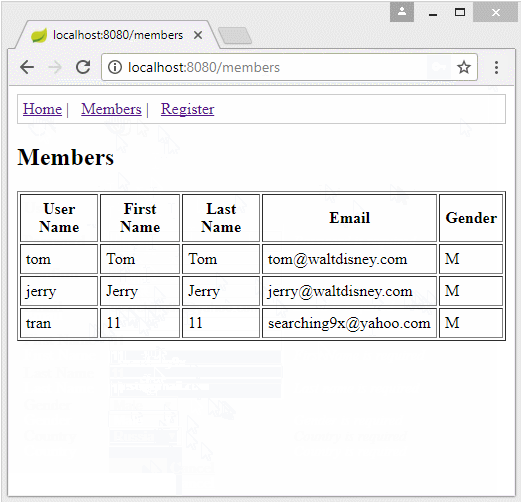
Die Applikation vorschauen
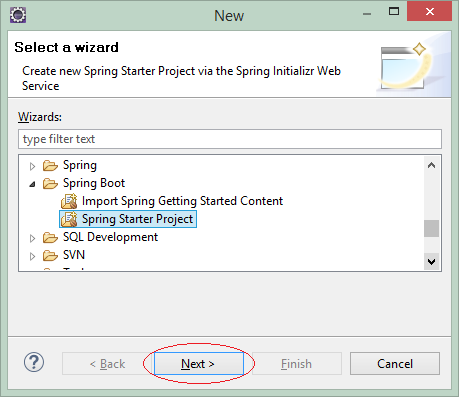
2. Spring Boot Projekt erstellen
Auf Eclipse erstellen Sie das Projekt Spring Boot.
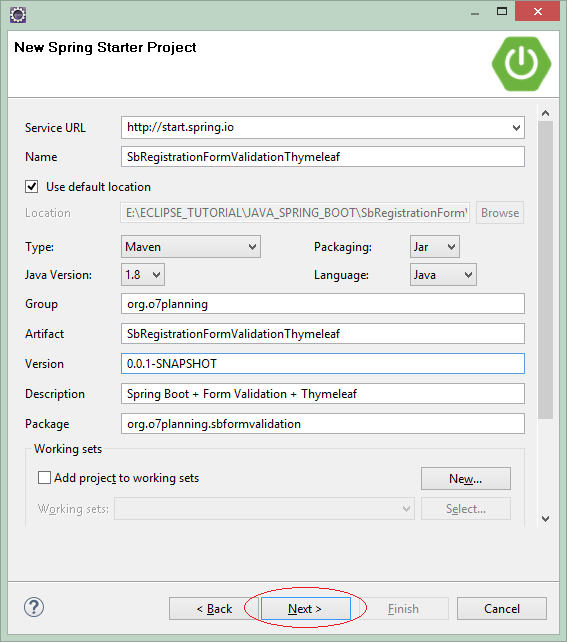
Geben Sie ein
- Name: SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleaf
- Group: org.o7planning
- Description: Spring Boot + Form Validation + Thymeleaf
- Package: org.o7planning.sbformvalidation
Die Technologie und die Bibliothek zur Verwendung auswählen
- Security
- Validation
- Web
- Thymeleaf
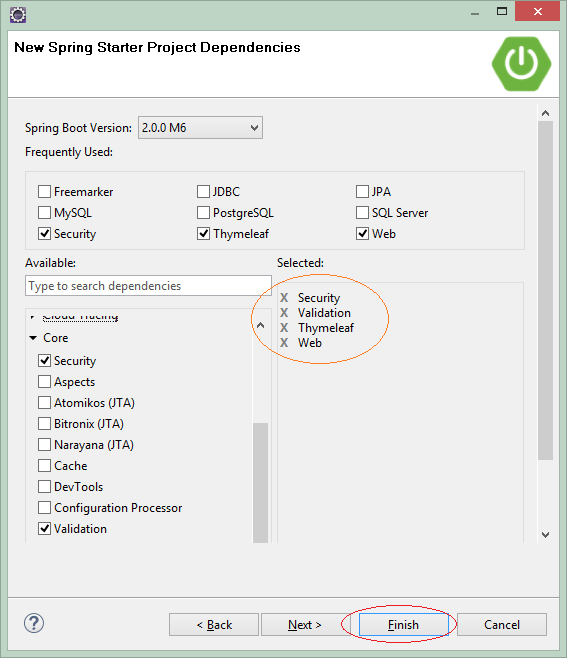
OK, Das Projekt wurde erstellt
SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleafApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleafApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleafApplication.class, args);
}
}3. pom.xml konfigurieren
In diesem Beispiel werden wir die Bibliothek Commons Validation verwenden um das Email des Benutzer zu prüfen, ob es ist richtig oder nicht. Deshalb sollen wir die Bibliothek in pom.xml deklarieren.
** Commons Validation **
<dependencies>
.....
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-validator/commons-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-validator</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-validator</artifactId>
<version>1.6</version>
</dependency>
.....
</dependencies>Die ganze Inhalt der File pom.xml:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SbRegistrationFormValidationThymeleaf</name>
<description>Spring Boot + Form Validation + Thymeleaf</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-validator/commons-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-validator</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-validator</artifactId>
<version>1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Security, MessageSource
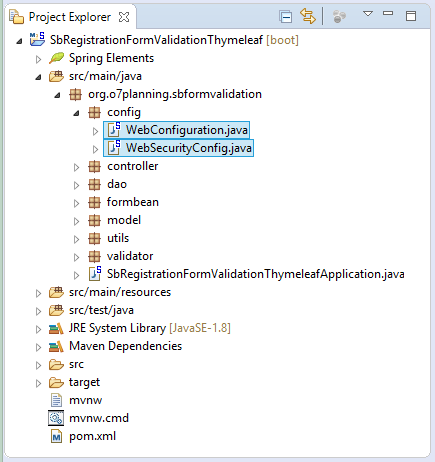
In diesem Beispiel fokusier ich auf die Sicherheit der Applikation nicht. Aber wir brauchen die Bibliothek Spring Security um das Passwort des Benutzer vor dem Speichern in der Database zu kodieren (encode). Und Sie ein Spring BEAN für die Kodierung des Passwort deklarieren
WebSecurityConfig.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
return bCryptPasswordEncoder;
}
// In this example we do not use Security.
// Override this method with empty code
// to disable the default Spring Boot security.
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// Empty code!
}
}Im Beispiel haben wir die File validation.properties. Die File enthaltet die Fehler-Kode (Error code), die verwendet wird um dem Benutzer bei der Eingabe der unrichtigen Information zu informieren
validation.properties
NotEmpty.appUserForm.userName=User name is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.firstName=First Name is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.lastName=Last name is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.email=Email is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.password=Password is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.confirmPassword=Confirm Password is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.gender=Gender is required
NotEmpty.appUserForm.countryCode=Country is required
Pattern.appUserForm.email=Invalid email
Duplicate.appUserForm.email=Email has been used by another account
Duplicate.appUserForm.userName=Username is not available
Match.appUserForm.confirmPassword=Password does not match the confirm passwordSie brauchen MessageResource Spring Bean deklarieren, damit Spring die Inhalt der File validation.properties in der Memory automatisch ladet
WebConfiguration.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.config;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
// Load file: validation.properties
messageSource.setBasename("classpath:validation");
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return messageSource;
}
}5. Model, DAO
Die Klasse AppUser vertritt ein Rekord der Tabelle APP_USER. Es ist ein Benutzer (user), der im System erfolgreich registriert hat
AppUser.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model;
public class AppUser {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private boolean enabled;
private String gender;
private String email;
private String encrytedPassword;
private String countryCode;
public AppUser() {
}
public AppUser(Long userId, String userName, String firstName, String lastName, //
boolean enabled, String gender, //
String email,String countryCode, String encrytedPassword) {
super();
this.userId = userId;
this.userName = userName;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.gender = gender;
this.email = email;
this.countryCode= countryCode;
this.encrytedPassword = encrytedPassword;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getEncrytedPassword() {
return encrytedPassword;
}
public void setEncrytedPassword(String encrytedPassword) {
this.encrytedPassword = encrytedPassword;
}
public String getCountryCode() {
return countryCode;
}
public void setCountryCode(String countryCode) {
this.countryCode = countryCode;
}
}Country.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model;
public class Country {
private String countryCode;
private String countryName;
public Country() {
}
public Country(String countryCode, String countryName) {
this.countryCode = countryCode;
this.countryName = countryName;
}
public String getCountryCode() {
return countryCode;
}
public void setCountryCode(String countryCode) {
this.countryCode = countryCode;
}
public String getCountryName() {
return countryName;
}
public void setCountryName(String countryName) {
this.countryName = countryName;
}
}Gender.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model;
public class Gender {
public static final String MALE = "M";
public static final String FEMALE = "F";
}Die Klasse DAO (Data Access Object) wird verwendet um mit der Ressourcen zu manipulieren, zum Beispiel query, insert, update, delete. Die Klasse werden oft durch @Repository annotiert damit Spring sie wie Spring BEAN verwaltet.
AppUserDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.formbean.AppUserForm;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.AppUser;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.Gender;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AppUserDAO {
// Config in WebSecurityConfig
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
private static final Map<Long, AppUser> USERS_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
initDATA();
}
private static void initDATA() {
String encrytedPassword = "";
AppUser tom = new AppUser(1L, "tom", "Tom", "Tom", //
true, Gender.MALE, "tom@waltdisney.com", encrytedPassword, "US");
AppUser jerry = new AppUser(2L, "jerry", "Jerry", "Jerry", //
true, Gender.MALE, "jerry@waltdisney.com", encrytedPassword, "US");
USERS_MAP.put(tom.getUserId(), tom);
USERS_MAP.put(jerry.getUserId(), jerry);
}
public Long getMaxUserId() {
long max = 0;
for (Long id : USERS_MAP.keySet()) {
if (id > max) {
max = id;
}
}
return max;
}
//
public AppUser findAppUserByUserName(String userName) {
Collection<AppUser> appUsers = USERS_MAP.values();
for (AppUser u : appUsers) {
if (u.getUserName().equals(userName)) {
return u;
}
}
return null;
}
public AppUser findAppUserByEmail(String email) {
Collection<AppUser> appUsers = USERS_MAP.values();
for (AppUser u : appUsers) {
if (u.getEmail().equals(email)) {
return u;
}
}
return null;
}
public List<AppUser> getAppUsers() {
List<AppUser> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.addAll(USERS_MAP.values());
return list;
}
public AppUser createAppUser(AppUserForm form) {
Long userId = this.getMaxUserId() + 1;
String encrytedPassword = this.passwordEncoder.encode(form.getPassword());
AppUser user = new AppUser(userId, form.getUserName(), //
form.getFirstName(), form.getLastName(), false, //
form.getGender(), form.getEmail(), form.getCountryCode(), //
encrytedPassword);
USERS_MAP.put(userId, user);
return user;
}
}CountryDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.Country;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class CountryDAO {
private static final Map<String, Country> COUNTRIES_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
initDATA();
}
private static void initDATA() {
Country vn = new Country("VN", "Vietnam");
Country en = new Country("EN", "England");
Country fr = new Country("FR", "France");
Country us = new Country("US", "US");
Country ru = new Country("RU", "Russia");
COUNTRIES_MAP.put(vn.getCountryCode(), vn);
COUNTRIES_MAP.put(en.getCountryCode(), en);
COUNTRIES_MAP.put(fr.getCountryCode(), fr);
COUNTRIES_MAP.put(us.getCountryCode(), us);
COUNTRIES_MAP.put(ru.getCountryCode(), ru);
}
public Country findCountryByCode(String countryCode) {
return COUNTRIES_MAP.get(countryCode);
}
public List<Country> getCountries() {
List<Country> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.addAll(COUNTRIES_MAP.values());
return list;
}
}6. Form Bean, Validator
Die Klasse AppUserForm vertritt die Daten, die der Benutzer in die Registration-Form eingeben soll
AppUserForm.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.formbean;
public class AppUserForm {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private boolean enabled;
private String gender;
private String email;
private String password;
private String confirmPassword;
private String countryCode;
public AppUserForm() {
}
public AppUserForm(Long userId, String userName, //
String firstName, String lastName, boolean enabled, //
String gender, String email, String countryCode, //
String password, String confirmPassword) {
this.userId = userId;
this.userName = userName;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.gender = gender;
this.email = email;
this.countryCode = countryCode;
this.password = password;
this.confirmPassword = confirmPassword;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getCountryCode() {
return countryCode;
}
public void setCountryCode(String countryCode) {
this.countryCode = countryCode;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getConfirmPassword() {
return confirmPassword;
}
public void setConfirmPassword(String confirmPassword) {
this.confirmPassword = confirmPassword;
}
}Die Klasse AppUserValidator wird verwendet um die vom Benutzer in die Form eingegebenen Information zu bestätigen (validate). Deshalb wird AppUserValidator die Wert der Felder (field) des Objekts AppUserForm validieren.
AppUserValidator.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.validator;
import org.apache.commons.validator.routines.EmailValidator;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.dao.AppUserDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.formbean.AppUserForm;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.AppUser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
@Component
public class AppUserValidator implements Validator {
// common-validator library.
private EmailValidator emailValidator = EmailValidator.getInstance();
@Autowired
private AppUserDAO appUserDAO;
// The classes are supported by this validator.
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return clazz == AppUserForm.class;
}
@Override
public void validate(Object target, Errors errors) {
AppUserForm appUserForm = (AppUserForm) target;
// Check the fields of AppUserForm.
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "userName", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.userName");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "firstName", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.firstName");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "lastName", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.lastName");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "email", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.email");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "password", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.password");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "confirmPassword", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.confirmPassword");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "gender", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.gender");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "countryCode", "NotEmpty.appUserForm.countryCode");
if (!this.emailValidator.isValid(appUserForm.getEmail())) {
// Invalid email.
errors.rejectValue("email", "Pattern.appUserForm.email");
} else if (appUserForm.getUserId() == null) {
AppUser dbUser = appUserDAO.findAppUserByEmail(appUserForm.getEmail());
if (dbUser != null) {
// Email has been used by another account.
errors.rejectValue("email", "Duplicate.appUserForm.email");
}
}
if (!errors.hasFieldErrors("userName")) {
AppUser dbUser = appUserDAO.findAppUserByUserName(appUserForm.getUserName());
if (dbUser != null) {
// Username is not available.
errors.rejectValue("userName", "Duplicate.appUserForm.userName");
}
}
if (!errors.hasErrors()) {
if (!appUserForm.getConfirmPassword().equals(appUserForm.getPassword())) {
errors.rejectValue("confirmPassword", "Match.appUserForm.confirmPassword");
}
}
}
}7. Controller
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.dao.AppUserDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.dao.CountryDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.formbean.AppUserForm;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.AppUser;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.model.Country;
import org.o7planning.sbformvalidation.validator.AppUserValidator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
// import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private AppUserDAO appUserDAO;
@Autowired
private CountryDAO countryDAO;
@Autowired
private AppUserValidator appUserValidator;
// Set a form validator
@InitBinder
protected void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder) {
// Form target
Object target = dataBinder.getTarget();
if (target == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("Target=" + target);
if (target.getClass() == AppUserForm.class) {
dataBinder.setValidator(appUserValidator);
}
// ...
}
@RequestMapping("/")
public String viewHome(Model model) {
return "welcomePage";
}
@RequestMapping("/members")
public String viewMembers(Model model) {
List<AppUser> list = appUserDAO.getAppUsers();
model.addAttribute("members", list);
return "membersPage";
}
@RequestMapping("/registerSuccessful")
public String viewRegisterSuccessful(Model model) {
return "registerSuccessfulPage";
}
// Show Register page.
@RequestMapping(value = "/register", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String viewRegister(Model model) {
AppUserForm form = new AppUserForm();
List<Country> countries = countryDAO.getCountries();
model.addAttribute("appUserForm", form);
model.addAttribute("countries", countries);
return "registerPage";
}
// This method is called to save the registration information.
// @Validated: To ensure that this Form
// has been Validated before this method is invoked.
@RequestMapping(value = "/register", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveRegister(Model model, //
@ModelAttribute("appUserForm") @Validated AppUserForm appUserForm, //
BindingResult result, //
final RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
// Validate result
if (result.hasErrors()) {
List<Country> countries = countryDAO.getCountries();
model.addAttribute("countries", countries);
return "registerPage";
}
AppUser newUser= null;
try {
newUser = appUserDAO.createAppUser(appUserForm);
}
// Other error!!
catch (Exception e) {
List<Country> countries = countryDAO.getCountries();
model.addAttribute("countries", countries);
model.addAttribute("errorMessage", "Error: " + e.getMessage());
return "registerPage";
}
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("flashUser", newUser);
return "redirect:/registerSuccessful";
}
}8. Thymeleaf Template
_menu.html
<div xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
style="border: 1px solid #ccc;padding:5px;margin-bottom:20px;">
<a th:href="@{/}">Home</a>
|
<a th:href="@{/members}">Members</a>
|
<a th:href="@{/register}">Register</a>
</div>membersPage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title th:utext="${title}"></title>
</head>
<style>
table th, table td {
padding: 5px;
}
.message {
color: blue;
}
</style>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>Members</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>User Name</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Gender</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each ="member : ${members}">
<td th:utext="${member.userName}">...</td>
<td th:utext="${member.firstName}">...</td>
<td th:utext="${member.lastName}">...</td>
<td th:utext="${member.email}">...</td>
<td th:utext="${member.gender}">...</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>registerPage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title th:utext="${title}"></title>
<style>
th, td {
padding: 5px;
}
td span {
font-size:90%;
font-style: italic;
color: red;
}
.error {
color: red;
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>Register</h2>
<div th:if="${errorMessage != null}"
th:utext="${errorMessage}" class="error">...</div>
<form th:action="@{/register}" th:object="${appUserForm}" method="POST">
<table>
<tr>
<td>User Name</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{userName}" /></td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('userName')}" th:errors="*{userName}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td><input type="password" th:field="*{password}" /> </td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('password')}" th:errors="*{password}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Confirm</td>
<td><input type="password" th:field="*{confirmPassword}" /> </td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('confirmPassword')}" th:errors="*{confirmPassword}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{email}" /> </td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('email')}" th:errors="*{email}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>First Name</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" /> </td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('firstName')}" th:errors="*{firstName}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Last Name</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" /> </td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('lastName')}" th:errors="*{lastName}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Gender</td>
<td>
<select th:field="*{gender}">
<option value=""> -- </option>
<option value="M">Male</option>
<option value="F">Female</option>
</select>
</td>
<td>
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('gender')}" th:errors="*{gender}">..</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Country</td>
<td>
<select th:field="*{countryCode}">
<option value=""> -- </option>
<option th:each="country : ${countries}"
th:value="${country.countryCode}"
th:utext="${country.countryName}"/>
</select>
<td><span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('countryCode')}" th:errors="*{countryCode}">..</span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
<a th:href="@{/}">Cancel</a>
</td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>registerSuccessfulPage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Successfully registered</title>
<style>
span {color: blue;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>You have successfully registered!</h2>
<div th:if="${flashUser != null}">
<ul>
<li>User Name: <span th:utext="${flashUser.userName}">..</span></li>
<li>Email: <span th:utext="${flashUser.email}">..</span></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>welcomePage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title th:utext="${title}"></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>Home Page!</h2>
</body>
</html>Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Installieren Sie die Spring Tool Suite für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum Sping für den Anfänger
- Die Anleitung zum Spring Boot für den Anfänger
- Gemeinsame Eigenschaften von Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Thymeleaf
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und FreeMarker
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Groovy
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Mustache
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und JSP
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Verwenden Sie Logging im Spring Boot
- Anwendungsüberwachung mit Spring Boot Actuator
- Erstellen Sie eine mehrsprachige Webanwendung mit Spring Boot
- Verwenden Sie im Spring Boot mehrere ViewResolver
- Verwenden Sie Twitter Bootstrap im Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot Interceptor
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Spring JDBC und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring JDBC
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, JPA und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Spring Data JPA
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Hibernate und Spring Transaction
- Spring Boot, JPA und H2-Datenbank integrieren
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und MongoDB
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und JPA
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und RoutingDataSource
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Erstellen Sie eine Benutzerregistrierungsanwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Beispiel für OAuth2 Social Login im Spring Boot
- Führen Sie geplante Hintergrundaufgaben in Spring aus
- CRUD Restful Web Service Beispiel mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Spring Boot Restful Client mit RestTemplate
- CRUD-Beispiel mit Spring Boot, REST und AngularJS
- Sichere Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Basic Authentication
- Sicherer Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Auth0 JWT
- Beispiel Upload file mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Download File mit Spring Boot
- Das Beispiel: Spring Boot File Upload mit jQuery Ajax
- Das Beispiel File Upload mit Spring Boot und AngularJS
- Erstellen Sie eine Warenkorb-Webanwendung mit Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Email
- Erstellen Sie eine einfache Chat-Anwendung mit Spring Boot und Websocket
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Tomcat Server bereit
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Oracle WebLogic Server bereit
- Installieren Sie ein kostenloses Let's Encrypt SSL-Zertifikat für Spring Boot
- Konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot so, dass HTTP zu HTTPS umgeleitet wird
Show More