Konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot so, dass HTTP zu HTTPS umgeleitet wird
1. Verwenden Sie sowohl HTTP als auch HTTPS
Standardmäßig verwendet die Anwendung Spring Boot entweder das Protokol HTTP oder HTTPS. Die Frage ist, wie diesen beiden Protokolle gleichzeitig verwendet werden können.
Öffnen Sie zum ersten die Datei application.properties und fügen Sie das Property server.http.port hinzu, um einen Port für HTTP und das Property server.port für HTTPS zu definieren.
Hinweis: server.http.port ist ein Property, die Sie definieren und die in SpringBoot nicht verfügbar ist.
application.properties (*)
# (User-defined Property)
# Port for HTTP and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.http.port:80}")
server.http.port=8080
# Port for HTTPS and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.port:443}")
server.port=8443
server.ssl.key-store=file:/home/tran/SSL/o7planning.org/o7planning_org.p12
server.ssl.key-store-password=P@ssword
server.ssl.key-alias=o7planningErstellen Sie zum Nächsten eine Klasse HttpHttpsConfigV1 und konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot, dass sowohl Protokoll http oder https gleichzeitig verwendet werden.
HttpHttpsConfigV1.java
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class HttpHttpsConfigV1 {
// (User-defined Property)
@Value("${server.http.port:80}")
private int httpPort;
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
Connector connector = new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setPort(this.httpPort);
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(connector);
return tomcat;
}
}2. Redirect HTTP to HTTPS (Way 2)
Der Hauptzweck der Konfiguration von Spring Boot für die Unterstützung von HTTP und HTTPS Protokollen besteht darin, die Anwendung zum Empfang eingehender Anforderungen über HTTP zu berechtigen und diese automatisch an HTTPS umzuleiten.
application.properties (*)
# (User-defined Property)
# Port for HTTP and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.http.port:80}")
server.http.port=8080
# Port for HTTPS and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.port:443}")
server.port=8443
server.ssl.key-store=file:/home/tran/SSL/o7planning.org/o7planning_org.p12
server.ssl.key-store-password=P@ssword
server.ssl.key-alias=o7planningJetzt erstellen wir eine zweite Version. Die Klasse HttpHttpsConfigV2 ersetzt die Klasse HttpHttpsConfigV1, sodass Ihre Anwendung Spring Boot sowohl HTTP als auch HTTPS verwenden kann. Alle Anforderungen über das Protokoll HTTP werden jedoch automatisch an HTTPS weitergeleitet:
HttpHttpsConfigV2.java
import org.apache.catalina.Context;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityCollection;
import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityConstraint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class HttpHttpsConfigV2 {
// IMPORTANT!!!
// If this parameter is empty then do not redirect HTTP to HTTPS
//
// Defined in application.properties file
@Value(value = "${server.ssl.key-store:}")
private String sslKeyStore;
// Defined in application.properties file
// (User-defined Property)
@Value(value = "${server.http.port:80}")
private int httpPort;
// Defined in application.properties file
@Value("${server.port:443}")
int httpsPort;
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
boolean needRedirectToHttps = sslKeyStore != null && !sslKeyStore.isEmpty();
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = null;
if (!needRedirectToHttps) {
tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
return tomcat;
}
tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
@Override
protected void postProcessContext(Context context) {
SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint();
securityConstraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL");
SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection();
collection.addPattern("/*");
securityConstraint.addCollection(collection);
context.addConstraint(securityConstraint);
}
};
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(redirectConnector());
return tomcat;
}
private Connector redirectConnector() {
Connector connector = new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setScheme("http");
connector.setPort(httpPort);
connector.setSecure(false);
connector.setRedirectPort(httpsPort);
return connector;
}
}3. Redirect HTTP to HTTPS (Way 3)
In einigen Fällen soll Spring Boot sowohl das Protokoll HTTP als auch HTTPS unterstützen, und nur automatisch mit den angegebenen Pfaden von HTTP zu HTTPS umleiten. Mit Interceptor ist das absolut machbar.
application.properties (*)
# (User-defined Property)
# Port for HTTP and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.http.port:80}")
server.http.port=8080
# Port for HTTPS and read by Spring Boot via @Value("${server.port:443}")
server.port=8443
server.ssl.key-store=file:/home/tran/SSL/o7planning.org/o7planning_org.p12
server.ssl.key-store-password=P@ssword
server.ssl.key-alias=o7planningMit der Klasse HttpHttpsConfigV3 kann die Anwendung Spring Boot sowohl HTTP als auch HTTPS Protokolle gleichzeitig verwenden.
HttpHttpsConfigV3.java
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
// @see HttpHttpsInterceptor
@Configuration
public class HttpHttpsConfigV3 {
@Value("${server.http.port:80}")
private int httpPort;
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
Connector connector = new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setPort(this.httpPort);
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(connector);
return tomcat;
}
}Interceptor ist eine mittlere Schicht zwischen dem Benutzer und dem Controller. Es kann die Anforderungen des Benutzer ablehnen,ändern oder umleiten. Basierend auf dieser Funktion von Interceptor können Sie damit HTTP Request erkennen und an HTTPS umleiten.
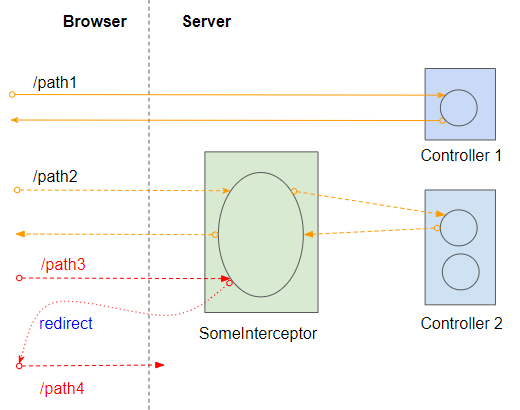
HttpHttpsInterceptor.java
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
@Component
public class HttpHttpsInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
// Defined in application.properties file
@Value(value = "${server.ssl.key-store:}")
private String sslKeyStore;
// Defined in application.properties file
@Value(value = "${server.http.port:80}")
private int httpPort;
// Defined in application.properties file
@Value("${server.port:443}")
int httpsPort;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// @return http or https
String schema = request.getScheme();
// System.out.println("Schema: " + schema);
if("https".equals(schema)) {
return true;
}
if(sslKeyStore == null || sslKeyStore.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
String serverName = request.getServerName();
// System.out.println("Server Name: " + serverName);
boolean isIP = this.isIP(serverName);
// System.out.println("isIP: " + isIP);
if (isIP) {
// System.out.println("No Redirect isIP = "+ isIP);
return true;
}
int requestedPort = request.getServerPort();
// System.out.println("requestedPort: " + requestedPort);
if (requestedPort == httpPort) { // This will still allow requests on :8080
// System.out.println("Redirect to https");
String queryString = request.getQueryString();
if (queryString == null || queryString.isEmpty()) {
if (httpsPort == 443) {
response.sendRedirect(
"https://" + request.getServerName() + request.getRequestURI());
} else {
response.sendRedirect(
"https://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + httpsPort + request.getRequestURI());
}
} else {
if (httpsPort == 443) {
response.sendRedirect(
"https://" + request.getServerName() + request.getRequestURI() + "?" + queryString);
} else {
response.sendRedirect(
"https://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + httpsPort + request.getRequestURI() + "?" + queryString);
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean isIP(String remoteHost) {
String s = remoteHost.replaceAll("\\.", "");
// System.out.println("isIP? " + s);
try {
Long.parseLong(s);
} catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}Zum Letzten sollen Sie die Klasse HttpHttpsInterceptor mit Spring Boot registrieren und angeben, welche Pfade durch diesen Interceptor verlaufen müssen. Das bedeutet, dass sie zu HTTPS umgeleitet werden und die anderen Pfade sowohl HTTP und HTTPS Protokolle verwenden.
WebMvcConfig.java
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@Transactional
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private HttpHttpsInterceptor httpHttpsInterceptor;
//
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(httpHttpsInterceptor);
registry.addInterceptor(httpHttpsInterceptor)//
.addPathPatterns("/path01", "path02/**");
}
// Other configs ...
}Anleitungen Spring Boot
- Installieren Sie die Spring Tool Suite für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum Sping für den Anfänger
- Die Anleitung zum Spring Boot für den Anfänger
- Gemeinsame Eigenschaften von Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Thymeleaf
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und FreeMarker
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Groovy
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Mustache
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und JSP
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Verwenden Sie Logging im Spring Boot
- Anwendungsüberwachung mit Spring Boot Actuator
- Erstellen Sie eine mehrsprachige Webanwendung mit Spring Boot
- Verwenden Sie im Spring Boot mehrere ViewResolver
- Verwenden Sie Twitter Bootstrap im Spring Boot
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot Interceptor
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Spring JDBC und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring JDBC
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, JPA und Spring Transaction
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und Spring Data JPA
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot, Hibernate und Spring Transaction
- Spring Boot, JPA und H2-Datenbank integrieren
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Boot und MongoDB
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und JPA
- Verwenden Sie mehrere DataSource mit Spring Boot und RoutingDataSource
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Erstellen Sie eine Login-Anwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Erstellen Sie eine Benutzerregistrierungsanwendung mit Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Beispiel für OAuth2 Social Login im Spring Boot
- Führen Sie geplante Hintergrundaufgaben in Spring aus
- CRUD Restful Web Service Beispiel mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Spring Boot Restful Client mit RestTemplate
- CRUD-Beispiel mit Spring Boot, REST und AngularJS
- Sichere Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Basic Authentication
- Sicherer Spring Boot RESTful Service mit Auth0 JWT
- Beispiel Upload file mit Spring Boot
- Beispiel Download File mit Spring Boot
- Das Beispiel: Spring Boot File Upload mit jQuery Ajax
- Das Beispiel File Upload mit Spring Boot und AngularJS
- Erstellen Sie eine Warenkorb-Webanwendung mit Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Die Anleitung zu Spring Email
- Erstellen Sie eine einfache Chat-Anwendung mit Spring Boot und Websocket
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Tomcat Server bereit
- Stellen Sie die Spring Boot-Anwendung auf Oracle WebLogic Server bereit
- Installieren Sie ein kostenloses Let's Encrypt SSL-Zertifikat für Spring Boot
- Konfigurieren Sie Spring Boot so, dass HTTP zu HTTPS umgeleitet wird
Show More