Die Anleitung zu CSS Backgrounds
1. Tổng quan về CSS Background
CSS bietet einige Property an, damit Sie die HIntergrund-Effekte für ein Element definieren. Sie sind:
- background-color
- background-image
- background-repeat
- background-attachment
- background-position
2. CSS background-color
CSS background-color wird benutzt um die Hintergrund-Farbe für ein Element festzulegen.
/* Keyword values */
background-color: red;
background-color: indigo;
/* Hexadecimal value */
background-color: #bbff00; /* Fully opaque */
background-color: #bf0; /* Fully opaque shorthand */
background-color: #11ffee00; /* Fully transparent */
background-color: #1fe0; /* Fully transparent shorthand */
background-color: #11ffeeff; /* Fully opaque */
background-color: #1fef; /* Fully opaque shorthand */
/* RGB value */
background-color: rgb(255, 255, 128); /* Fully opaque */
background-color: rgba(117, 190, 218, 0.5); /* 50% transparent */
/* HSL value */
background-color: hsl(50, 33%, 25%); /* Fully opaque */
background-color: hsla(50, 33%, 25%, 0.75); /* 75% transparent */
/* Special keyword values */
background-color: currentcolor;
background-color: transparent;
/* Global values */
background-color: inherit;
background-color: initial;
background-color: unset;Die Verwendung der Funktion RGBA hilft Ihnen bei der Erstellung einer Farbe mit der Opazität. Sie können diese Farbe als die Hintergrund-Farbe (background color) für ein Element verwenden- Diese Opazität wirkt sich mit der Hintergrundsfarbe vom Element. Sie wirkt mit der Inhalt und die Sub-Elementen nicht.
<div style="background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.1);">
{background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.1);}
</div>
<div style="background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.3);">
{background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.3);}
</div>
<div style="background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.6);">
{background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.6);}
</div>
<div style="background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80);">
{background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80);}
</div>ZB: Erstellen Sie ein fast transparentes Box, das die Bezeichnungstext vom Bild enthält.
background-color-grba-example2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS background-color</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<style>
.img-container {
display: inline-block;
position: relative;
}
.img-desc {
position: absolute;
left: 5px;
right: 5px;
bottom: 15px;
padding: 5px;
text-align: center;
background-color: rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.3);
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS background-color with GRBA function</h3>
<div class = "img-container">
<img src="../images/image.png" width="320" height="178"/>
<div class="img-desc">
This is an Image
</div>
</div>
<p style="font-style: italic;">
{ background-color: GRBA(76, 175, 80, 0.3); }
</p>
</body>
</html>mehr sehen:
- Hướng dẫn sử dụng CSS Colors
3. CSS background-image
CSS background-image wird verwendet um ein oder viele Hintergrungsfoto für ein Element festzulegen.
div {
padding: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
height: 115px;
}
.bg-a {
background-image: url('../images/bg1.png');
}
.bg-b {
background-image: url('../images/bg2.png');
}
.bg-ab {
background-image: url('../images/bg1.png'), url('../images/bg2.png');
}Jedes Hintergrundsfoto wird in einer transparenten Schicht (transparent layer) gezeichnet. Die Schichte werden überlappt.
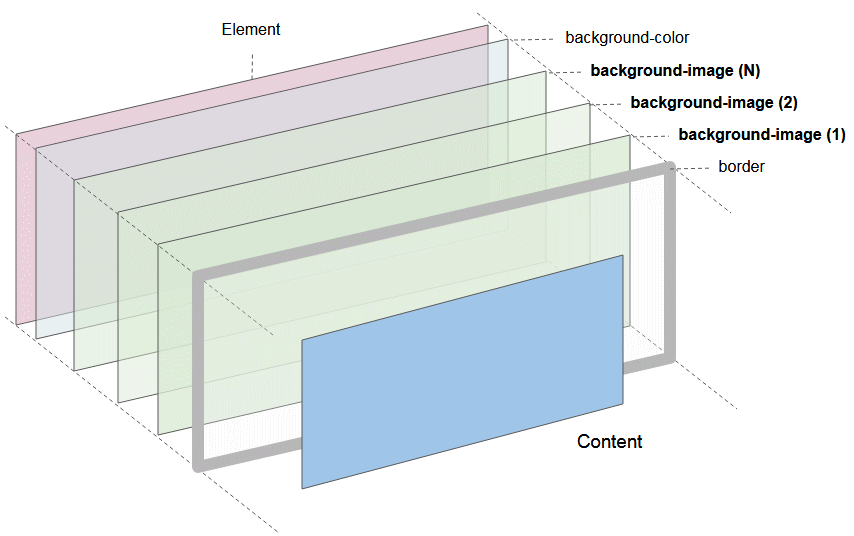
Das Illustrationsfoto eines Element mit der Teinahme von der Komponenten: background-color, background-images, borders.
- Die Element-Grenze vom Element wird in die Schicht gezeichnet, die dem Benutzer am nächsten liegt.
- Zunächst sind das die Schichte zur Zeichnung des Hintergrundsfoto (background image), und die Schicht zur Zeichnung der HIntergrungsfarbe (background color).
Syntax
background-image: none;
background-image: «image»;
background-image: «image», «image», «image»;none
Das ist ein Schlüsselwort , das die Abwesenheit vom Foto symbolisiert.
«image»
Inzwischen kann «image» ein der folgenden Funkionen sein:
- url( url-string )
- image( image-tags? [ image-src? , color? ] )
- image-set( image-set-option# )
- element( id-selectors )
- paint( ident , declaration-value )
- cross-fade( cf-mixing-image, cf-final-image)
- linear-gradient( [ angle | to side-or-corner ]? , color-stop-list )
- repeating-linear-gradient( [ angle | to side-or-corner ]? , color-stop-list )
- radial-gradient( [ ending-shape> || size ]? [ at position ]? , color-stop-list )
- repeating-radial-gradient( [ ending-shape || size ]? [ at position ]? , color-stop-list )
- conic-gradient( [ from angle ]? [ at position ]?, angular-color-stop-list )
Zum Beispiel:
background-image: none;
background-image: url( '../images/bg.png' );
background-image: image(ltr 'arrow.png#xywh=0,0,16,16', red);
background-image: image-set( "cat.png" 1x, "cat-2x.png" 2x, "cat-print.png" 600dpi);
background-image: element( #myElementId );
(!) paint( ident , declaration-value ) ;
background-image: cross-fade( url(red.png) 33.33%, url(yellow.png) 33.33%, url(blue.png) 33.33%);
background-image: linear-gradient(red, yellow, blue);
background-image: repeating-linear-gradient(45deg, #3f87a6, #ebf8e1 15%, #f69d3c 20%);
background-image: repeating-radial-gradient(#e66465, #9198e5 20%);
background-image: conic-gradient(at 50% 50%, yellow 0deg, orange 360deg);4. CSS background-repeat
CSS background-repeat wird benutzt um einzustellen, wie eine Hintergrundsfarbe wiederholt wird. Sie kann horizontal, vertikal oder beide wiederholt werden oder nicht wiederholt.
/* Keyword values */
background-repeat: repeat-x;
background-repeat: repeat-y;
background-repeat: repeat;
background-repeat: space;
background-repeat: round;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/* Two-value syntax: horizontal | vertical */
background-repeat: repeat space;
background-repeat: repeat repeat;
background-repeat: round space;
background-repeat: no-repeat round;
/* Global values */
background-repeat: inherit;
background-repeat: initial;
background-repeat: unset;Die Syntax eines Wert ist die Abkürzungsform von ganzen Syntax von beider Werten:
Single value | Two-value equivalent |
repeat-x | repeat no-repeat |
repeat-y | no-repeat repeat |
repeat | repeat repeat |
space | space space |
round | round round |
no-repeat | no-repeat no-repeat |
repeat
Das Foto (image) wird so oft wiederholt dass es den gesamten Bereich des Element abdeckt. Das endgültige Foto kann abgeschnitten werden um sicherzustellen, dass es nicht über das Element gezogen wird.
space
Das Image wird so oft wie möglich ohne Beschneiden wiederholt (clip). Die ersten und letzten Bilder werden auf beiden Seiten des Elements angehelft und der Leerraum wird gleichmäßig zwischen den Bildern verteilt. CSS background-position wird ignoriert außer wenn nur ein Bild ohne Beschneiden angezeigt wird. Der einzige Fall, in dem das Beschneiden passiert ist wen es keinen genügenden Platz zum Bild-Anzeigen.
round
Die Bilder wird wie {background-repeat: space} wiedergeholt aber die Bilder können eingezoomt werden um sicherzustellen, dass es keinen leeren Raum zwischen 2 Bilder gibt.
no-repeat
Das Bild wird wiederholt (und dann wird das Hintergrungsbild Zeichnungsbereich notwendig ganz abgedeckt sein).
background-repeat-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS background-repeat</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<script>
function setBgRepeat(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundRepeat = value;
}
</script>
<style>
#my-div {
border: 1px solid gray;
height:110px;
width: 310px;
margin-top: 10px;
background-image: url('../images/flower.png');
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS background-repeat</h3>
Background Image:
<img src="../images/flower.png" /> <hr/>
<p style="color:blue;">Set CSS background-repeat:</p>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-x')" /> repeat-x <br/>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-y')" /> repeat-y <br/>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat')" checked/> repeat <br/>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('space')" /> space <br/>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('round')" /> round <br/>
<input name ="abc" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('no-repeat')" /> no-repeat <br/>
<div id = "my-div"> </div>
</body>
</html>5. CSS background-origin
CSS background-orgin wird benutzt um die originelle Position des Hintergrundsfarbe einzustellen. Es kann einen der folgenden Wert erhalten:
- border-box
- padding-box (Default)
- content-box
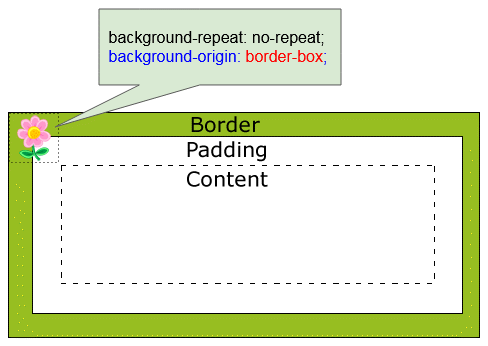
CSS {background-origin: border-box}
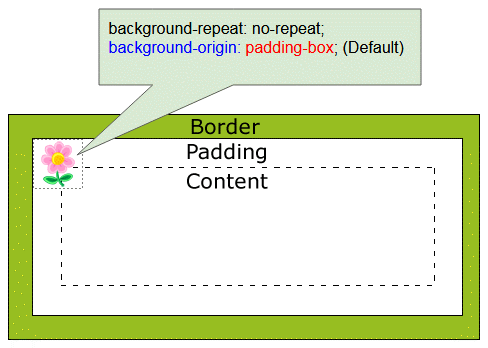
CSS {background-origin: padding-box}
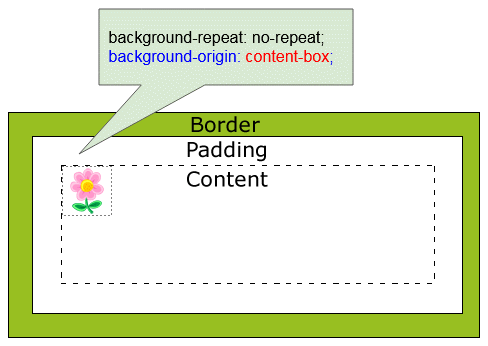
CSS {background-origin: content-box}
background-origin-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS background-origin</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<script>
function setBgOrigin(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundOrigin = value;
}
function setBgRepeat(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundRepeat = value;
}
</script>
<style>
.option {
padding: 5px;
width: 160px;
display:inline-block;
border: 1px solid gray;
}
#my-div {
border: 20px dashed gray;
height:110px;
width: 310px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 15px;
background-image: url('../images/flower.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS background-origin</h3>
Background Image:
<img src="../images/flower.png" /> <hr/>
<div class="option">
<p style="color:blue;">background-origin:</p>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('border-box')" /> border-box <br/>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('padding-box')" checked/> padding-box <br/>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('content-box')" /> content-box
</div>
<div class="option">
<p style="color:blue;">background-repeat:</p>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-x')" /> repeat-x <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-y')" /> repeat-y <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat')" /> repeat <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('space')" /> space <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('round')" /> round <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('no-repeat')" checked/> no-repeat
</div>
<div id = "my-div"> </div>
</body>
</html>6. CSS background-position
CSS background-position wird verwendet um die Beginntspunkt (starting position) jedes Hintergrundsbild zu sehen (Die relative Position im Vergleich von der originellen Position).
/* Keyword values */
background-position: top;
background-position: bottom;
background-position: left;
background-position: right;
background-position: center;
/* <percentage> values */
background-position: 25% 75%;
/* <length> values */
background-position: 0 0;
background-position: 1cm 2cm;
background-position: 10ch 8em;
/* Multiple images */
background-position: 0 0, center;
/* Edge offsets values */
background-position: bottom 10px right 20px;
background-position: right 3em bottom 10px;
background-position: bottom 10px right;
background-position: top right 10px;
/* Global values */
background-position: inherit;
background-position: initial;
background-position: unset;Zum Beispiel:
background-position-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS background-position</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<script src="background-position-example.js"> </script>
<style>
.option {
padding: 5px;
display:inline-block;
border: 1px solid gray;
}
#my-div {
border: 20px dashed gray;
height:110px;
width: 310px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 15px;
background-image: url('../images/flower.png');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS background-position</h3>
Background Image:
<img src="../images/flower.png" /> <hr/>
<div class="option">
<p style="color:red;">background-position:</p>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('1px 2px 5px 10px')" /> top <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('bottom')" /> bottom <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('left')" /> left <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('right')" /> right <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('center')" /> center <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('left top')" checked/> left top <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('left bottom')" /> left bottom <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('bottom 10px right')" />
bottom 10px right <br/>
<input name ="x" type="radio" onClick="setBgPosition('bottom 10px right 20px')" />
bottom 10px right 20px <br/>
... <br/>
</div>
<div class="option">
<p style="color:blue;">background-origin:</p>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('border-box')" /> border-box <br/>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('padding-box')" checked/> padding-box <br/>
<input name ="a" type="radio" onClick="setBgOrigin('content-box')" /> content-box
</div>
<div class="option">
<p style="color:blue;">background-repeat:</p>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-x')" /> repeat-x <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat-y')" /> repeat-y <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('repeat')" /> repeat <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('space')" /> space <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('round')" /> round <br/>
<input name ="b" type="radio" onClick="setBgRepeat('no-repeat')" checked/> no-repeat
</div>
<div id = "my-div"> </div>
</body>
</html>background-position-example.js
function setBgPosition(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundPosition = value;
}
function setBgOrigin(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundOrigin = value;
}
function setBgRepeat(value) {
var myElement = document.getElementById("my-div");
myElement.style.backgroundRepeat = value;
}CSS background-position akzeptiert die 1-Wert, 2-Wert, 3-Wert oder 4-Wert Syntax.
1-value syntax
CSS background-position in die 1-value syntax akzeptiert die folgenden Werten
- center
- left, top, right, bottom
- 10px, 5cm, 20%,...
/* Keyword values */
background-position: top;
background-position: bottom;
background-position: left;
background-position: right;
background-position: center;
/* <percentage> values */
background-position: 25% 75%;
/* <length> values */
background-position: 0;
background-position: 1cm;
background-position: 10ch;2-value syntax
CSS background-position in die 2-Wert Syntax (2-value syntax) akzeptiert die folgenden Werten:
Value | Same As |
left top | top left |
left bottom | bottom left |
right top | top right |
right bottom | bottom right |
10px 20cm | |
10% 20px | |
... |
Achtung: In die 2-Wert Syntax (2-value syntax) wenn Sie einen ungültigen Wert anbieten, wird es durch den Browser ignoriert. Z.B CSS {background-position: left left} ist ein ungültiger Wert.
3-value syntax
Die 3 Wert Syntax (3-value syntax) ist die Ausweiterung des 2 Wert Syntax. Sie können ihn durch die folgenden Illustration kennenlernen:
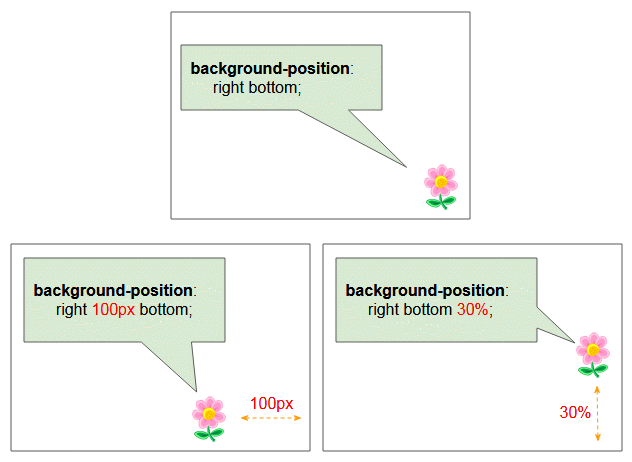
/* Edge offsets values */
background-position: bottom 10px right;
background-position: top right 10px;4-value syntax
Die 4-Wert Syntax ist die Ausweiterung der 2-Wert-Syntax. Sie können es durch die folgende Illustration verstehen:
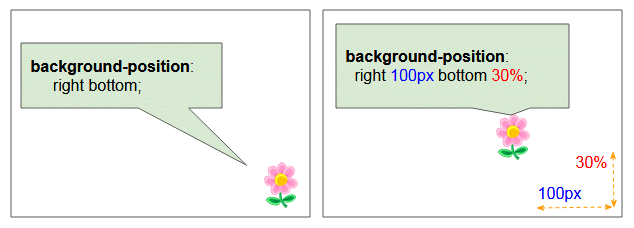
/* Edge offsets values */
background-position: bottom 10px right 20px;
background-position: right 3em bottom 10px;Anleitungen CSS
- Einheiten in CSS
- Die Anleitung zu Grundlegende CSS Selectors
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Attribute Selector
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Combinator Selectors
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Backgrounds
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Opacity
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Padding
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Margins
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Borders
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Outline
- Die Anleitung zu CSS box-sizing
- Die Anleitung zu CSS max-width und min-width
- Die Schlüsselwörter min-content, max-content, fit-content, stretch in CSS
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Links
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Fonts
- Grundlegendes zu Generic Font Family Names in CSS
- Die Anleitung zu CSS @font-face
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Align
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Cursors
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Overflow
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Lists
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Tables
- Die Anleitung zu CSS visibility
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Display
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Grid Layout
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Float und Clear
- Die Anleitung zu CSS Position
- Die Anleitung zu CSS line-height
- Die Anleitung zu CSS text-align
- Die Anleitung zu CSS text-decoration
Show More