Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Transformation
1. Was ist Transformation?
Transformation ist ein Geometriebegriff, der die Form eines Objekt zur anderen Form ändert. Es gibt einige üblichen Transformation wie
- Translation
- Scale
- Rotation
- Shearing
- ...
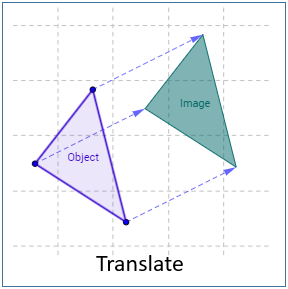
Translation
Reflection
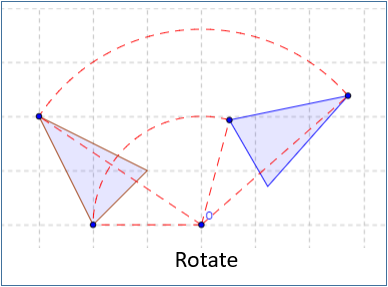
Rotation
Shearing/Skewing
Shear by x axis
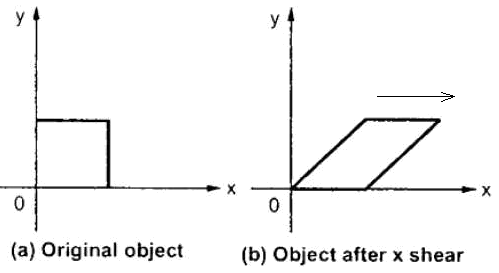
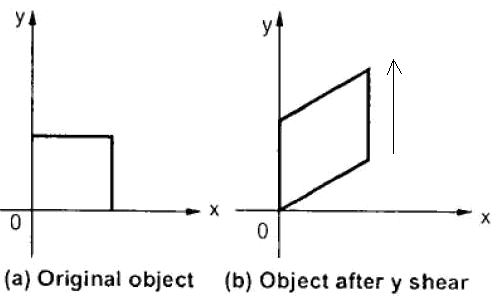
Shear by y axis
2. Translation Transformation
Translation transformation bewegt ein Objekt nach einer anderen Postion nach einer bestimmten Richtung. Z.B eine Punkt nach einer anderen Position bewegen.
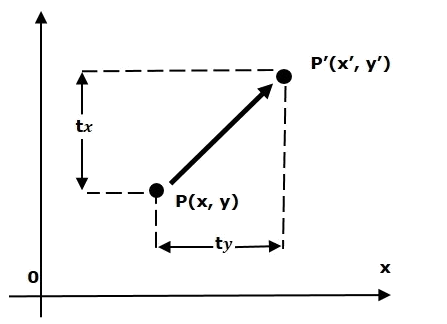
Alle Punkt auf dem GeometrieObjekt bewegen nach einer Richtung und mit einem gleichen Abstand
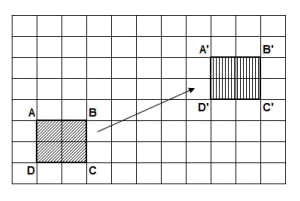
Zum Beispiel:
Zum Beispiel: Es gibt 2 Rechsteck in die gleichen Stelle und Größe. Wir machen die Translation transformation um den 2.Rechsteck zu bewegen. Und schauen Sie bitte das Ergebnisse
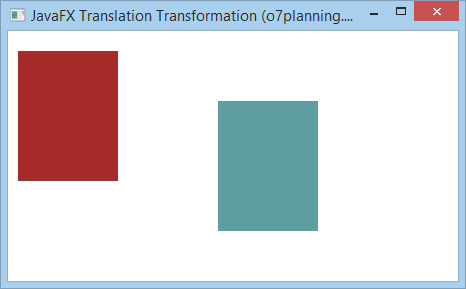
TranslationExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Translate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TranslationExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 10;
final int y = 20;
final int width = 100;
final int height = 130;
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
// Rectangle2 (Same position and size to rectangle1)
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BROWN);
rectangle1.setStrokeWidth(20);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.CADETBLUE);
rectangle2.setStrokeWidth(20);
// Creating the translation transformation
Translate translate = new Translate();
// Set arguments for translation
translate.setX(200);
translate.setY(50);
translate.setZ(100);
// Adding transformation to rectangle2
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(translate);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 250);
stage.setTitle("JavaFX Translation Transformation (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}3. Rotation Transformation
Rotation Transformation rotiert ein Objekt um eine Punkt. Die feste Punkt ist pivot genannt
Zum Beispiel
Zum Beispiel: 2 Rechsteck haben gleichen Größe und sind in gleichen Position. Wir benutzen mal die Rotation Transformation um den 2.Rechsteck einen 20-Grad-Winkeln um die pivot zu rotieren. Schauen Sie mal das Ergebnis
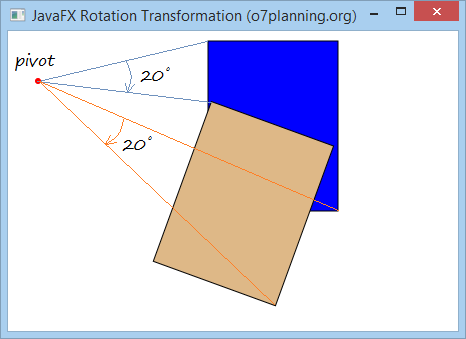
RotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class RotationExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 200;
final int y = 10;
final int width = 130;
final int height = 170;
int pivotX = 30;
int pivotY = 50;
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rectangle1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// Rectangle2
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
Circle pivot = new Circle(pivotX, pivotY, 3);
pivot.setFill(Color.RED);
// Creating the rotation transformation
Rotate rotate = new Rotate();
// Setting the angle for the rotation (20 degrees)
rotate.setAngle(20);
// Setting pivot points for the rotation
rotate.setPivotX(pivotX);
rotate.setPivotY(pivotY);
// Adding the transformation to rectangle2
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(rotate);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2, pivot);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 300);
stage.setTitle("JavaFX Rotation Transformation (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}4. Scaling Transformation
Scaling Transformation wird benutzt um die Größe eines Geometrieobjekt zu ändern. Sie können sie benutzen um die Dimension des Objekt zu skalieren.
Eine Punkt wird als ein Ursprung des Koordinate System. Scaling kann durch die Multiplikation der Koordinate des Objekt mit der Scaling-Factor gemacht wird um das gewünschte Ergebnis zu schaffen. Schauen Sie das Beispiel wie folgend
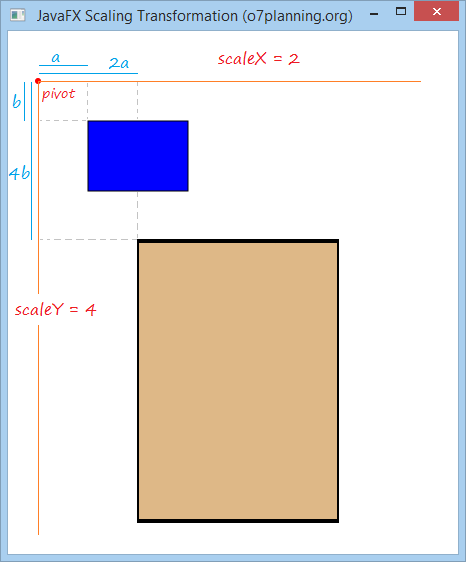
Zum Beispiel:
2 Rechtecke sind in der gleichen Größe und Position. Wählen Sie eine Punkt als der Ursprung des neuen Koordinate System. Und benutzen Sie Scaling Transformation um die Koordinate des Objekt durch die X-Achse 2 Mals und durch die Y-Achse 4 Mals zu skalieren
ScalingExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Scale;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ScalingExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 80;
final int y = 90;
final int width = 100;
final int height = 70;
int pivotX = 30;
int pivotY = 50;
double scaleX = 2;
double scaleY = 4;
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rectangle1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// Rectangle2
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
Circle pivot = new Circle(pivotX, pivotY, 3);
pivot.setFill(Color.RED);
// Creating the Scale transformation
Scale scale = new Scale();
// Setting the scaliing factor.
scale.setX(scaleX);
scale.setY(scaleY);
// Setting Orgin of new coordinate system
scale.setPivotX(pivotX);
scale.setPivotY(pivotY);
// Adding the transformation to rectangle2
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(scale);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2, pivot);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 500);
stage.setTitle("JavaFX Scaling Transformation (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}5. Shearing Transformation
Shearing - verformt ein Objekt durch die Verschiebung es nach einer bestimmten Richtung
Vielleicht kennen Sie "shear a sheep", Das ist eine Aktion zum Haarschneiden. Shearing Transformation plant, eine Teile aus dem Geometrie-Objekt zu schneiden. Sie verformt die ursprungliche Image
Shearing benutzt eine Punkt als pivot um das Objekt zu verformen
Wenn pivot in dem Ursprung des Koordinate System (origin of the coordinate system) liegt, shearing factor vom Objekt durch X Richtung und Y Richtung ist jeweils shearX, shearY, dann:
- (x, y) ==> (x + y * shearY, y + x * shearX)
Wenn pivot in die Koordinate (pivotX, pivotY) liegt und shearing factor nach der X Richtung und Y Richtung sind jeweils shearX, shearY, dann:
- (x, y) ===> (X", Y")
- X" = pivotX + (x-pivotX) + (y-pivotY) * shearY
- Y" = pivotY + (y-pivotY) + (x-pivotX) * shearX
Zum Beispiel:
Schauen Sie das folgende Beispiel
- Annehmend, die pivot Punkt liegt in der Koordinate.
- Der shearing factor nach X Achse ist shearX = 2.
- Der shearing factor nach Y Achse ist là shearY = 0.
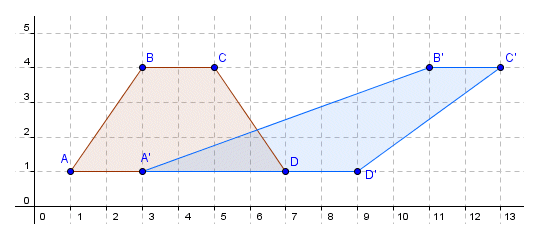
Wir haben das Ergebnis
- xA" = xA + shearY * yA = 1 + 2 * 1 = 3
- yA" = yA + shearX * xA = 1 + 0 * 1 = 1
- xB" = xB + shearY * yB = 3 + 2 * 4 = 11
- yB" = yB + shearX + yB = 4 + 0 * 4 = 4
Zum Beispiel JavaFX:
Es gibt 2 Rechtecke (Rectangle) in der gleichen Größe und Stelle. Wählen Sie die pivot Punkte und benutzen Shearing Transformation für das 2. Rechtsteck. Schauen Sie das Beispiel
ShearingExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Shear;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ShearingExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 120;
final int y = 80;
final int width = 150;
final int height = 100;
int pivotX = 40;
int pivotY = 50;
double shearX = 0.2;
double shearY = 0.5;
// (all)
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rectangle1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// (all)
// Rectangle2
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
Circle pivot = new Circle(pivotX, pivotY, 3);
pivot.setFill(Color.RED);
// Shearing Transformation erstellen
Shear shear = new Shear();
// Die pivot Punkte einstellen.
shear.setPivotX(pivotX);
shear.setPivotY(pivotY);
// Der shearing Factor einstellen
shear.setX(shearX);
shear.setY(shearY);
// Die transformation in dem 2.Rechteck
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(shear);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2, pivot);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 300);
stage.setTitle("Shearing Transformation (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}Das Beispiel durchführen
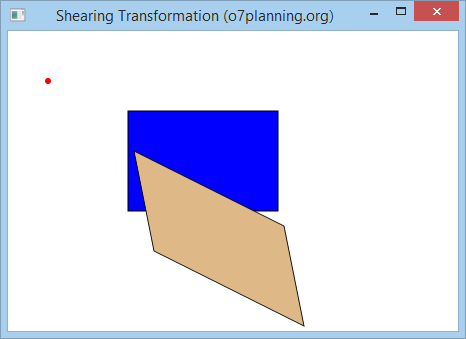
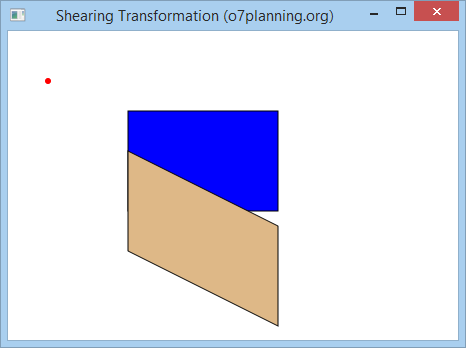
Ändern Sie die oben Beispiele mit
- double shearX = 0;
- double shearY = 0.5;
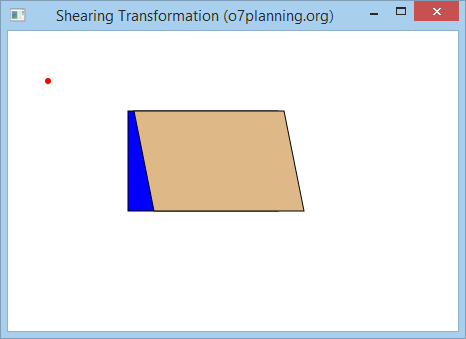
Ändern Sie das oben Beispiel mit der Werte:
- double shearX = 0.2;
- double shearY = 0;
6. Affine Transformation
Affine ist ein Linear transformation, die ein Objekt aus einem zwei oder drei demensionalen Raum zum anderen zwei oder drei dimensionalen Raum verformt. Gleichzeitig haltet sie die Geradheit (straightness) und die Paralle (parallelness) von der Linie (lines).
Eine Punkte A mit der Koordinate (x, y, z) im 3 dimensional Raum wird nach der Position A" mit der Koordinate (x", y", z") durch eine matrix Multiplikation

Die Klasse Affine im JavaFX hat einige Constructor, folgend sind das die üblichen structructor
// Constructor to create 2D Affine.
public Affine(double mxx, double mxy, double tx,
double myx, double myy, double ty);
// Constructor to create 3D Affine.
public Affine(double mxx, double mxy, double mxz, double tx,
double myx, double myy, double myz, double ty,
double mzx, double mzy, double mzz, double tz) ;Zum Beispiel
AffineExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Affine;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class AffineExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 80;
final int y = 90;
final int width = 100;
final int height = 70;
double mxx = 0.2;
double mxy = 1.5;
double myx = 1.5;
double myy = 0.5;
double tx = 40;
double ty = 50;
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rectangle1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// Rectangle2
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
Circle pivot = new Circle(tx, ty, 3);
pivot.setFill(Color.RED);
// Creating the 2D Affine transformation
Affine affine = new Affine(mxx, mxy, tx, myx, myy, ty);
// Adding the transformation to rectangle2
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(affine);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2, pivot);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 500);
stage.setTitle("JavaFX Affine Transformation (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}Das Beispiel durchführen
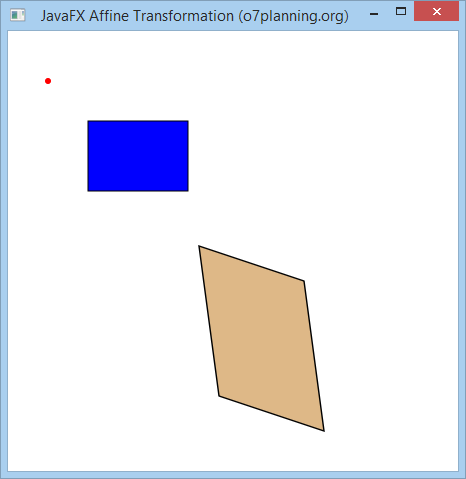
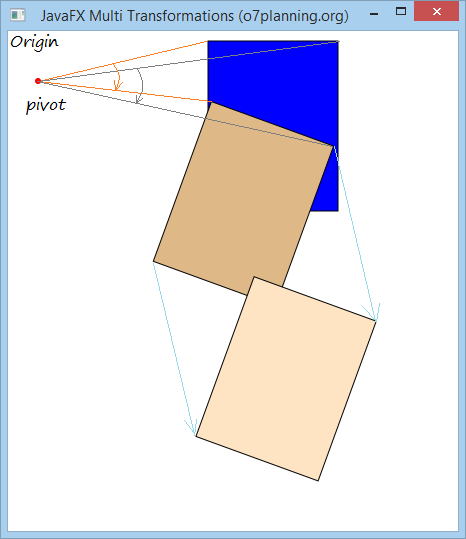
7. Die Kombination der Transformations
Sie können die Transformation in einem Geometrie-Objekt anwenden
Zum Beispiel:
Im Dokument haben Sie 3 Rechtecke (Rectangle) in der gleichen Größe und Stelle. 2 Transformation wie Rotation und Translation erstellen. Fügen Sie Rotation in dem 2. Rechteck und die beiden Transformation in dem 3. Rechteck hinzu. Schauen Sie das Ergebnis
MultipleTransformationsExample.java
package org.o7planning.javafx.transformation;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.scene.transform.Translate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class MultipleTransformationsExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
final int x = 200;
final int y = 10;
final int width = 130;
final int height = 170;
int pivotX = 30;
int pivotY = 50;
// Rectangle1
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rectangle1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// Rectangle2
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle2.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
rectangle2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
// Rectangle3
Rectangle rectangle3 = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle3.setFill(Color.BISQUE);
rectangle3.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
Circle pivot = new Circle(pivotX, pivotY, 3);
pivot.setFill(Color.RED);
// Creating the rotation transformation
Rotate rotate = new Rotate();
// Setting the angle for the rotation (20 degrees)
rotate.setAngle(20);
// Setting pivot points for the rotation
rotate.setPivotX(pivotX);
rotate.setPivotY(pivotY);
// Adding the transformation to rectangle2
rectangle2.getTransforms().addAll(rotate);
// Create Translation Transformation.
Translate translate = new Translate(100, 150);
// Adding 2 transformations to rectangle3
rectangle3.getTransforms().addAll(rotate, translate);
Group root = new Group(rectangle1, rectangle2,rectangle3, pivot);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 450, 500);
stage.setTitle("JavaFX Multi Transformations (o7planning.org)");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}No ADS
Die Anleitungen JavaFX
- Öffnen Sie ein neues Fenster (window) in JavaFX
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ChoiceDialog
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Alert Dialog
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TextInputDialog
- Installieren Sie e(fx)clipse für Eclipse (JavaFX Tooling)
- Installieren Sie JavaFX Scene Builder für Eclipse
- Die Anleitung zum JavaFX für den Anfänger - Hello JavaFX
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX FlowPane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TilePane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX HBox, VBox Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX BorderPane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX AnchorPane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TitledPane
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Accordion
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ListView
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Group
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ComboBox
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Transformation
- Effekte (Effects) in JavaFX
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX GridPane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX StackPane Layout
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ScrollPane
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX WebView und WebEngine
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX HTMLEditor
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TableView
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TreeView
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TreeTableView
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Menu
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ContextMenu
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Image und ImageView
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Label
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Hyperlink
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Button
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ToggleButton
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX RadioButton
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX MenuButton und SplitMenuButton
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TextField
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX PasswordField
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX TextArea
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Slider
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Spinner
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ProgressBar und ProgressIndicator
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ChoiceBox
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Tooltip
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX DatePicker
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX ColorPicker
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX FileChooser und DirectoryChooser
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX PieChart
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX AreaChart und StackedAreaChart
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX BarChart und StackedBarChart
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Line
- Die Anleitung zu JavaFX Rectangle und Ellipse
Show More