Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Scrollspy
1. Bootstrap Scrollspy
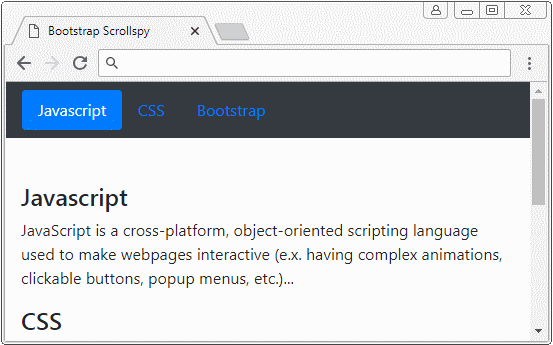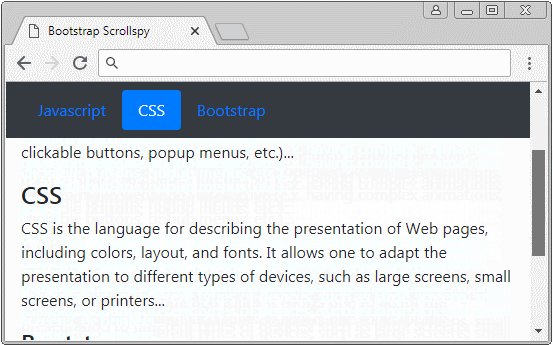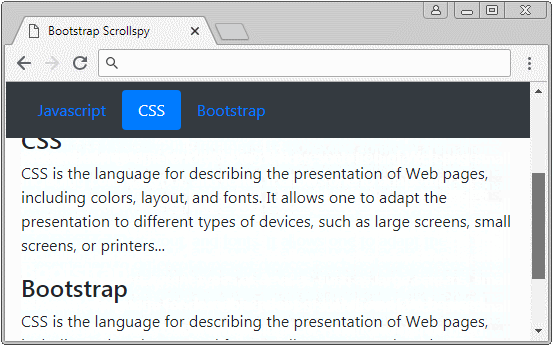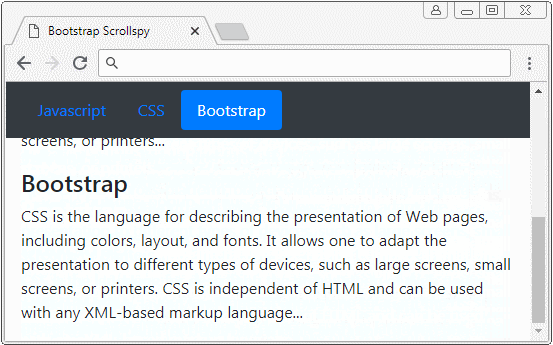
Zuerst beobachten Sie ein folgendes Scrollspy :
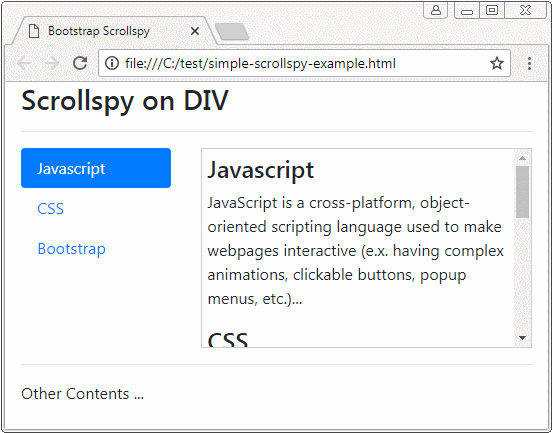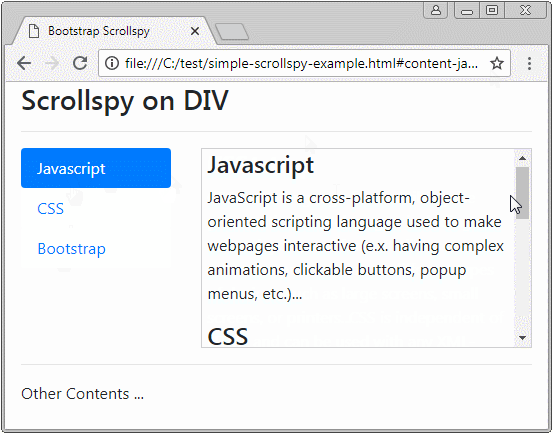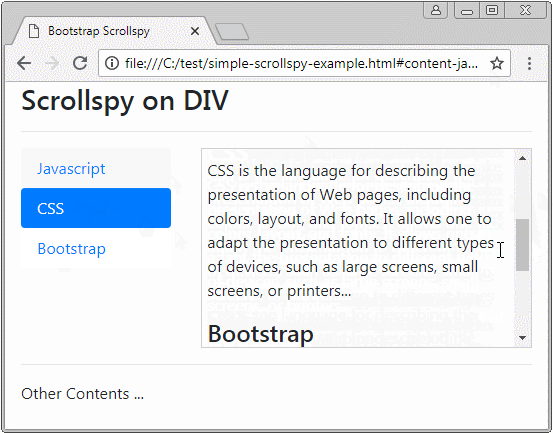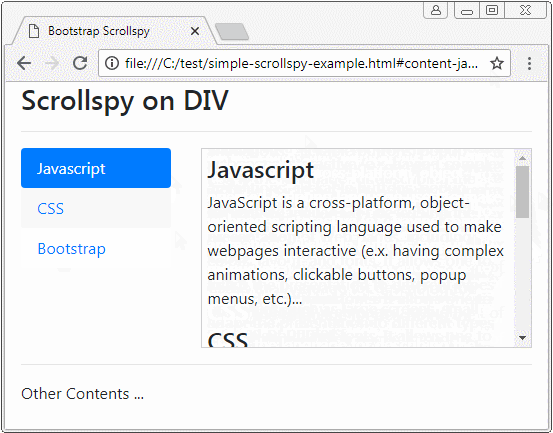
Scrollspy heißt nach seinem Name Scroll + Spy (scrollen + auskundschaften). Scrollspy funktioniert nach 2 Elemente:
- Das erste Element ist ein Nav (oder List-Group).
- Das zweite Element ist ein scrollbare Inhaltsraum (scrollable), der <body> oder <div>,<span> sein kann.... Wenn die Inhalt kein <body> ist, soll sie height und overflow-y: scroll.
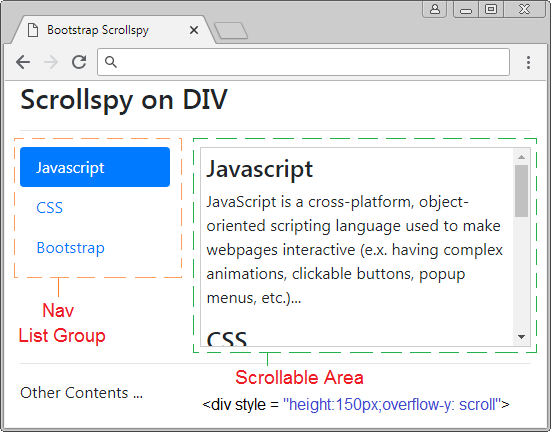
Der Operationsgrundsatz:
- In Komponent 1 klickt der Benutzer auf einem Item vom Nav (oder List-Group). Die Scroll-Leiste auf Komponent 2 wird funktionieren um die dem Item übereinstimmende richtige Inhalt, auf die der Benutzer klickt anzuzeigen.
- In Komponent 2 wenn der Benutzer die Scroll-Leiste zieht, wird Item vom Komponent 1, die der anzeigenden Inhalt, aktiv.
simple-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy on DIV</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>2. Scrollspy + BODY
In diesem Beispiel werde ich ein Scrollspy machen um die Inhalt auf <body> auszukundschaften (spy). Achten Sie darauf, das Default <body> die vertikale Scroll-Leiste (vertical scrollbar). Das ist die Leiste des Browser. Unter ist es die Illustrator der Struktur des Beispiel:
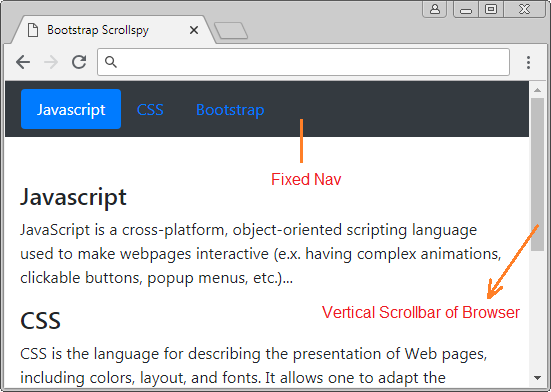
body-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body data-spy="scroll" data-target="#scrollspy-nav" data-offset="110">
<div class="container-fluid">
<nav id="scrollspy-nav" class="navbar bg-dark fixed-top">
<ul class="nav nav-pills">
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-css">CSS</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div style="margin-top:100px;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
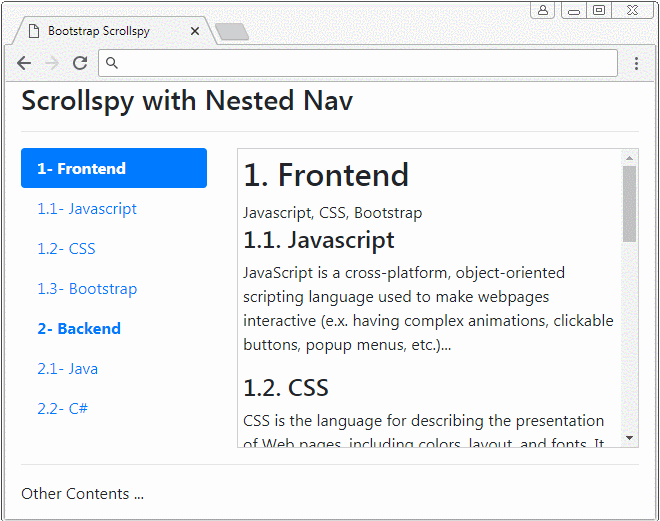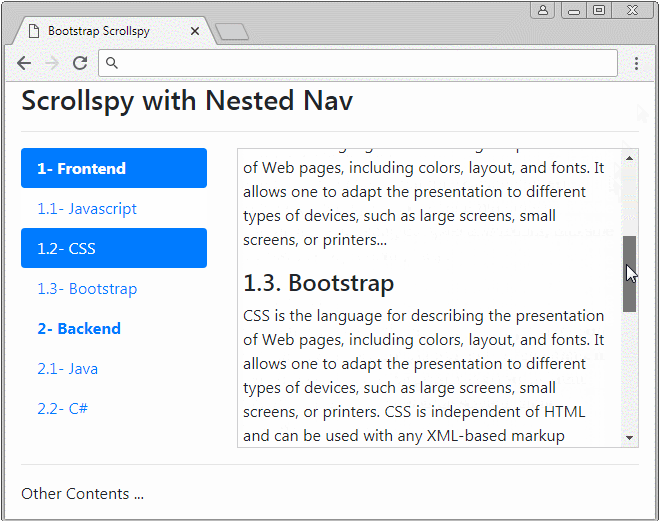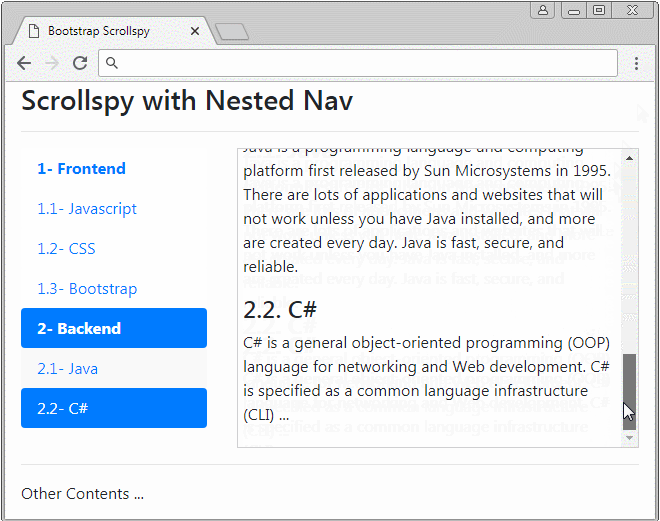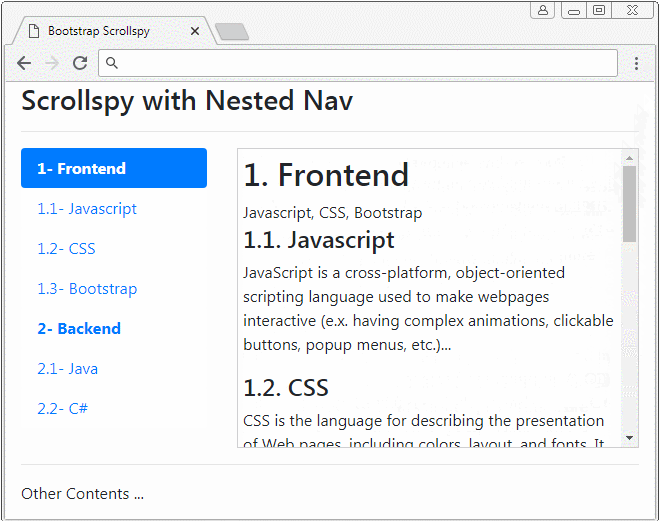
</html>3. Das Beispiel mit dem verschachtelten Nav (Nested Nav)
Scrollspy kann auch mit den verschachtelten Nav (Nested Navs) arbeiten. Wenn ein Nav aktiviert wird, wird Vater Nav aktiviert.
nested-nav-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with Nested Navs</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<nav id="myScrollspy">
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-frontend">
<strong>1- Frontend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-javascript"> 1.1- Javascript</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-css"> 1.2- CSS</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-bootstrap"> 1.3- Bootstrap</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-backend">
<strong>2- Backend</strong>
</a>
<ul class="nav nav-pills flex-column">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-java"> 2.1- Java</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#content-csharp"> 2.2- C#</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:300px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h2 id="content-frontend">1. Frontend</h2>
Javascript, CSS, Bootstrap
<h4 id="content-javascript">1.1. Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language
used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">1.2. CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">1.3. Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages,
including colors, layout, and fonts.
It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
<h2 id="content-backend">2. Backend</h2>
Java, C#
<h4 id="content-java">2.1. Java</h4>
<p>
Java is a programming language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995.
There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed,
and more are created every day. Java is fast, secure, and reliable.
</p>
<h4 id="content-csharp">2.2. C#</h4>
<p>
C# is a general object-oriented programming (OOP) language for networking and Web development.
C# is specified as a common language infrastructure (CLI) ...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>4. Das Beispiel mit List Group
Scrollspy kann mit List Group arbeiten. Das ist ein Beispiel unten:
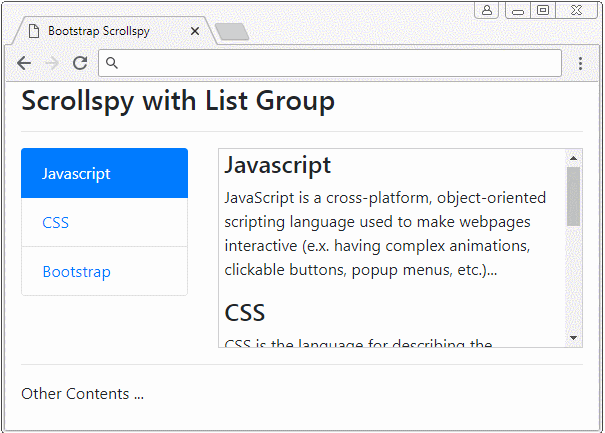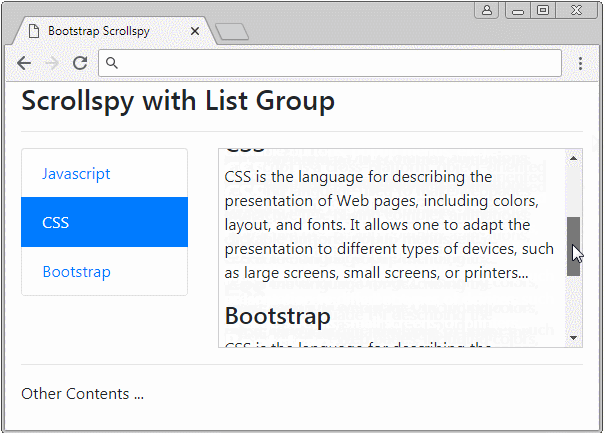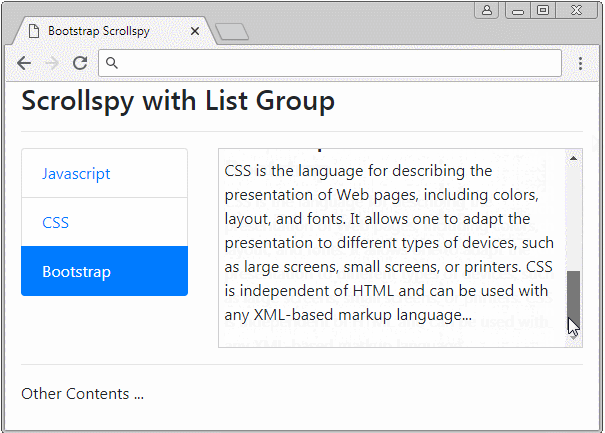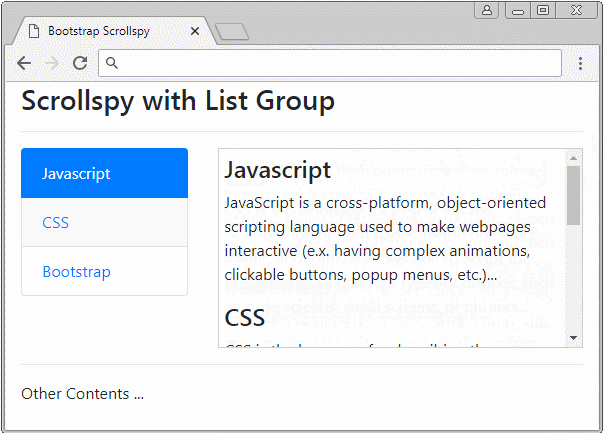
list-group-scrollspy-example.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Bootstrap Scrollspy</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container-fluid">
<h3>Scrollspy with List Group</h3>
<hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4">
<div class="list-group" id="myScrollspy">
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-javascript">Javascript</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-css">CSS</a>
<a class="list-group-item" href="#content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-8">
<div data-spy="scroll" data-target="#myScrollspy" data-offset="10"
style="height:200px;overflow-y: scroll;padding:5px; border: 1px solid #ccc;">
<h4 id="content-javascript">Javascript</h4>
<p>
JavaScript is a cross-platform, object-oriented scripting language used to make webpages interactive
(e.x. having complex animations, clickable buttons, popup menus, etc.)...
</p>
<h4 id="content-css">CSS</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers...
</p>
<h4 id="content-bootstrap">Bootstrap</h4>
<p>
CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors,
layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices,
such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML
and can be used with any XML-based markup language...
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<hr>
Other Contents ...
</div>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Anleitungen Bootstrap
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Jumbotron
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Dropdown
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Alert
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Button
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Button Group
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Popover (Tooltip)
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Spinner
- Einführung in Bootstrap
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Grid System
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Card
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Container
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Nav, Tab, Pill
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap NavBar
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Table
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Modal
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Form
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Pagination
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Badge
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Input Group
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap List Group
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap ProgressBar
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Collapse und Accordion
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Scrollspy
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Breadcrumb
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Carousel
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Spacing Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Border Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Color Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Text Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Sizing Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Position Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Flex Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Display Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Visibility Utility
- Die Anleitung zu Bootstrap Embed Utility
Show More