if else Anweisung in JavaScript
1. Das Statement if
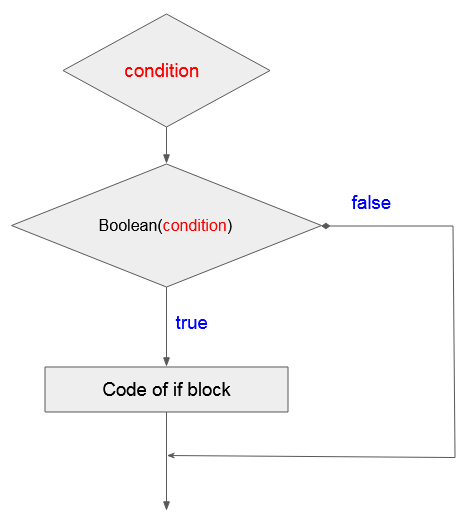
Im ECMAScript bewertet das Statement if(condition) eine Bedingung um zu entscheiden, ob sein Statement Block durchgeführt wird oder nicht
Unten ist das die Struktur vom if Statement
if (condition) {
// Do something here!
}condition kann eine Wert, ein Typ oder eine Ausdruck sein. ECMAScript benutzt die Funktion Boolean(condition) zu bewerten. Diese Funktion gibt true oder false zurück.
Function: Boolean(condition)?Die Funktion Boolean(condition) gibt false zurück wenn condition die Wert von false, 0, "", null, undefined, NaN, Number.Infinite hat. Umgekehrt gibt die Funktion true zurück.
Die folgende Figur bezeichnet die Bewertung einer Bedingung vom ECMAScript:
Zum Beispiel
simple-if-example.js
if(true) { // Work
console.log("Test 1");
}
if(false) { // Not work!
console.log("Test 2");
}Output:
Test 1if-example.js
if(true) { // Work
console.log("if(true)");
}
if(false) { // Not work!
console.log("if(false)");
}
if('true') { // Work
console.log("if('true')");
}
if('false') { // Work
console.log("if('false')");
}
var obj = new Object();
if(obj) { // Work
console.log("if(obj)");
}
if('') { // Not work!
console.log("if('')");
}
if(undefined) { // Not work!
console.log("if(undefined)");
}
if(0) { // Not work!
console.log("if(0)");
}Output:
if(true)
if('true')
if('false')
if(obj)if-example2.js
var number0 = 0;
if(number0) { // Not work!
console.log("number 0 (primitive)");
}
if(false) { // Not work!
console.log("boolean false (primitive)");
}
// A not null Object
var myObj = {};
if(myObj) { // Work!
console.log("A not null Object");
}
// A not null Object
var numberObject = new Number(0);
if(numberObject) { // Work!
console.log("A not null Object (Number)");
}
// A not null Object
var booleanObject = new Boolean(false);
if(booleanObject) { // Work!
console.log("A not null Object (Boolean)");
}Output:
A not null Object
A not null Object (Number)
A not null Object (Boolean)if-example3.js
// Declare a variable, representing your age
let age = 30;
console.log("Your age: " + age);
// The condition to test is 'age> 20'
if (age > 20) {
console.log("Okey!");
console.log("Age is greater than 20");
}
// The code blow the 'if' block.
console.log("Done!");Output:
Your age: 30
Okey!
Age is greater than 20
Done!2. Das Statement if - else
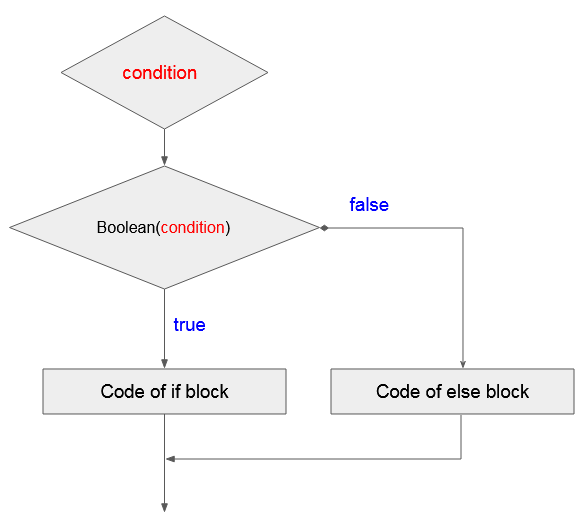
Das Statement if-else wird auch benutzt um eine Bedingung zu prüfen. ECMAScript benutzt die Funktion Boolean(condition) um eine Bedingung zu prüfen. Wenn das Ergebnis von der Bewertung true ist, wird das Statement if durchgeführt. Umgekehrt wird das Statement else durchgeführt
if( condition ) {
// Do something here
}
// Else
else {
// Do something here
}
Zum Beispiel
if-else-example.js
// Declare a variable, representing your age
let age = 15;
console.log("Your age: " + age);
// The condition to test is 'age> 18'
if (age >= 18) {
console.log("Okey!");
console.log("You are accepted!");
} else {
console.log("Sorry!");
console.log("Age is less than 18");
}
// The code after the 'if' block and 'else' block.
console.log("Done!");Output:
Your age: 15
Sorry!
Age is less than 18
Done!3. Das Statement if - else if - else
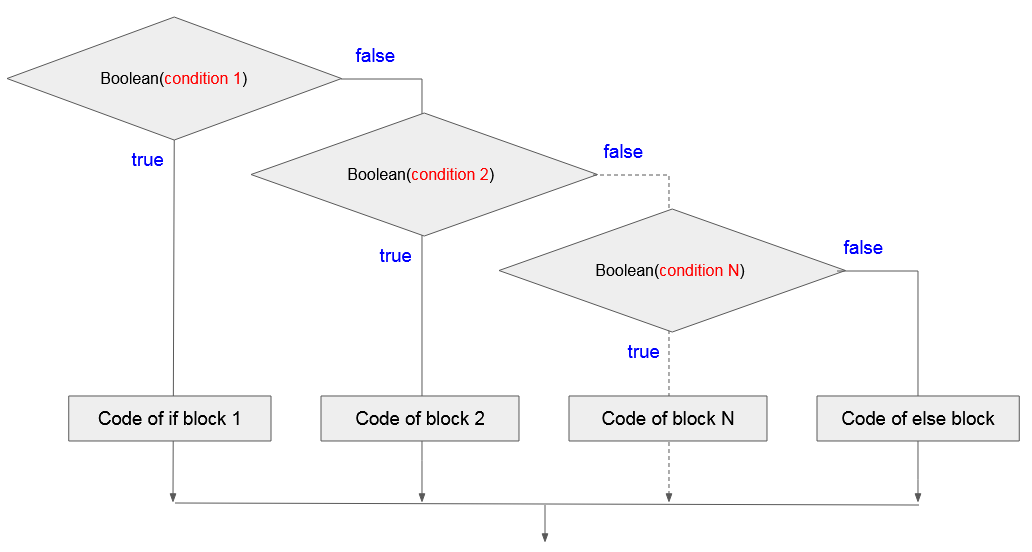
Die Struktur des Statement if - else if - else ist:
if(condition 1) {
// Do something here
} else if(condition 2) {
// Do something here
} else if(condition 3) {
// Do something here
}
// Else
else {
// Do something here
}
if-elseif-else-example.js
// Declaring a varible
// Represent your test scores.
let score = 70;
console.log("Your score =" + score);
// If the score is less than 50
if (score < 50) {
console.log("You are not pass");
}
// Else if the score more than or equal to 50 and less than 80.
else if (score >= 50 && score < 80) {
console.log("You are pass");
}
// Remaining cases (that is greater than or equal to 80)
else {
console.log("You are pass, good student!");
}Output:
Your age: 15
Sorry!
Age is less than 18
Done!Die Wert von der Variable "score" in Beispiel oben ändern und das Beispiel noch einmal durchführen
let score = 20;Output:
Your score =20
You are not pass4. Die Operatoren zur Teilnahme an dem Bedingungsausdruck
Unten ist die Liste der Operatoren, die in dem Bedingungsausdruck (conditional expression) verwendet werden.
- > größer
- < kleiner
- >= größer oder gleich
- <= kleiner oder gleich
- && und
- || oder
- == gleiche Vergleich
- != unterschiedliche Vergleich
- ! negativ
Zum Beispiel
if-elseif-else-example2.js
// Declare a variable, represents your age.
let age = 20;
// Test if age less than or equal 17
if (age <= 17) {
console.log("You are 17 or younger");
}
// Test age equals 18
else if (age == 18) {
console.log("You are 18 year old");
}
// Test if age greater than 18 and less than 40
else if (age > 18 && age < 40) {
console.log("You are between 19 and 39");
}
// Remaining cases (Greater than or equal to 40)
else {
// Nested if statements
// Test age not equals 50.
if (age != 50) {
console.log("You are not 50 year old");
}
// Negative statements
if (!(age == 50)) {
console.log("You are not 50 year old");
}
// If age is 60 or 70
if (age == 60 || age == 70) {
console.log("You are 60 or 70 year old");
}
}Output:
You are between 19 and 39Sie können die Wert von der Variable 'age' ändern und das Beispiel noch einmal durchführen um das Beispiel zu sehen
Anleitungen ECMAScript, Javascript
- Einführung in Javascript und ECMAScript
- Schnellstart mit Javascript
- Dialogfeld Alert, Confirm, Prompt in Javascript
- Schnellstart mit JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Variable
- Bitweise Operationen
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Array
- Schleifen in JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Function
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Number
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Boolean
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript String
- if else Anweisung in JavaScript
- Switch Anweisung in JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Error
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Date
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Module
- Die Geschichte der Module in JavaScript
- Die Funktionen setTimeout und setInterval in JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Form Validation
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Web Cookie
- Schlüsselwort void in JavaScript
- Klassen und Objekte in JavaScript
- Klasse und Vererbung Simulationstechniken in JavaScript
- Vererbung und Polymorphismus in JavaScript
- Das Verständnis über Duck Typing in JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Symbol
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Set Collection
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Map Collection
- Das Verständnis über JavaScript Iterable und Iterator
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Reguläre Ausdrücke
- Die Anleitung zu JavaScript Promise, Async Await
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Window
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Console
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Screen
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Navigator
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Geolocation API
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Location
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript History API
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Statusbar
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Locationbar
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Scrollbars
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Menubar
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript JSON
- Ereignisbehandlung in JavaScript
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript MouseEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript WheelEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript KeyboardEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript FocusEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript InputEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript ChangeEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript DragEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript HashChangeEvent
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript URL Encoding
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript FileReader
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript XMLHttpRequest
- Die Anleitung zu Javascript Fetch API
- Analysieren Sie XML in Javascript mit DOMParser
- Einführung in Javascript HTML5 Canvas API
- Hervorhebung Code mit SyntaxHighlighter Javascript-Bibliothek
- Was sind Polyfills in der Programmierwissenschaft?
Show More