Die Anleitung zu Android Fragment
1. Was ist Android Fragment?
Um eine Interface zu bauen können Sie viele Fragmente bauen und miteinander verbinden. In dem Beispiel gebe ich Sie die Hinweise beim Umgang mit fragment.
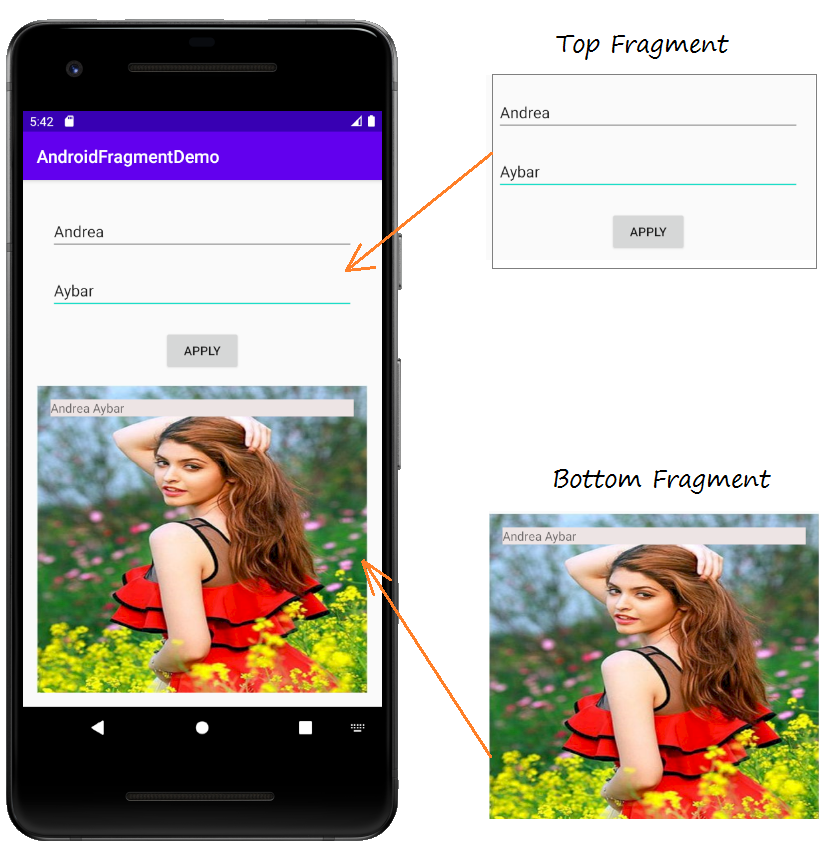
Und behandeln Sie die Interaktion zwischen 2 fragment
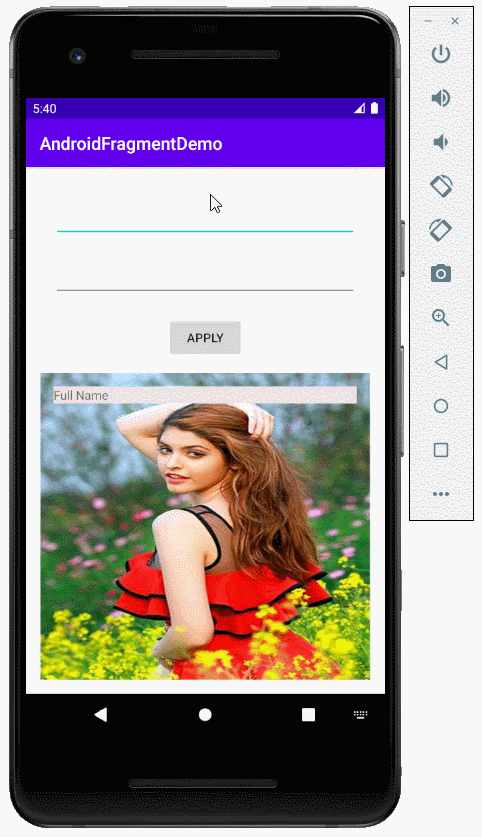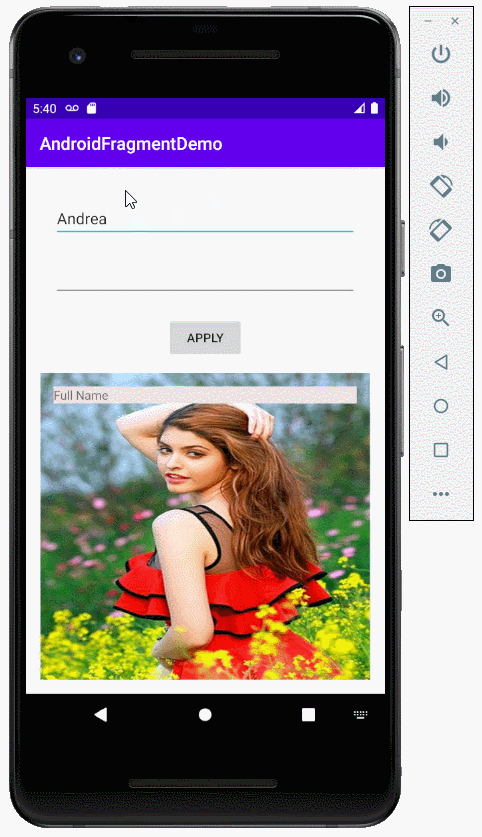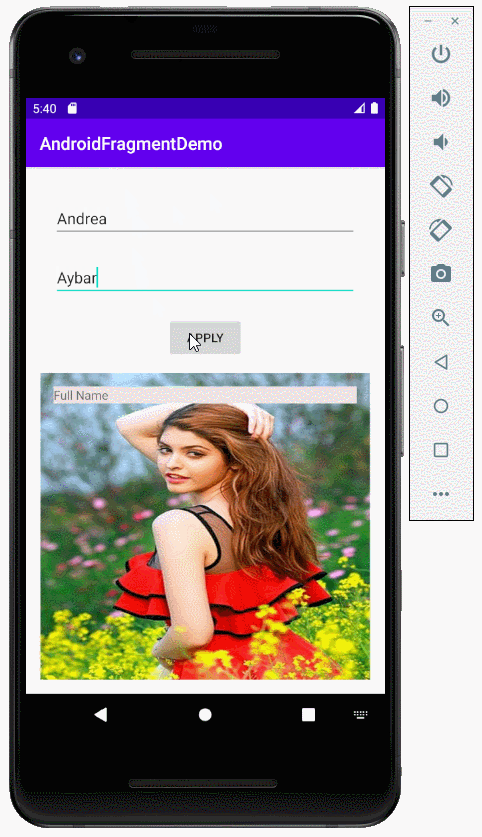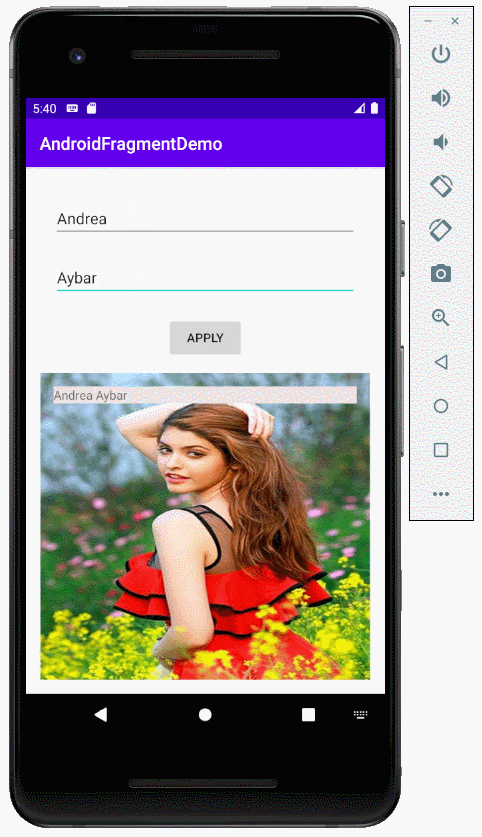
2. Zum Beispiel über die Benutzung von fragment
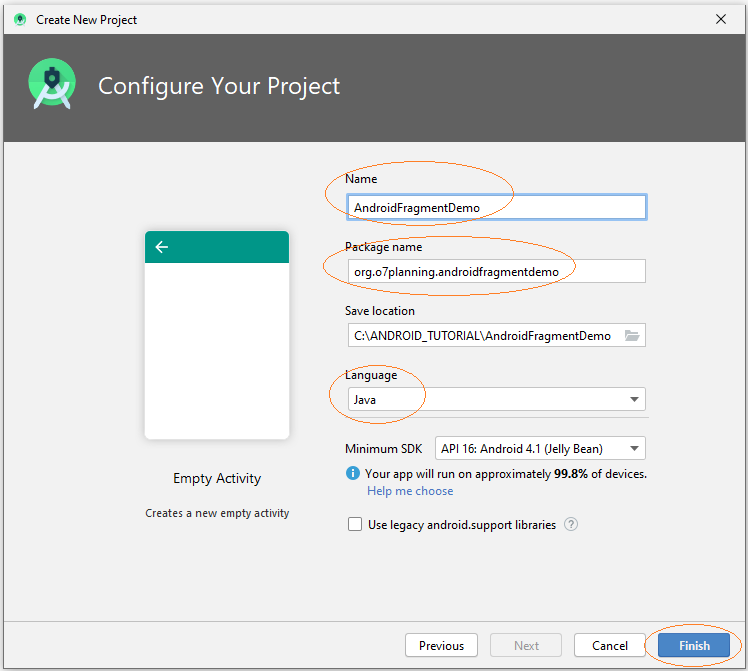
Erstellen Sie ein Projekt mit dem Name von AndroidFragmentDemo
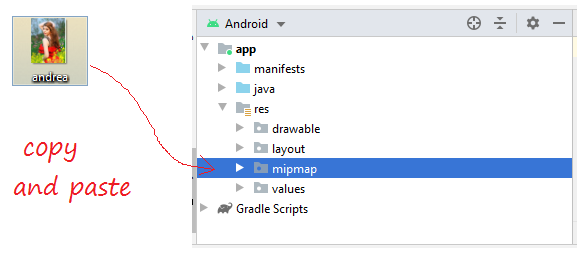
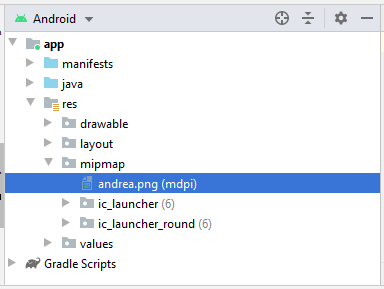
Bereiten Sie eine Foto-File, zum Beispiel:
- andrea.png

Kopieren und kleben Sie die File andrea.jpg in dem Ordner mipmap vom Projekt auf
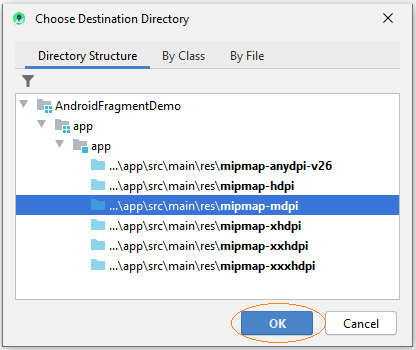
Android Studio wird Sie fordern, die erstellte Foto-Qualiät zu wählen. Wählen Sie mipmap-mdpi . Das ist das Foto mit der durchschnittlichen Qualität.
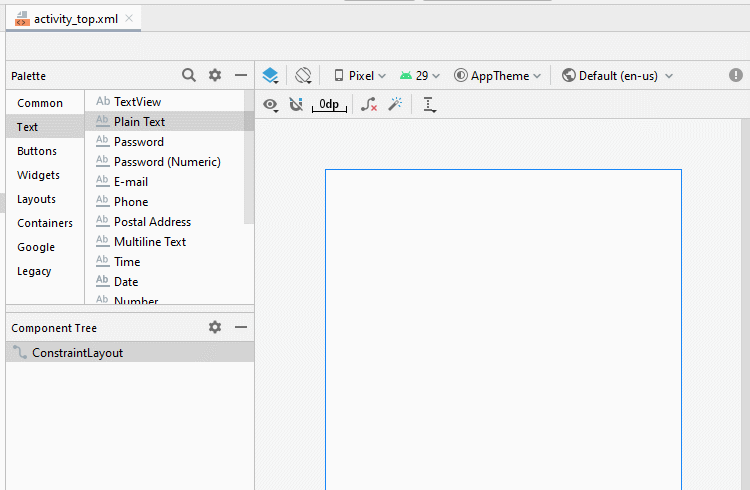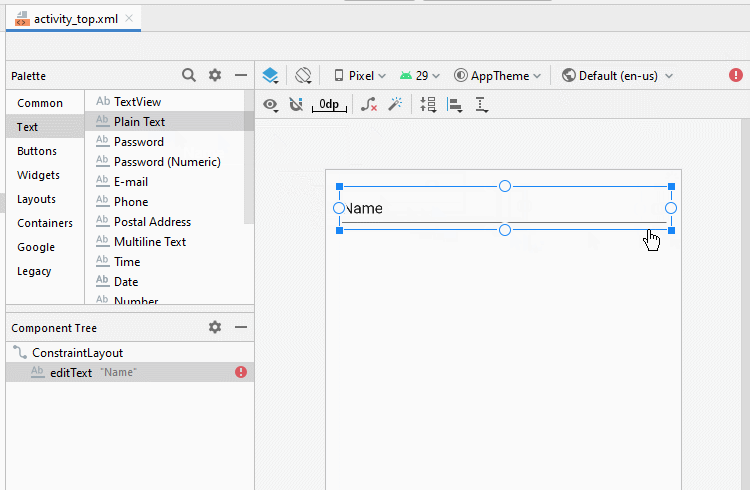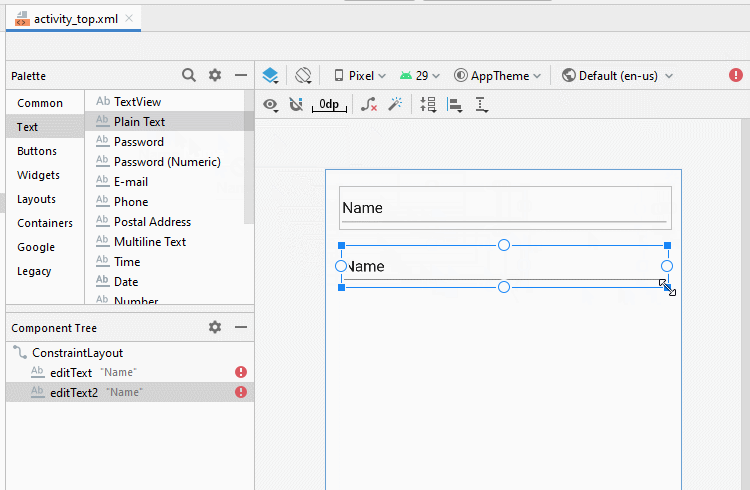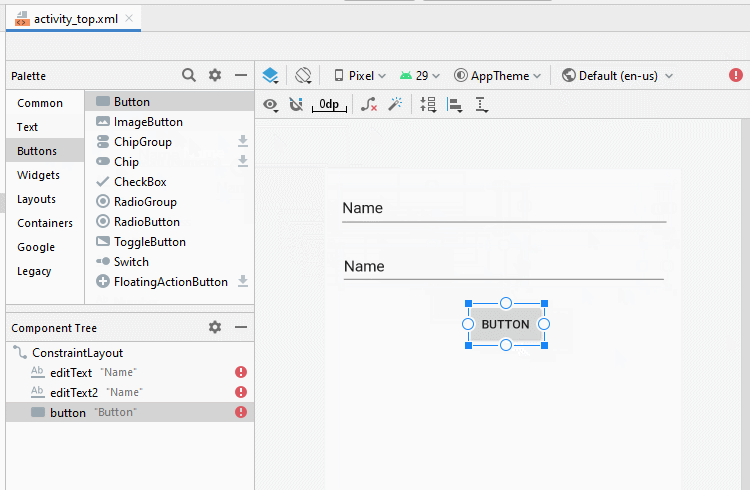
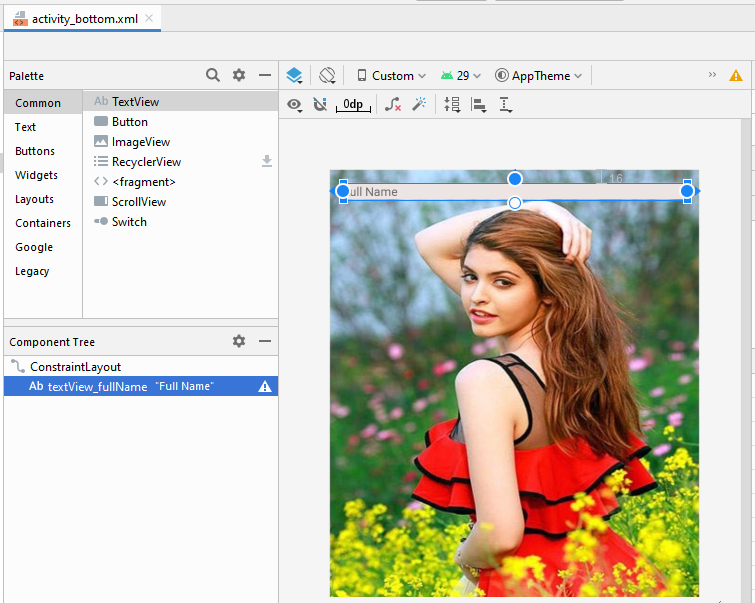
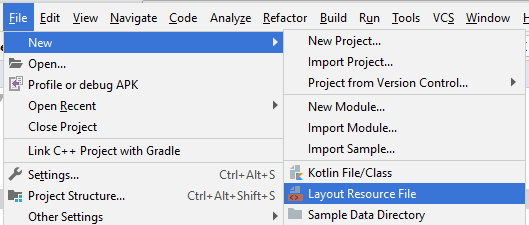
Zunächst erstellen wir eine File activity_top.xml:
Auf Android Studio wählen Sie:
- File > New > Layout Resource file
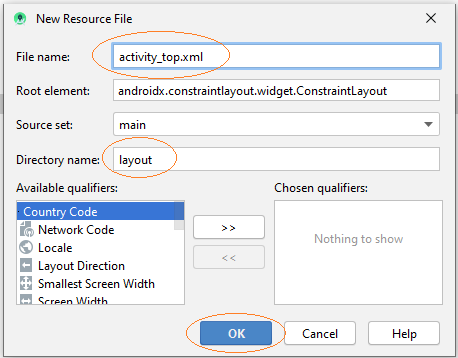
Geben Sie ein
- File name: activity_top.xml
- Root element: androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
- Directory name: layout
Es ist so gleich wie die Erstellung der File activity_bottom.xml
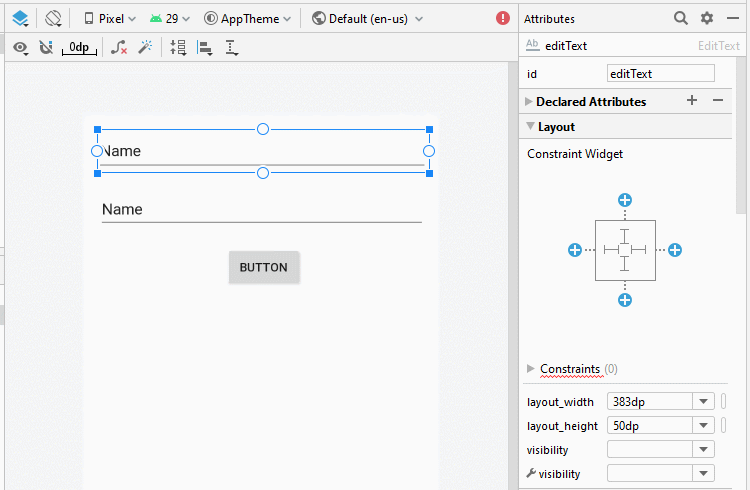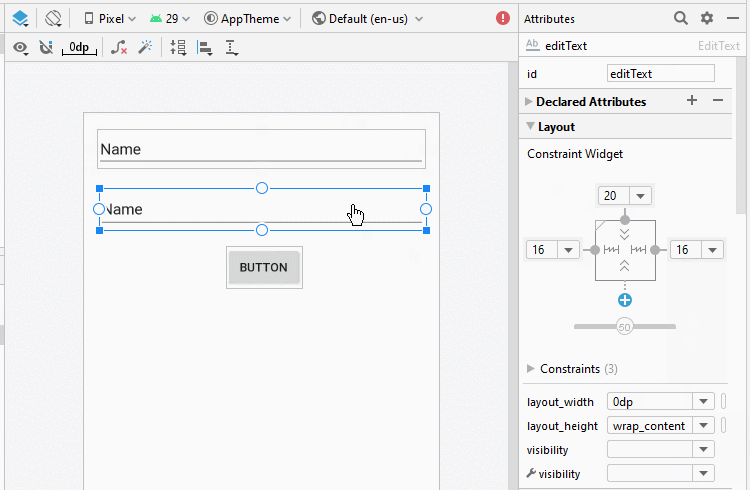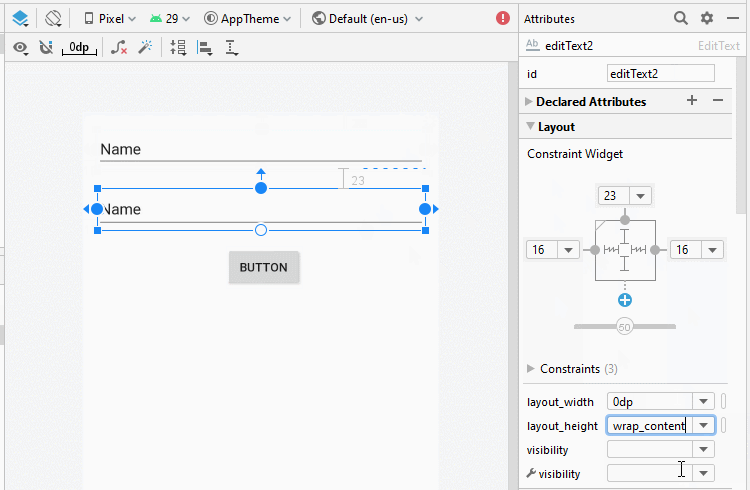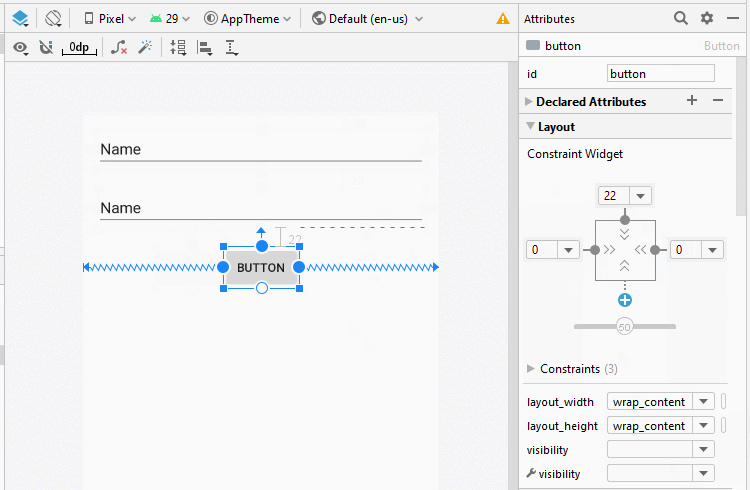
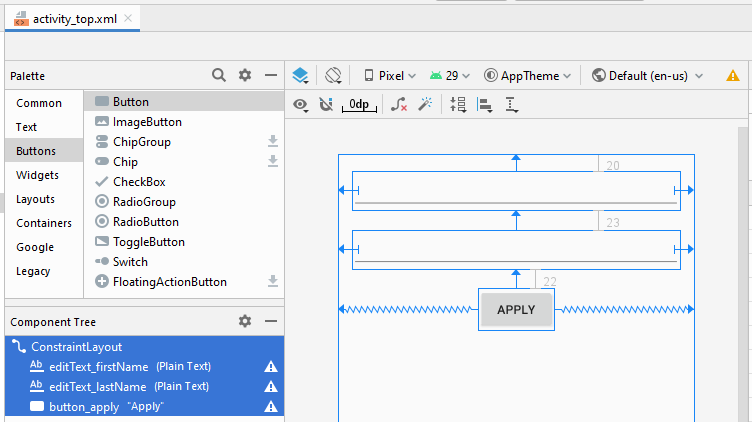
Bauen Sie die Interface auf activity_top.xml
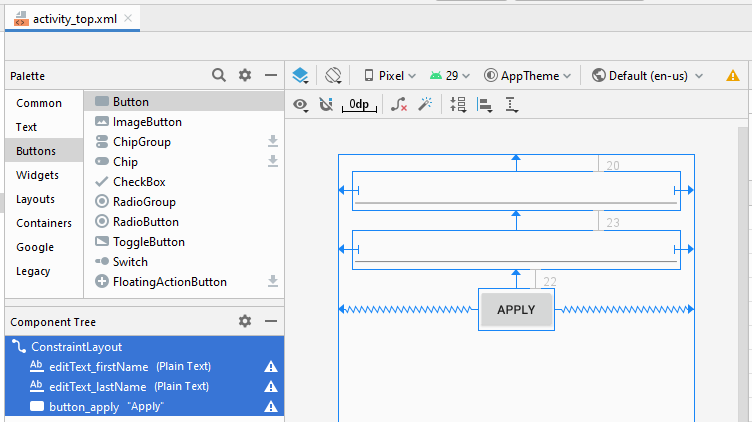
activity_top.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText_firstName"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText_lastName"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="23dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/editText_firstName" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_apply"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="22dp"
android:text="Apply"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/editText_lastName" />
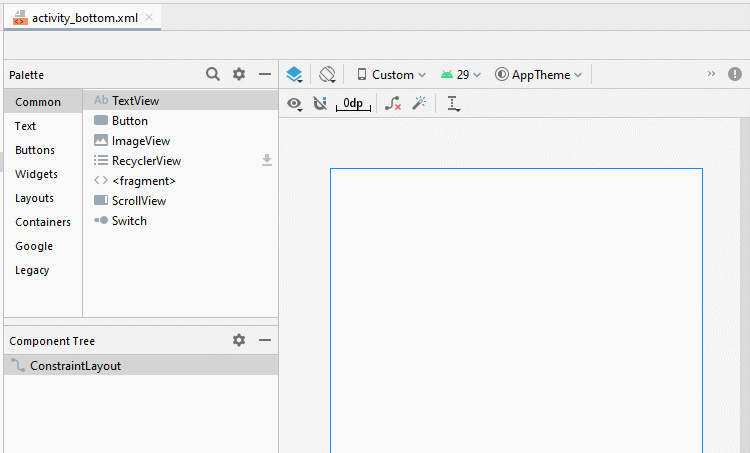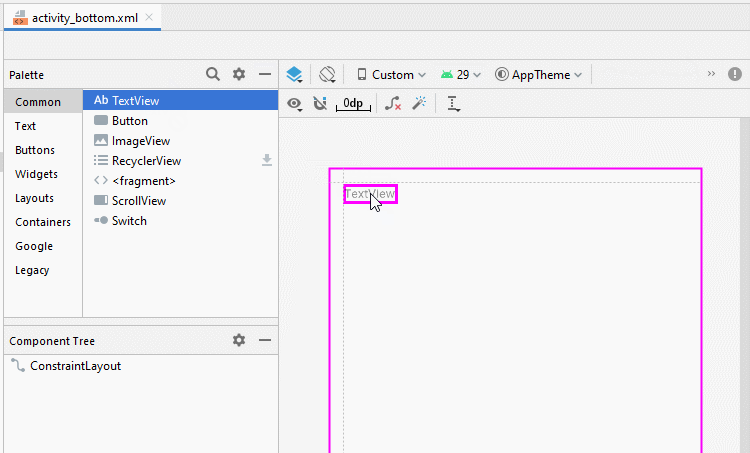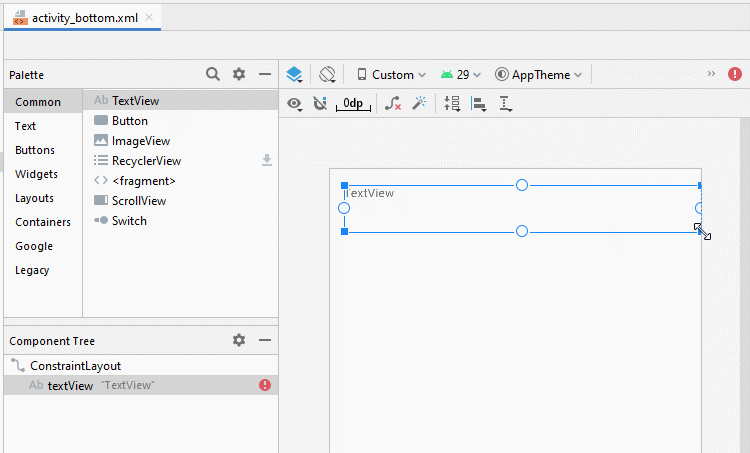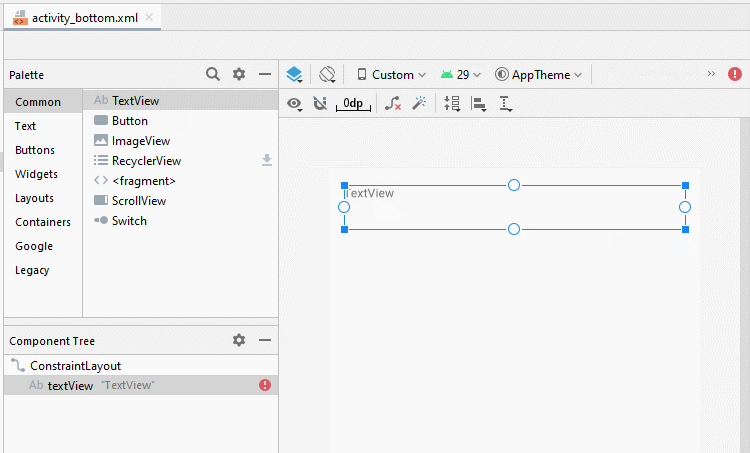
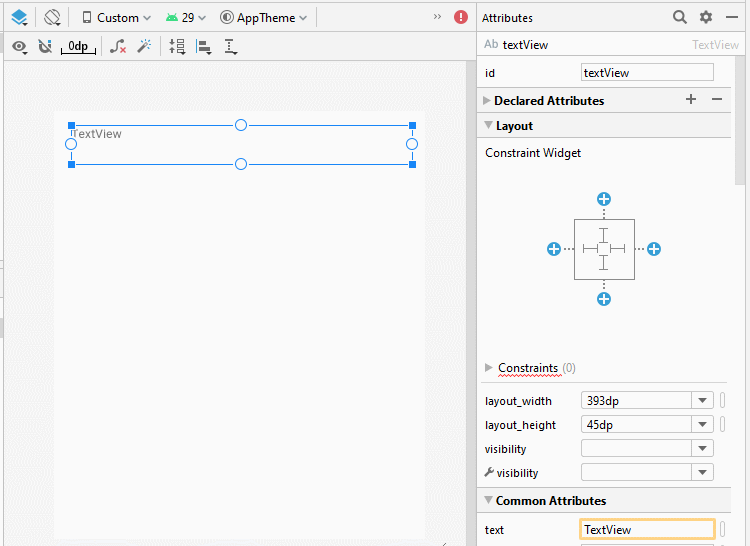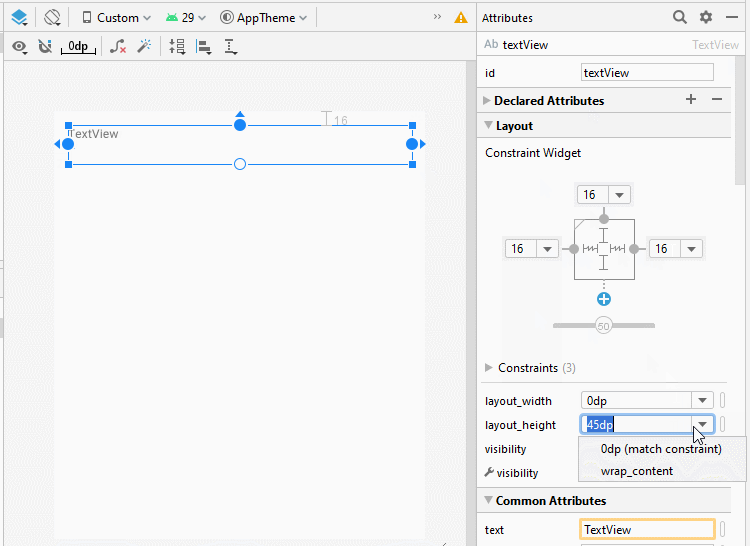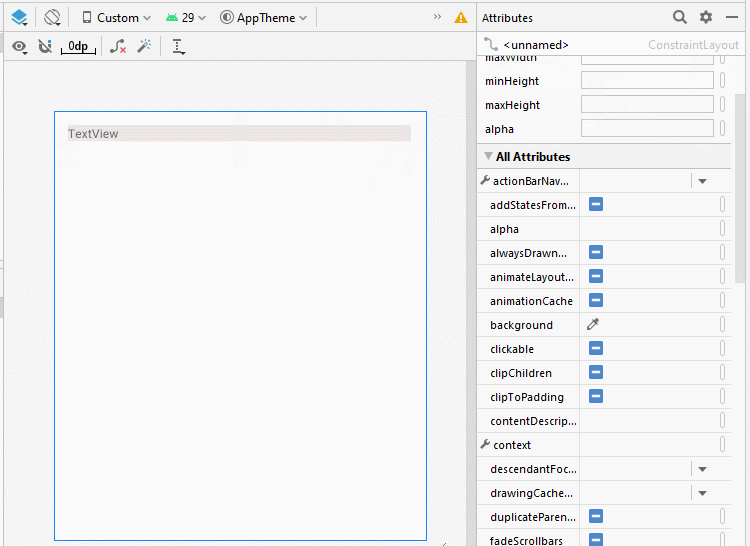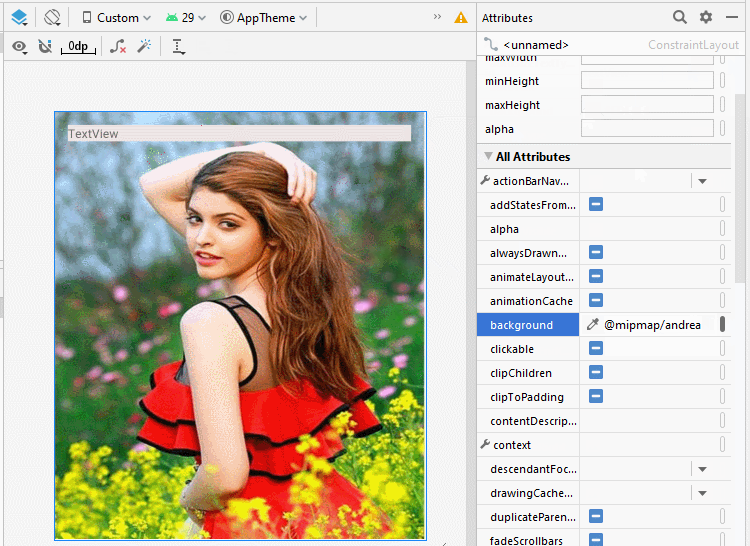
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>Bauen Sie die Interface auf activity_bottom.xml
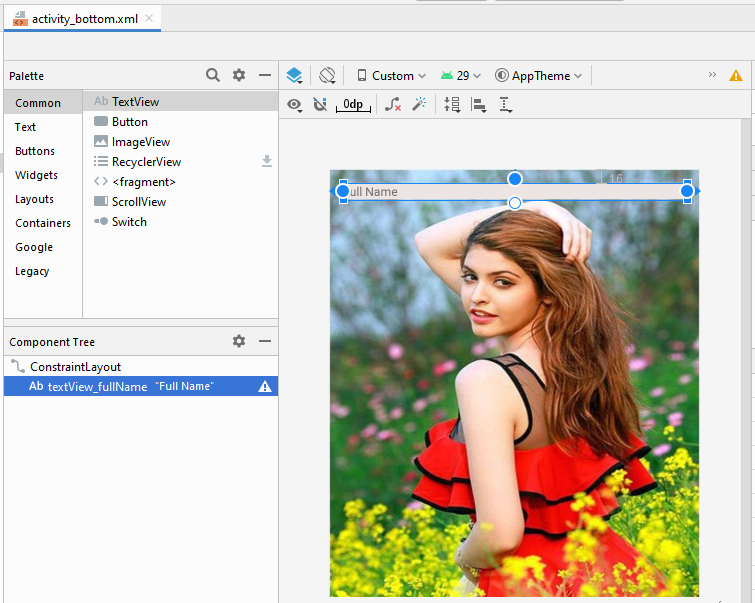
activity_bottom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/andrea">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView_fullName"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:background="#EDE4E4"
android:text="Full Name"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>Wenn Sie an den Schritten zum Entwerfen der Benutzerinterface dieser Anwendung interessiert sind, lesen Sie den Anhang am Ende des Artikels.
Jeder Fragment entspricht einer Klasse im Java. Die Klasse erweitert aus der Klasse Fragment.
Erstellen Sie 2 Klasse TopFragment und BottomFragment und ändern Sie ihre Kode
TopFragment .java
package org.o7planning.androidfragmentdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
public class TopFragment extends Fragment {
private EditText editTextFirstName;
private EditText editTextLastName;
private Button buttonApply;
private MainActivity mainActivity;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Read xml file and return View object.
// inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.activity_top, container, false);
editTextFirstName = (EditText) view.findViewById(R.id.editText_firstName);
editTextLastName = (EditText) view.findViewById(R.id.editText_lastName);
buttonApply = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.button_apply);
buttonApply.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
applyText();
}
});
return view;
}
// Called when a fragment is first attached to its context.
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
if (context instanceof MainActivity) {
this.mainActivity = (MainActivity) context;
}
}
private void applyText() {
String firstName = this.editTextFirstName.getText().toString();
String lastName = this.editTextLastName.getText().toString();
this.mainActivity.showText(firstName, lastName);
}
}BottomFragment.java
package org.o7planning.androidfragmentdemo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
public class BottomFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView textViewFullName;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Read xml file and return View object.
// inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.activity_bottom, container, false);
textViewFullName = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.textView_fullName);
return view;
}
public void showText(String firstName, String lastName) {
textViewFullName.setText(firstName + " " + lastName);
}
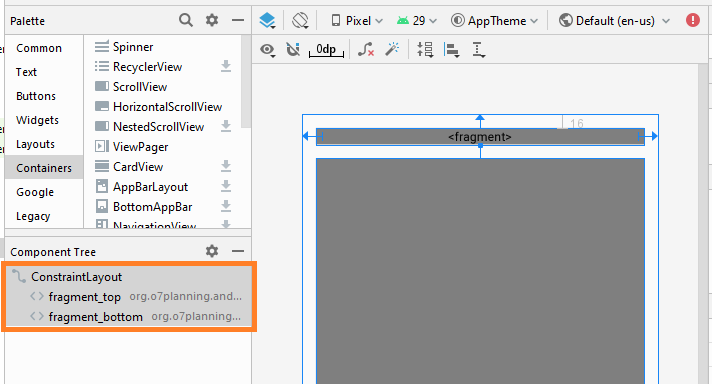
}Jetzt gliedern Sie die fragment auf die Hauptinterface von Activity auf. Öffnen Sie die File activity_main.xml
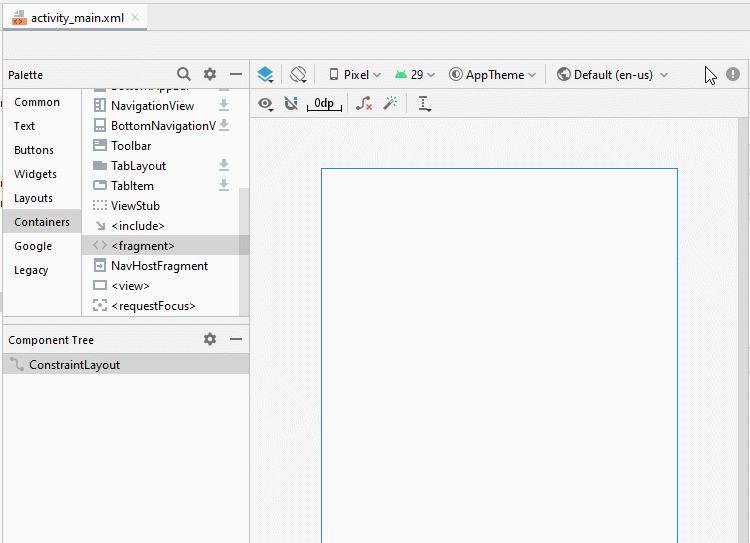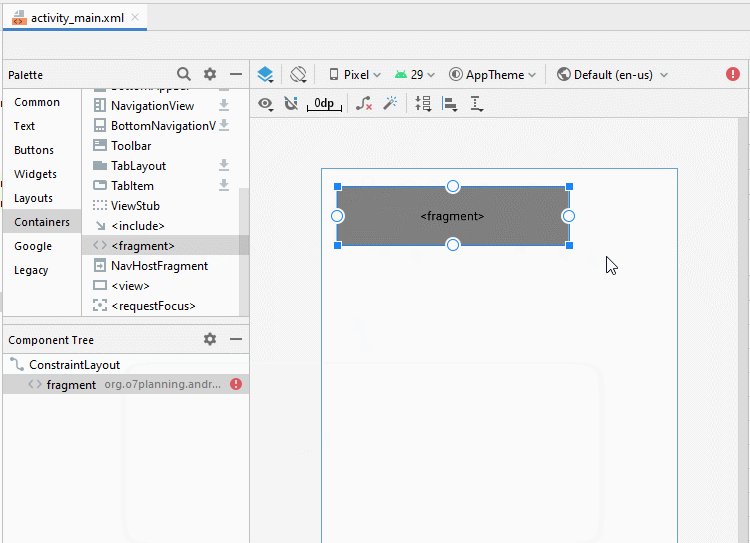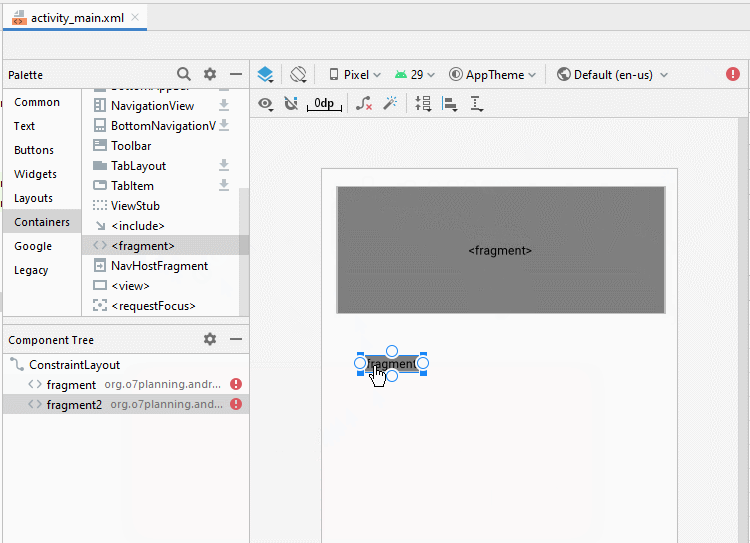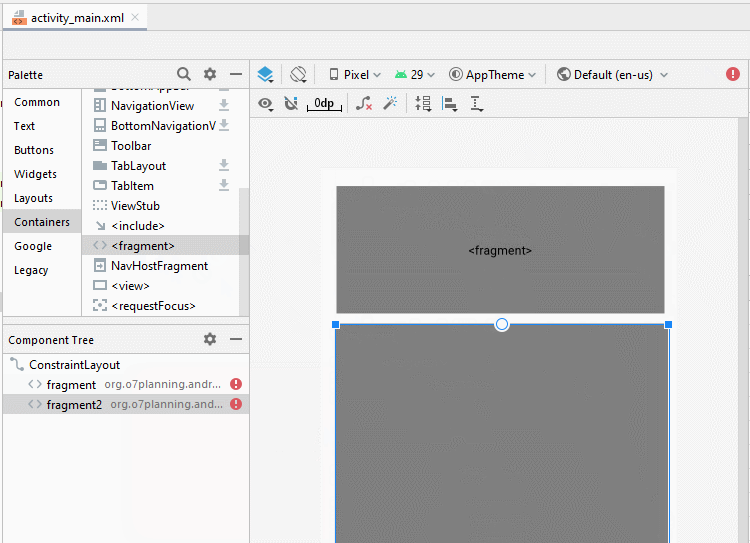
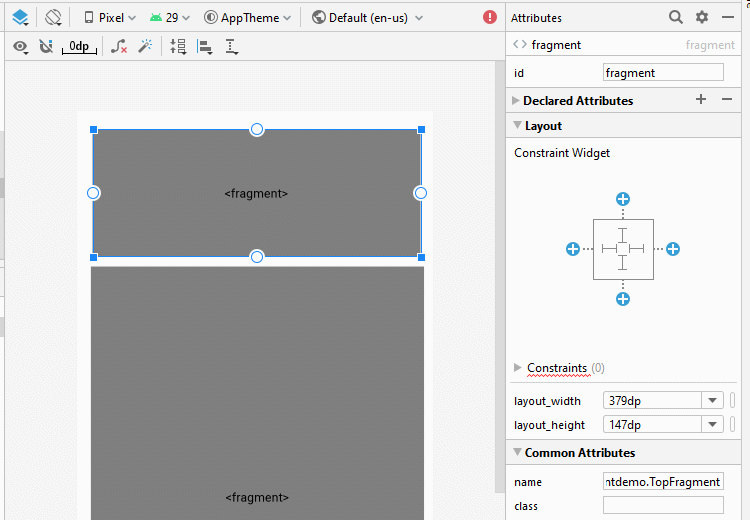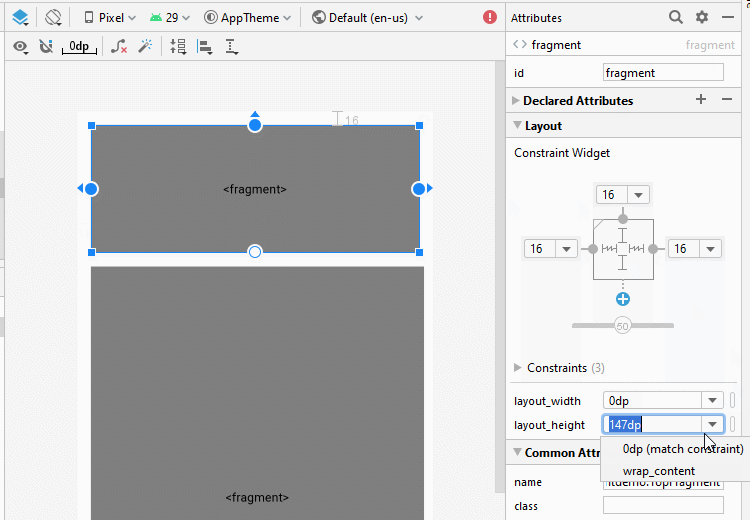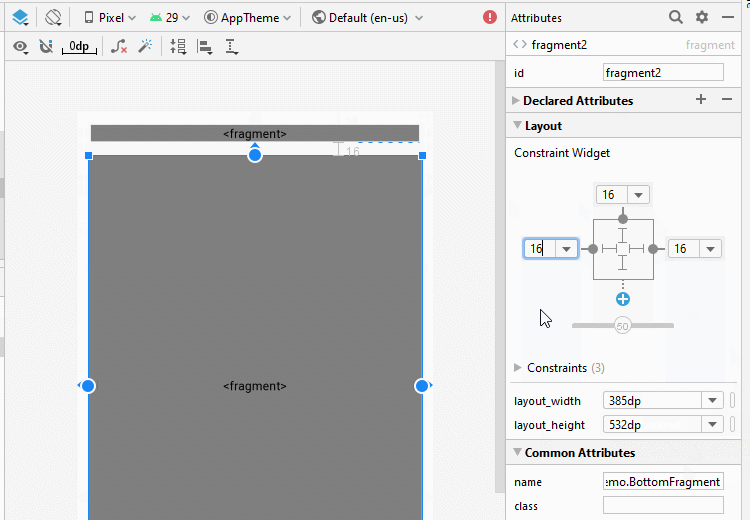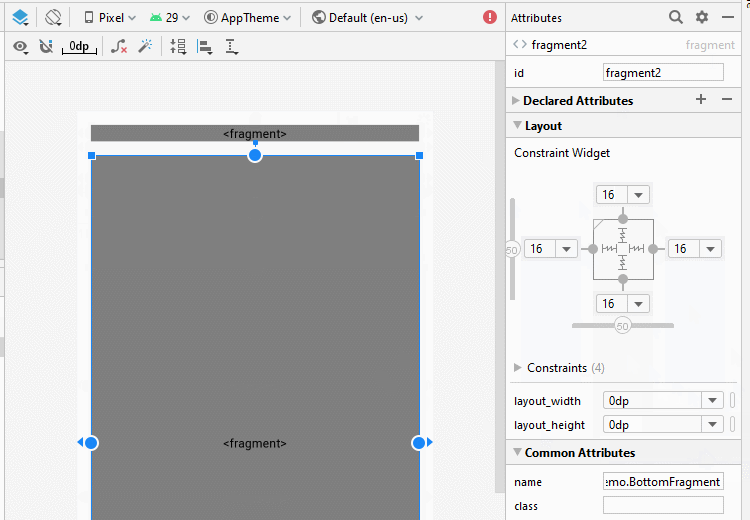
Ändern Sie ID für fragment.
- fragment_top
- fragment_bottom
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment_top"
android:name="org.o7planning.androidfragmentdemo.TopFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment_bottom"
android:name="org.o7planning.androidfragmentdemo.BottomFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/fragment_top" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>MainActivity.java
package org.o7planning.androidfragmentdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void showText(String topImageText, String bottomImageText) {
BottomFragment bottomFragment
= (BottomFragment) this.getSupportFragmentManager()
.findFragmentById(R.id.fragment_bottom);
bottomFragment.showText(topImageText, bottomImageText);
}
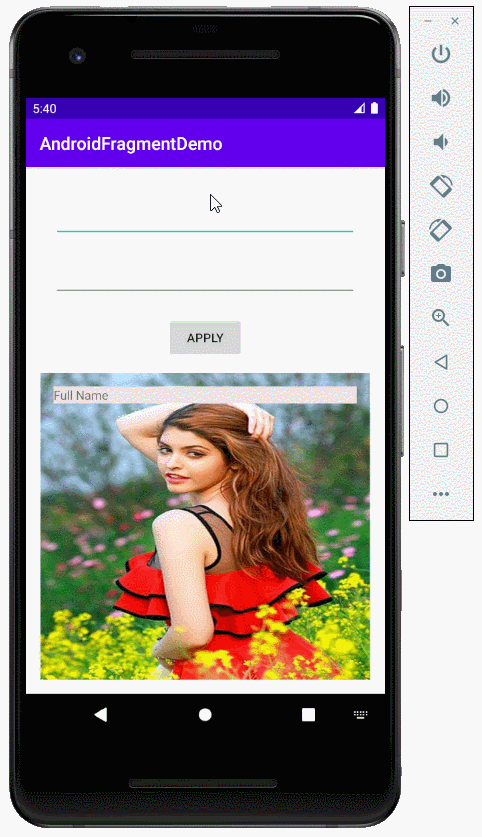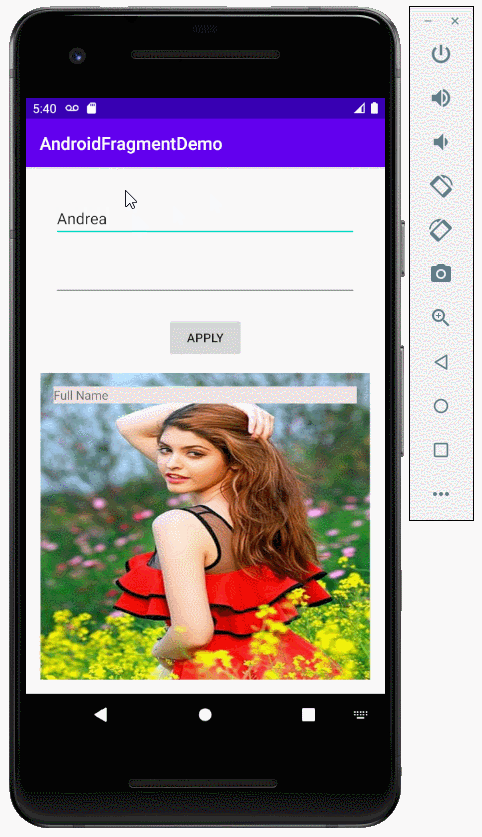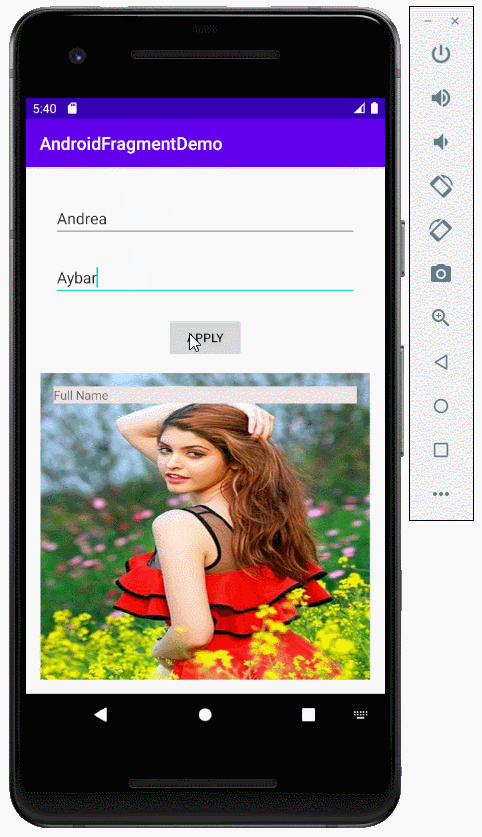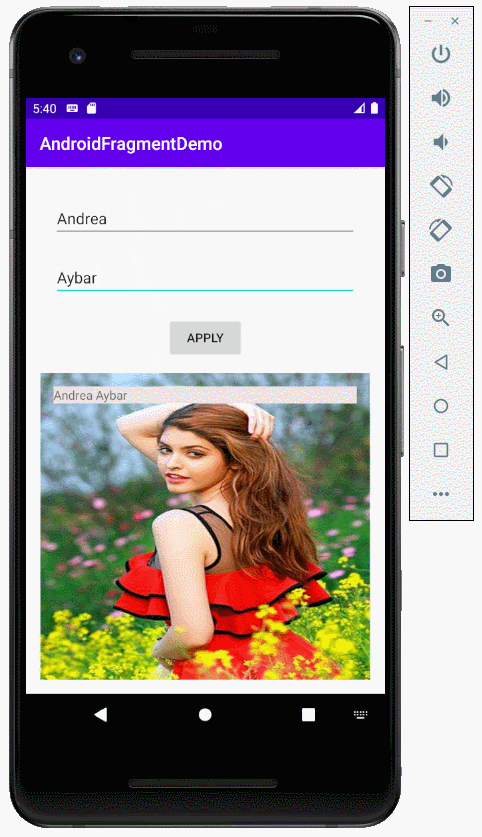
}Starten Sie die Applikation
Anleitungen Android
- Konfigurieren Sie Android Emulator in Android Studio
- Die Anleitung zu Android ToggleButton
- Erstellen Sie einen einfachen File Finder Dialog in Android
- Die Anleitung zu Android TimePickerDialog
- Die Anleitung zu Android DatePickerDialog
- Was ist erforderlich, um mit Android zu beginnen?
- Installieren Sie Android Studio unter Windows
- Installieren Sie Intel® HAXM für Android Studio
- Die Anleitung zu Android AsyncTask
- Die Anleitung zu Android AsyncTaskLoader
- Die Anleitung zum Android für den Anfänger - Grundlegende Beispiele
- Woher weiß man die Telefonnummer von Android Emulator und ändere es
- Die Anleitung zu Android TextInputLayout
- Die Anleitung zu Android CardView
- Die Anleitung zu Android ViewPager2
- Holen Sie sich die Telefonnummer in Android mit TelephonyManager
- Die Anleitung zu Android Phone Calls
- Die Anleitung zu Android Wifi Scanning
- Die Anleitung zum Android 2D Game für den Anfänger
- Die Anleitung zu Android DialogFragment
- Die Anleitung zu Android CharacterPickerDialog
- Die Anleitung zum Android für den Anfänger - Hello Android
- Verwenden des Android Device File Explorer
- Aktivieren Sie USB Debugging auf einem Android-Gerät
- Die Anleitung zu Android UI Layouts
- Die Anleitung zu Android SMS
- Die Anleitung zu Android SQLite Database
- Die Anleitung zu Google Maps Android API
- Text zu Sprache in Android
- Die Anleitung zu Android Space
- Die Anleitung zu Android Toast
- Erstellen Sie einen benutzerdefinierten Android Toast
- Die Anleitung zu Android SnackBar
- Die Anleitung zu Android TextView
- Die Anleitung zu Android TextClock
- Die Anleitung zu Android EditText
- Die Anleitung zu Android TextWatcher
- Formatieren Sie die Kreditkartennummer mit Android TextWatcher
- Die Anleitung zu Android Clipboard
- Erstellen Sie einen einfachen File Chooser in Android
- Die Anleitung zu Android AutoCompleteTextView und MultiAutoCompleteTextView
- Die Anleitung zu Android ImageView
- Die Anleitung zu Android ImageSwitcher
- Die Anleitung zu Android ScrollView und HorizontalScrollView
- Die Anleitung zu Android WebView
- Die Anleitung zu Android SeekBar
- Die Anleitung zu Android Dialog
- Die Anleitung zu Android AlertDialog
- Die Anleitung zu Android RatingBar
- Die Anleitung zu Android ProgressBar
- Die Anleitung zu Android Spinner
- Die Anleitung zu Android Button
- Die Anleitung zu Android Switch
- Die Anleitung zu Android ImageButton
- Die Anleitung zu Android FloatingActionButton
- Die Anleitung zu Android CheckBox
- Die Anleitung zu Android RadioGroup und RadioButton
- Die Anleitung zu Android Chip und ChipGroup
- Verwenden Sie Image Asset und Icon Asset von Android Studio
- Richten Sie die SDCard für den Emulator ein
- ChipGroup und Chip Entry Beispiel
- Hinzufügen externer Bibliotheken zu Android Project in Android Studio
- Wie deaktiviere ich die Berechtigungen, die der Android-Anwendung bereits erteilt wurden?
- Wie entferne ich Anwendungen aus dem Android Emulator?
- Die Anleitung zu Android LinearLayout
- Die Anleitung zu Android TableLayout
- Die Anleitung zu Android FrameLayout
- Die Anleitung zu Android QuickContactBadge
- Die Anleitung zu Android StackView
- Die Anleitung zu Android Camera
- Die Anleitung zu Android MediaPlayer
- Die Anleitung zu Android VideoView
- Spielen Sie Sound-Effekte in Android mit SoundPool
- Die Anleitung zu Android Networking
- Die Anleitung zu Android JSON Parser
- Die Anleitung zu Android SharedPreferences
- Die Anleitung zu Android Internal Storage
- Die Anleitung zu Android External Storage
- Die Anleitung zu Android Intents
- Beispiel für eine explizite Android Intent, nennen Sie eine andere Intent
- Beispiel für implizite Android Intent, Öffnen Sie eine URL, senden Sie eine Email
- Die Anleitung zu Android Services
- Die Anleitung zu Android Notifications
- Die Anleitung zu Android DatePicker
- Die Anleitung zu Android TimePicker
- Die Anleitung zu Android Chronometer
- Die Anleitung zu Android OptionMenu
- Die Anleitung zu Android ContextMenu
- Die Anleitung zu Android PopupMenu
- Die Anleitung zu Android Fragment
- Die Anleitung zu Android ListView
- Android ListView mit Checkbox verwenden ArrayAdapter
- Die Anleitung zu Android GridView
Show More